Nuclear secret: India’s space program uses plutonium pellets to power missions
Rt.com 5 Feb 24
New Delhi is experimenting with radioisotopes to charge its robotic missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond.
Indians are ecstatic over their space program’s string of successes in recent months. The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has a couple of well-kept tech secrets – one of them nuclear – that will drive future voyages to the cosmos.
In the Hollywood sci-fi movie ‘The Martian’, astronaut Mark Watney, played by Matt Damon, is presumed dead and finds ways to stay alive on the red planet, mainly thanks to a big box of Plutonium known as a Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (RTG).
In the film, Watney uses it to travel in his rover to the ‘Pathfinder’, a robotic spacecraft which launched decades ago, to use its antenna to communicate with his NASA colleagues and tell them he’s still alive. Additionally, the astronaut dips this box into a container of water to thaw it.
In real life, the RTG generates electricity from the heat of a decaying radioactive substance, in this case, Plutonium-238. This unique material emits steady heat due to its natural radioactive decay. Its continuous radiation of heat, often lasting decades, made it the material of choice for producing electrical power onboard several deep-space missions of the erstwhile USSR and the US.
For short-duration voyages, Soviet missions used other isotopes, such as a Polonium-210 heat source in the Lunokhod lunar rovers, two of which landed on the Moon, in 1970 and 1973.
NASA has employed Plutonium-238 to produce electricity for a wide variety of spacecraft and hardware, from the science experiments deployed on the Moon by the Apollo astronauts to durable robotic explorers, such as the Curiosity Mars rover and the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft, which are now at the edge of the solar system.
The ISRO first used nuclear fuel to keep the instruments and sensors going amid frigid conditions during a successful lunar mission, Chandrayaan-3. A pellet or two of Plutonium-238 inside a scaled-down version of the RTG known as the radioisotope heating unit (RHU) made its way to space aboard the rocket. It was provided by India’s atomic energy experts.
RHUs are similar to RTGs but smaller. They weigh 40 grams and provide about one watt of heat each. Their ability to do so is derived from the decay of a few grams of Plutonium-238. However, other radioactive isotopes could be used by today’s space explorers……………………………………………………………………………………..
Meanwhile, the Indian space agency has also kept under wraps two critical technologies developed for future missions by a Bengaluru-based space tech startup, Bellatrix Aerospace.
These unique propulsion systems – engines that utilize electricity instead of conventional chemical propellants onboard satellites – were tested in space aboard POEM-3 (PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3), which was launched by PSLV on January 1, 2024. The crew also tried replacing hazardous Hydrazine with a non-toxic and environment-friendly, high-performing proprietary propellant.
Hydrazine, an inorganic compound that is used as a long-term storable propellant has been used in the past by various space agencies; even for thrusters on board NASA’s space shuttles. However, it poses a host of health hazards; engineers wear space suits to protect themselves while loading it before the launch of a satellite or a deep-space probe.
In 2017, the European Union recommended banning its use as a satellite fuel, prompting the European Space Agency (ESA) to research alternatives to Hydrazine. The US administration has proposed a ban on the use of Hydrazine to propel satellites in outer space by 2025……… https://www.rt.com/india/591138-india-space-program-plutonium-pellets/
The new space race Is Causing New Pollution Problems.

NY Times, Ed Friedman Tue, 30 Jan 2024
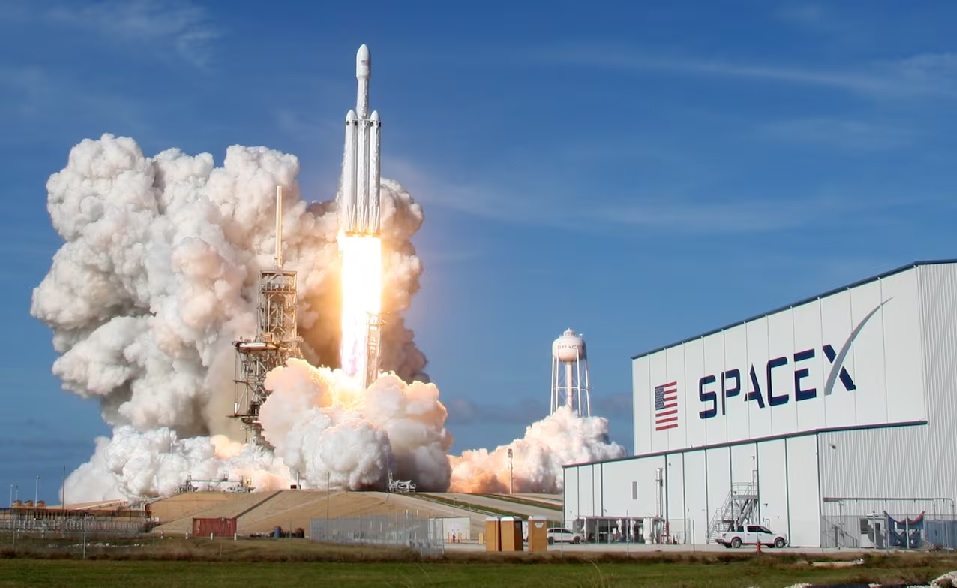
The high-altitude chase started over Cape Canaveral on Feb. 17, 2023, when a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launched. Thomas Parent, a NASA research pilot, was flying a WB-57 jet when the rocket ascended past the right wing — leaving him mesmerized before he hit the throttle to accelerate.
For roughly an hour, Mr. Parent dove in and out of the plume in the rocket’s wake while Tony Casey, the sensor equipment operator aboard the jet, monitored its 17 scientific instruments. Researchers hoped to use the data to prove they could catch a rocket’s plume and eventually characterize the environmental effects of a space launch.
In the past few years, the number of rocket launches has spiked as commercial companies — especially SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk — and government agencies have lofted thousands of satellites into low-Earth orbit. And it is only the beginning. Satellites could eventually total one million, requiring an even greater number of space launches that could yield escalating levels of emissions.
SpaceX declined to comment about pollution from rockets and satellites. Representatives for Amazon and Eutelsat OneWeb, two other companies working toward satellite mega-constellations, said they are committed to sustainable operations. But scientists worry that more launches will scatter more pollutants in pristine layers of Earth’s atmosphere. And regulators across the globe, who assess some risks of space launches, do not set rules related to pollution.
Image
The exhaust plume from a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket taking off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California in 2018,Credit…Matt Hartman/Associated Press
Experts say they do not want to limit the booming space economy. But they fear that the steady march of science will move slower than the new space race — meaning we may understand the consequences of pollution from rockets and spacecraft only when it is too late. Already, studies show that the higher reaches of the atmosphere are laced with metals from spacecraft that disintegrate as they fall back to Earth.
“We are changing the system faster than we can understand those changes,” said Aaron Boley, an astronomer at the University of British Columbia and co-director of the Outer Space Institute. “We never really appreciate our ability to affect the environment. And we do this time and time again.”
……………………………… By the time a rocket curves into orbit, it will have dumped in the middle and upper layers of the atmosphere as much as two-thirds of its exhaust, which scientists predict will rain down and collect in the lower layer of the middle atmosphere, the stratosphere.
The stratosphere is home to the ozone layer, which shields us from the sun’s harmful radiation. But it is extremely sensitive: Even the smallest of changes can have enormous effects on it — and the world below.
………………………….Just how rockets will affect that relatively clear top, the stratosphere, remains uncertain. But scientists are concerned that black carbon, or soot, that is released from current rockets will act like a continuous volcanic eruption, a change that could deplete the ozone layer and affect the Earth below.
……………………………………………… A Race Against the Space Race
As space companies set records for launches and satellites deployed, scientists are starting to quantify the potential effects.
In a paper published in 2022, soot from rockets was shown to be nearly 500 times as efficient at heating the atmosphere as soot released from sources like airplanes closer to the surface. It’s the muddy-barrel effect.
“That means that as we start to grow the space industry and launch more rockets, we’re going to start to see that effect magnify very quickly,” said Eloise Marais, an associate professor in physical geography at University College London and an author of the study.
That said, Dr. Maloney’s team did not quantify how much more radiation exposure could occur.
The exact amounts of soot emitted by different rocket engines used around the globe are also poorly understood. Most launched rockets currently use kerosene fuel, which some experts call “dirty” because it emits carbon dioxide, water vapor and soot directly into the atmosphere. But it might not be the predominant fuel of the future. SpaceX’s future rocket Starship, for example, uses a mix of liquid methane and liquid oxygen propellants.
Still, any hydrocarbon fuel produces some amount of soot. And even “green rockets,” propelled by liquid hydrogen, produce water vapor, which is a greenhouse gas at these dry high altitudes.
“You can’t take what’s green in the troposphere and necessarily think of it being green in the upper atmosphere,” Dr. Boley said. “There is no such thing as a totally neutral propellant. They all have different impacts.”
Smithereens of Satellites
What goes up must come down. Once satellites in low-Earth orbit reach the end of their operational lifetimes, they plunge through the atmosphere and disintegrate, leaving a stream of pollutants in their wake. Although scientists do not yet know how this will influence Earth’s environment, Dr. Ross thinks that it will be the most significant impact from spaceflight.
A study published in October found that the stratosphere is already littered with metals from re-entering spacecraft. It used the same NASA WB-57 jet that chased the SpaceX rocket plume last year, studying the stratosphere over Alaska and much of the continental U.S.
When the researchers began analyzing the data, they saw particles that didn’t belong. Niobium and hafnium, for example, do not occur naturally but are used in rocket boosters. Yet these metals, along with other distinct elements from spacecraft, were embedded within roughly 10 percent of the most common particles in the stratosphere.
The findings validate earlier theoretical work, and Dr. Boley, who was not involved in the study, argues that the percentage will only increase given that humanity is at the beginning of the new satellite race.
Of course, researchers cannot yet say how these metals will affect the stratosphere.
“That’s a big question that we have to answer moving forward, but we can’t presume that it won’t matter,” Dr. Boley said.
…………………………………..scientists argue, satellite operators and rocket companies need regulations. Few are currently in place.
“Space launch falls into a gray area,” said Gavin Schmidt, director of the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies, who has been involved in a working group on this research. “It falls between the cracks of all the regulatory authorities.”
The Montreal Protocol, for instance, is a treaty that successfully set limits on chemicals known to harm the ozone layer. But it does not address rocket emissions or satellites.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency is not responsible for analyzing rocket launches. The Federal Communications Commission licenses large constellations of satellites but does not consider their potential harm to the environment. (The Government Accountability Office called for changes to that F.C.C. policy in 2022, but they have yet to occur.) And the Federal Aviation Administration assesses environmental impacts of rocket launches on the ground, but not in the atmosphere or space.
That could put the stratosphere’s future in the hands of Elon Musk, Jeff Bezos and other private space company executives — which is particularly worrying to Dr. Boley, who says the space industry does not want to slow down.
“Unless it immediately affects their bottom line, they’re simply not interested,” he said. “The environmental impact is an inconvenience.”……… https://www.nytimes.com/2024/01/09/science/astronomy-telescopes-satellites-spacex-starlink.html?action=click&module=RelatedLinks&pgtype=Article—
Nuclear power on the moon: NASA wraps up 1st phase of ambitious reactor project
By Andrew Jones. Space, 3 Feb 24
1The project aims to get a reactor up and running on the moon in the early 2030s. NASA is wrapping up the design phase of a project to develop concepts for a small, electricity-generating nuclear fission reactor for use on the moon…..
NASA and the U.S. Department of Energy announced contracts to three companies — Lockheed Martin, Westinghouse and IX (a joint venture of Intuitive Machines and X-Energy) — for the initial phase back in 2022. ……….. https://www.space.com/nasa-moon-nuclear-reactor-project-first-phase-complete
The reactor plan is one of a number of new nuclear plans for space, including launching a nuclear-powered spacecraft, named DRACO, by early 2026.
Nuclear industry takes control of NASA
Global Network Against Weapons & Nuclear Power in Space 31 Jan 24
globalnet@mindspring.com
here has long been an attempt by the nuclear industry to move their deadly toxic project into space. The industry drools when it considers the profits by linking the atomic age with the space race.
Early on the Pentagon developed nuclear devices to power military satellites. Accidents happened during those days.
Then in the 1980-1990’s NASA put deadly plutonium-238 on interplanetary space missions to provide on-board power sources. The Galileo, Ulysses and Cassini missions were loaded with pu-238. The Florida Coalition for Peace & Justice and the Global Network Against Weapons & Nuclear Power in Space organized international campaigns and lawsuits in federal courts to challenge those missions.
Before the Cassini launch from the space center in Florida in 1997 more than 1,000 people joined a protest there to oppose the launch. Even CBS’s ’60 Minutes’ news show covered our resistance to the launch.
The NASA rovers currently driving around Mars taking soil samples for future mining operations are powered by plutonium-238.
In addition the mission is about developing space nuclear power for weapons.
A 1989 Congressional study (endorsed by the likes of former Sen. John Glenn and current NASA administrator Bill Nelson) entitled Military Space Forces: The Next 50 Years concluded that “Nuclear reactors thus remain the only known long-lived, compact source able to supply military space forces with electric power….Larger versions could meet multi-megawatt needs of space-based lasers, neutral particle beams, mass drivers, and railguns. Nuclear reactors must support major bases on the moon until better options, yet identified, become available.”
“Safety factors, rather than technological feasibility, will remain the principal impediment to nuclear power in space, unless officials convince influential critics that risks are acceptably low.”
SpaceX rockets keep tearing blood-red ‘atmospheric holes’ in the sky, and scientists are concerned
By Harry Baker 29 NOV 23 , https://www.livescience.com/space/space-exploration/spacex-rockets-keep-tearing-blood-red-atmospheric-holes-in-the-sky-and-scientists-are-concerned—
Astronomers have discovered a new type of “aurora” created by falling SpaceX rocket boosters that punch temporary holes in the ionosphere. Experts are concerned that these blood-red light shows could be causing unknown problems for astronomy and communication.
De-orbiting SpaceX rockets are smashing temporary holes in the upper atmosphere, creating bright blobs of light in the sky. Now, scientists have warned that these “SpaceX auroras,” which look like glowing red orbs of light, could be causing unrecognized problems — though they are not a threat to the environment or life on Earth.
Researchers have known for decades that launching rockets into space can punch holes in the upper ionosphere — the part of the atmosphere between 50 and 400 miles (80 and 644 kilometers) above Earth’s surface where gas is ionized, or stripped of electrons. These “ionospheric holes” can excite gas molecules in this part of the atmosphere and trigger vibrant streaks of red, aurora-like light.
For example, in July, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, which was carrying Starlink satellites into orbit, ripped open a hole above Arizona that made the sky bleed. And, in September, a U.S. Space Force rocket accidentally punched an ionospheric hole above California, which created a faint red glow.
Now, astronomers at the McDonald Observatory in Texas have spotted similar but unique red lights appearing long after SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rockets have left Earth’s atmosphere. These lights, which are smaller and more spherical than the long streaks created by launching rockets, are the result of ionospheric holes carved out by the rockets’ secondary boosters as they fall back to Earth after detaching from the rockets, Spaceweather.com reported.
Astronomers spotted the first of these SpaceX auroras above the observatory in February, and now are seeing “2 to 5 of them each month,” Stephen Hummel, an astronomer and outreach program coordinator at McDonald Observatory, told Spaceweather.com. The red orbs are “very bright” and “easily visible with the naked eye,” he added.
Ascending rockets and de-orbiting boosters both trigger ionospheric holes by releasing fuel into the ionosphere, which causes ionized oxygen atoms to recombine, or turn back into regular gas molecules.
This transformation excites the molecules and causes them to release red light, similar to when the gas is excited by solar radiation during traditional auroral displays. This essentially creates a hole in the surrounding plasma, or ionized gas. But the recombined molecules are are reionized, which closes up the holes within 10 to 20 minutes.
SpaceX’s de-orbiting boosters release fuel during short burns in order to manouver the falling debris to touch down in the southern Atlantic Ocean instead of crashing onto land. The resulting holes typically form above the south-central U.S. around 90 minutes after launch at an altitude of about 185 miles (300 km), according to Spaceweather.com. These holes are smaller and more circular than the holes torn open by launching rockets, so the resulting lights are more spherical and do not linger as long. But they are appearing more frequently.
Just like the larger light shows, the ionospheric holes pose no danger to life on Earth’s surface. However, “their impact on astronomical science is still being evaluated,” Hummel said. As a result, it is “a growing area of attention” among researchers, he added.
Changes to the ionosphere can also disrupt shortwave radio communication and interfere with GPS signals, according to Spaceweather.com.
Studying these holes could also help scientists learn more about the ionosphere.
“The ionospheric density is different night to night, so we can learn something about the efficiency of the [ionosphere’s] chemistry by observing many events,” Jeffrey Baumgardner, a physicist at Boston University, told Spaceweather.com.
The red blobs are not the only light shows created by SpaceX rockets. The company’s rocket boosters spin and dump their leftover fuel in space before they de-orbit, which creates a cloud of tiny ice crystals. These crystals can occasionally reflect sunlight back toward Earth, and the illuminated fuel creates bright spirals in the night sky, known as “SpaceX spirals.”
There have already been two major SpaceX spirals this year: The first was in January, which was spotted forming above Mauna Kea in Hawaii, and the second occurred in April, which shone during a traditional auroral display in Alaska.
The number of SpaceX launches is rapidly increasing so the auroras and spirals are both likely to become more common in the future.
South Texans are publicly fighting SpaceX after second Starship launch
Starship’s second launch brought more outcry from local organizations.
Chron, By Andrea Guzmán, Nov 22, 2023
SpaceX’s second launch attempt of its Starship rocket on Saturday has been commended for its improvement from the first launch, which ended with the rocket exploding after reaching 24 miles into the air.
But for some South Texas residents, SpaceX’s operations are not a cause for celebration.
In a press release after Saturday’s launch, South Texas organizations said that local residents again experienced their homes shaking and debris falling on the community.
“Musk and his pet vanity project continue to pollute and destroy our beautiful beach, coastline, and wildlife. SpaceX, an unnecessary, private money grab that only serves the wealthy, refuses to follow safety regulations, environmental regulations, and the wishes of local communities and the original people of the land,” said Christopher Basaldú with South Texas Environmental Justice Network.
Meanwhile, grassroots collaborative Another Gulf Is Possible, which has members from Brownsville, Texas, to Pensacola, Florida, has invited the public to a documentary screening in Brownsville about community objection to SpaceX on Dec. 1. The film will explore how Brownsville residents and the Carrizo/Comecrudo Tribe of Texas have battled “the encroachment of SpaceX on pristine lands,” an event invitation says. The documentary will also look at how South Texans have fought against two proposed LNG projects. ……………………………………………………………………………………… Next Friday’s documentary screening will be held at Brownsville’s Rio Bravo Office Space from 6 p.m. to 9 p.m.
more https://www.chron.com/culture/article/texas-starship-second-launch-18508949.php—
U.S. Space Force and the dangerous clutter of human-produced stuff in space

What Does the U.S. Space Force Actually Do? Inside the highly secretive military branch responsible for protecting American interests in a vulnerable new domain
NYT, By Jon Gertner, Nov. 8, 2023
Chief Master Sgt. Ron Lerch of the U.S. Space Force sat down in his office in Los Angeles one morning in September to deliver a briefing known as a threat assessment. The current “threats” in space are less sci-fi than you might expect, but there are a surprising number of them: At least 44,500 space objects now circle Earth, including 9,000 active satellites and 19,000 significant pieces of debris.
What’s most concerning isn’t the swarm of satellites but the types. “We know that there are kinetic kill vehicles,” Lerch said — for example, a Russian “nesting doll” satellite, in which a big satellite releases a tiny one and the tiny one releases a mechanism that can strike and damage another satellite. There are machines with the ability to cast nets and extend grappling hooks, too. China, whose presence in space now far outpaces Russia’s, is launching unmanned “space planes” into orbit, testing potentially unbreakable quantum communication links and adding A.I. capabilities to satellites.
An intelligence report, Lerch said, predicted the advent, within the next decade, of satellites with radio-frequency jammers, chemical sprayers and lasers that blind and disable the competition. All this would be in addition to the cyberwarfare tools, electromagnetic instruments and “ASAT” antisatellite missiles that already exist on the ground. In Lerch’s assessment, space looked less like a grand “new ocean” for exploration — phrasing meant to induce wonder that has lingered from the Kennedy administration — and more like a robotic battlefield, where the conflicts raging on Earth would soon extend ever upward.
The Space Force, the sixth and newest branch of the U.S. military, was authorized by Congress and signed into law by President Donald Trump in December 2019. Its creation was not a partisan endeavor, though Trump has boasted that the idea for the organization was his alone. The initiative had in fact been shaped within the armed forces and Congress over the previous 25 years, based on the premise that as satellite and space technologies evolved, America’s military organizations had to change as well……………………………………………………………………………….
nearly every aspect of modern warfare and defense — intelligence, surveillance, communications, operations, missile detection — has come to rely on links to orbiting satellites………………
the strategic exploitation of space now extends well beyond military concerns. Satellite phone systems have become widespread. Positioning and timing satellites, such as GPS (now overseen by the Space Force), allow for digital mapping, navigation, banking and agricultural management. A world without orbital weather surveys seems unthinkable. Modern life is reliant on space technologies to an extent that an interruption would create profound economic and social distress…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Guardians tend to think of the realm they patrol as a kind of structured multilevel terrain — Earth as being surrounded by three highways, or three rings. The nearest level, low Earth orbit (LEO), is host to constellations like SpaceX’s Starlink network and the International Space Station, which moves about 250 miles above us at 17,500 miles per hour. A medium Earth orbit (MEO), between 1,200 and 22,000 miles above, is where GPS satellites circle. At the highest ring — at least for now — is a track known as “geosynchronous” orbit (GEO), because an object in such an orbit keeps pace with Earth’s rotation. This band is home to DirectTV satellites, weather-tracking instruments from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and crucial Defense Department communication links.
It’s a technological zoo up there. The satellite mix is foreign and domestic, young and old, sinister and peaceful. The technologies are all different sizes, flying at different speeds and altitudes. The challenge for the force is to monitor all movement but also to track the threatening presence of debris, some of which is naturally occurring (tiny rocks, for instance) and some of which has human origins (like shards of old rockets). Because space junk can move at extraordinary velocities, a floating screw might pack a destructive punch equivalent to a small bomb……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Capt. Raymond Pereira, drawing on a white board, pointed me to another concern: the crowd of satellites in low Earth orbit. “I would say we’re probably already entering into an area where congestion is a problem,” he said, “and anything that would generate debris would be catastrophic for the domain.” One plausible theory is known as the Kessler Syndrome, named after the former NASA scientist Donald Kessler, which posits that a release of wreckage and fragments in this orbit could eventually lead to a domino effect of unstoppable destruction. Pereira pointed out that if someone (or something) were to touch off such an event, “they would not only be harming their adversary; they would be harming themselves.” But even short of that, a single collision or attack might hamstring science missions to the moon, or to Mars, or lead to failures for GPS and communications systems, a problem that could have huge consequences for life on Earth.
………………………. A treaty from the late 1960s, signed by most of the major nations on Earth, prohibits the use of nuclear weapons in space and designates the moon for peaceful purposes. But recently, I was told, satellites from foreign adversaries have been coming close to machines from the United States and its allies. The treaty says nothing about such provocations — or about grappling hooks, nesting dolls and cyberwarfare.
Space Force leaders readily describe their guardians as working toward a state of combat readiness…………………………………………………………..
Debris has led military strategists to ponder a related issue: In space, it’s difficult to get out of the way of conflict……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………….. “And then potentially every satellite becomes more debris,” Saltzman remarked. “Every peaceful satellite could become a weapon accidentally.”…………………………………………………………………………………. more https://www.nytimes.com/2023/11/08/magazine/space-force.html
At SpaceX, worker injuries soar in Elon Musk’s rush to Mars
Reuters documented at least 600 previously unreported workplace injuries at Musk’s rocket company: crushed limbs, amputations, electrocutions, head and eye wounds and one death. SpaceX employees say they’re paying the price for the billionaire’s push to colonize space at breakneck speed.
A REUTERS INVESTIGATION, By MARISA TAYLOR , Nov. 10, 2023,
One windy night at Elon Musk’s SpaceX facility in McGregor, Texas, Lonnie LeBlanc and his co-workers realized they had a problem.
They needed to transport foam insulation to the rocket company’s main hangar but had no straps to secure the cargo. LeBlanc, a relatively new employee, offered a solution to hold down the load: He sat on it.
After the truck drove away, a gust blew LeBlanc and the insulation off the trailer, slamming him headfirst into the pavement. LeBlanc, 38, had retired nine months earlier from the U.S. Marine Corps. He was pronounced dead from head trauma at the scene.
Federal inspectors with the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) later determined that SpaceX had failed to protect LeBlanc from a clear hazard, noting the gravity and severity of the violation. LeBlanc’s co-workers told OSHA that SpaceX had no convenient access to tie-downs and no process or oversight for handling such loads. SpaceX acknowledged the problems, and the agency instructed the company to make seven specific safety improvements, including more training and equipment, according to the inspection report.
It was hardly the last serious accident at SpaceX. Since LeBlanc’s death in June 2014, which hasn’t been previously reported, Musk’s rocket company has disregarded worker-safety regulations and standard practices at its inherently dangerous rocket and satellite facilities nationwide, with workers paying a heavy price, a Reuters investigation found. Through interviews and government records, the news organization documented at least 600 injuries of SpaceX workers since 2014.
Many were serious or disabling. The records included reports of more than 100 workers suffering cuts or lacerations, 29 with broken bones or dislocations, 17 whose hands or fingers were “crushed,” and nine with head injuries, including one skull fracture, four concussions and one traumatic brain injury. The cases also included five burns, five electrocutions, eight accidents that led to amputations, 12 injuries involving multiple unspecified body parts, and seven workers with eye injuries. Others were relatively minor, including more than 170 reports of strains or sprains.
Current and former employees said such injuries reflect a chaotic workplace where often under-trained and overtired staff routinely skipped basic safety procedures as they raced to meet Musk’s aggressive deadlines for space missions. SpaceX, founded by Musk more than two decades ago, takes the stance that workers are responsible for protecting themselves, according to more than a dozen current and former employees, including a former senior executive.
Musk himself at times appeared cavalier about safety on visits to SpaceX sites: Four employees said he sometimes played with a novelty flamethrower and discouraged workers from wearing safety yellow because he dislikes bright colors.
The lax safety culture, more than a dozen current and former employees said, stems in part from Musk’s disdain for perceived bureaucracy and a belief inside SpaceX that it’s leading an urgent quest to create a refuge in space from a dying Earth.
“Elon’s concept that SpaceX is on this mission to go to Mars as fast as possible and save humanity permeates every part of the company,” said Tom Moline, a former SpaceX senior avionics engineer who was among a group of employees fired after raising workplace complaints. “The company justifies casting aside anything that could stand in the way of accomplishing that goal, including worker safety.”
One severe injury in January 2022 resulted from a series of safety failures that illustrate systemic problems at SpaceX, according to eight former SpaceX employees familiar with the accident. In that case, a part flew off during pressure testing of a Raptor V2 rocket engine – fracturing the skull of employee Francisco Cabada and putting him in a coma.
The sources told Reuters that senior managers at the Hawthorne, California site were repeatedly warned about the dangers of rushing the engine’s development, along with inadequate training of staff and testing of components. The part that failed and struck the worker had a flaw that was discovered, but not fixed, before the testing, two of the employees said……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
NASA said it has paid SpaceX $11.8 billion to date as a private space contractor. The agency did not comment on the company’s safety record but said it has the option of enforcing contract provisions that require SpaceX to “have a robust and effective safety program and culture.”……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Shortcutting safety
On Jan. 18 of last year, part of a Raptor V2 engine broke away during pressure testing at the SpaceX facility in Hawthorne, California. The part, a fuel-controller assembly cover, careened into the head of Cabada, a SpaceX technician. Nearly two years later, the father of three young children remains in a coma with a hole in his skull, family members said.
The accident generated news last year but little has emerged until now about the causes. The incident stemmed from several safety lapses at the Hawthorne site, according to Reuters interviews with eight former SpaceX employees familiar with the incident and the testing preparations…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
SpaceX’s rejection of a more rigorous training program, its moves to limit testing, and the discovery of the cover’s defect before the accident haven’t been previously reported……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Flamethrowers and safety yellow
Musk is well-known as a hands-on manager. He was directly involved in handing down sometimes unrealistic deadlines, said current and former employees. Musk’s heavy involvement in scheduling resulted in “significantly more unsafe working conditions than would have existed otherwise,” said Moline, the engineer.
One former SpaceX executive defended Musk, saying he would listen to employees who were willing to go “toe-to-toe” with him on safety issues and took them seriously.
Another former executive said Musk cared about his workers and was bothered when they got hurt, but that safety was not one of Musk’s priorities. Musk, the ex-manager said, thought that “workers take care of their safety themselves.”
This former executive said that top company officials knew its injury rates ran high but attributed the problem to employing a largely young workforce in a dangerous industry. SpaceX leaders also believed the company shouldn’t be held to the same standard as competitors because SpaceX oversees more missions and manufacturing, the two former executives said.
That attitude is a red flag that a company is rationalizing a fundamentally unsafe environment, according to four worker-safety experts interviewed by Reuters, including Barab, the former OSHA deputy assistant secretary.
“SpaceX shouldn’t be exempt from protecting workers from being injured or killed,” Barab said, “just because they’re doing innovative work.
A video posted widely online shows Elon Musk playing with a novelty flamethrower produced by his tunneling firm, the Boring Company.
Four SpaceX employees told Reuters they were disturbed by Musk’s habit of playing with a flamethrower when he visited the SpaceX site in Hawthorne. The device was marketed to the public in 2018 as a $500 novelty item by Musk’s tunnel-building firm, the Boring Company. Videos posted online show it can shoot a thick flame more than five feet long. Boring later renamed the device the “Not-A-Flamethrower” amid reports of confiscations by authorities.
For years, Musk and his deputies found it “hilarious” to wave the flamethrower around, firing it near other people and giggling “like they were in middle school,” one engineer said. Musk tweeted in 2018 that the flamethrower was “guaranteed to liven up any party!” At SpaceX, Musk played with the device in close-quarters office settings, said the engineer, who at one point feared Musk would set someone’s hair on fire……………………………………………………………………………………………..
A death and a $7,000 fine
SpaceX has faced few consequences from safety regulators for its failure to report annual safety data and to protect workers in incidents reviewed by federal and state inspectors, agency records show.
OSHA and CalOSHA have fined the billionaire’s rocket company a total of $50,836 for violations stemming from one worker’s death and seven serious safety incidents, regulatory records show.
OSHA did not comment on the modest penalties that resulted from inspections of SpaceX.
SpaceX’s history of injuries and regulatory run-ins in California underscores the limits of worker-safety regulation. Fines are capped by law and pose little deterrent for major companies, experts in U.S. worker safety regulation said. Federal and state regulators also suffer from chronic understaffing of inspectors, they said. OSHA did not address questions about staffing levels but said it “focuses its resources on hazardous workplaces.”……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Safety at SpaceX: How Reuters analyzed workplace injuries
Reuters documented at least 600 injuries at SpaceX through a variety of public records, including the company’s own injury logs at three facilities that were inspected by regulators…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. more https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/spacex-musk-safety/—
Book Review: Are We Ready to Head to Mars? Not So Fast.

“A City on Mars” is Kelly and Zach Weinersmith’s cheeky account of the many challenges to visiting the red planet.
Undark, BY CHRISTIE ASCHWANDEN, 11.10.2023
IN AUGUST 1998, 700 people came to Boulder, Colorado to attend the founding convention of the Mars Society. The group’s co-founder and president, Robert Zubrin, extolled the virtues of sending humans to Mars to terraform the planet and establish a human colony. The Mars Society’s founding declaration began, “The time has come for humanity to journey to the planet Mars,” and declared that “Given the will, we could have our first crews on Mars within a decade.” That was two and a half decades ago.
In their hilarious, highly informative and cheeky book, “A City on Mars: Can We Settle Space, Should We Settle Space, and Have We Really Thought This Through?”, Kelly and Zach Weinersmith inventory the challenges standing in the way of Zubrin-like visions for Mars settlement. The wife-and-husband team serves a strong, but never stern, counterargument to the visionaries promising that we’ll put humans on Mars in the very near future. “Think of this book as the straight-talking homesteader’s guide to the rest of the solar system,” they write.
Just as in their previous book, “Soonish: Ten Emerging Technologies That’ll Improve and/or Ruin Everything,” the authors — she’s a faculty member in the biosciences department at Rice University and he’s a cartoonist — use humor and science to douse techno dreams with a dose of reality. “After a few years of researching space settlements, we began in secret to refer to ourselves as the ‘space bastards’ because we found we were more pessimistic than almost everyone in the space-settlement field,” they write. “We weren’t always this way. The data made us do it.”
While working on their deeply researched book, the Weinersmiths came to view sending people to Mars as a problem far more complicated and difficult than you’d know by listening to enthusiasts like Elon Musk or Robert Zubrin. It’s a challenge that “won’t be solved simply by ambitious fantasies or giant rockets.” Eventually humans are likely to expand into space, the Weinersmiths write, but for now, “the discourse needs more realism — not in order to ruin everyone’s fun, but to provide guardrails against genuinely dangerous directions for planet Earth.”………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Living on Mars, which has no birds or rain, gets less than half the sunlight per area that Earth does, and is often plagued by dust storms that further blot out the sun, could be a soul-deadening experience.
………………………………………. They also run through a list of “Bad Arguments for Space Settlement,” which include “Space Will Save Humanity from Near-Term Calamity by Providing a New Home,” and “Space Exploration Is a Natural Human Urge.” These detailed examinations of the stark realities regarding space travel and habitation serve as a foil to the breathlessly optimistic accounts that are so ubiquitous in popular media……………………. more https://undark.org/2023/11/10/review-city-on-mars/?utm_source=Undark%3A+News+%26+Updates&utm_campaign=448a889155-RSS_EMAIL_CAMPAIGN&utm_medium=email&utm_term=0_5cee408d66-185e4e09de-%5BLIST_EMAIL_ID%5D
Nuclear lobby and NASA propagandising to schoolkids

NASA Seeks Students to Imagine Nuclear Powered Space Missions
NASA 8 Nov 23
The third Power to Explore Student Challenge from NASA is underway. The writing challenge invites K-12th grade students in the United States to learn about radioisotope power systems, a type of nuclear battery integral to many of NASA’s far-reaching space missions, and then write an essay about a new powered mission for the agency.
For more than 60 years, radioisotope power systems have helped NASA explore the harshest, darkest, and dustiest parts of our solar system and has enabled many spacecrafts to conduct otherwise impossible missions in total darkness. Ahead of the next total solar eclipse in the United States in April 2024, which is a momentary glimpse without sunlight and brings attention to the challenge of space exploration without solar power, NASA wants students to submit essays about these systems.
Entries should detail where students would go, what they would explore, and how they would use the power of radioisotope power systems to achieve mission success in a dusty, dark, or far away space destination with limited or obstructed access to light. Submissions are due Jan. 26, 2024.
“The Power to Explore Student Challenge is part of NASA’s ongoing efforts to engage students in space exploration and inspire interest in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics,” said Nicola Fox, associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. “This technology has been a gamechanger in our exploration capabilities and we can’t wait to see what students – our future explorers – dream up; the sky isn’t the limit, it’s just the beginning.”……………………………..
The Power to Explore Student Challenge is funded by the NASA Science Mission Directorate’s Radioisotope Power Systems Program Office and managed and administered by Future Engineers under the direction of the NASA Tournament Lab, a part of the Prizes, Challenges, and Crowdsourcing Program in NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate. https://www.nasa.gov/news-release/nasa-seeks-students-to-imagine-nuclear-powered-space-missions/ #nuclear #antinuclear #nuclearfree #NoNukes #radioactive
Number of planned low-orbit satellites NOW EXCEEDS ONE MILLION
ARTHUR FIRSTENBERG, NOV 1, 2023
https://arthurfirstenberg.substack.com/p/number-of-planned-low-orbit-satellites?utm_source=profile&utm_medium=reader2
On Sunday, SpaceX launched 23 satellites from Cape Canaveral in the morning, and 22 more from Vandenberg Air Force Base in the evening. This brought the total number of operating satellites irradiating the Earth to about 8,800.
SpaceX has been sending up satellite-laden rockets every few days this year, in its haste to satisfy an insatiable demand for bandwidth by the billions of human beings who use cell phones. But SpaceX is not the only one. Hundreds of companies are competing for a share of the global market to supply Internet from the sky to the world’s population.
On January 5, 2022, I sent out a newsletter listing 147 companies and government agencies from 34 countries that were operating, launching, or planning fleets of satellites that, if they were all launched, would total about half a million in our skies, far outnumbering the visible stars. On October 17, 2023, the journal Science, reviewing filings with the International Telecommunication Union, informed the world that the number of filings and the number of planned satellites have again more than doubled. There are more than 90 filings for constellations of over 1,000 satellites each. Twenty-three have over 5,000 satellites, and eight have over 10,000 satellites. As of December 31, 2022, the number of satellites being planned by 300 companies and governments exceeded one million. And in June, 2023, E-Space, a company based in France and founded by Greg Wyler in 2022, filed a plan for a single megaconstellation containing 116,640 satellites. E-Space had previously filed a plan, via the government of Rwanda, for an even larger constellation containing 327,320 satellites. Two days after his new filing with the ITU, Wyler clarified that “Our filing in France is in addition to our filings in Rwanda.”
Our new network, People Without Cell Phones, is more important than ever. The only way to diminish the demand for bandwidth that is turning the Earth into a giant computer, with all living beings electrocuted inside of it, is to stop using cell phones. Not to use them less frequently, but to throw them away. The ability to use them, no matter how infrequently, requires the entire planet to be irradiated. Please join our network by forming a local chapter where you live. You can set your own rules, but it is important to have meetings in person. Please contact me if you need help and let me know that you are doing it. Our goal is to establish an expanding global presence of communities that do not use cell phones. It is up to us. #nuclear #antinuclear #nuclearfree #NoNukes
Arthur Firstenberg
President, Cellular Phone Task Force
Author, The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and Life
P.O. Box 6216
Santa Fe, NM 87502 USA
phone: +1 505-471-0129
arthur@cellphonetaskforce.org
Space debris

https://interconnectedrisks.org/tipping-points/space-debris 25 Oct 23
Thousands of satellites orbit the Earth, gathering and distributing vital information for weather monitoring, disaster early warning systems and communications. Recent technological advancements have made it easier and more affordable for countries, companies and even individuals to put satellites into space. Satellites make our lives safer, more convenient and connected, and represent critical infrastructure that is now essential for a functioning society. However, as the number of satellites increases, so does the problem of space debris, which poses a threat to both functioning satellites and the future of our orbit.
Space debris consists of various objects, from minuscule flecks of paint to massive chunks of metal. Out of 34,260 objects tracked in orbit, only around 25 per cent are working satellites while the rest are junk, such as broken satellites or discarded rocket stages. Additionally, there are likely around 130 million pieces of debris too small to be tracked, measuring between 1 mm and 1 cm. Given that these objects travel over 25,000 kilometres per hour, even the smallest debris can cause significant damage. Each piece of debris becomes an obstacle in the orbital “highway”, making it increasingly difficult for functional satellites to avoid collisions.
Key Numbers
8,300 functioning satellites in orbit
34,260 tracked objects in orbit
25,000 kilometres per hour travel speed
The danger is more than just theoretical. In 2009, a collision between a defunct satellite and an active communications satellite created thousands of debris pieces that still orbit Earth today. This debris can impact other objects, such as the International Space Station, which conducts manoeuvres around once per year to avoid such debris. Satellites can be warned of impending collisions; in fact, the European Sentinel-2 satellite registered more than 8,000 alerts between 2015 and 2017. Collision avoidance even between active satellites can also be difficult since agencies often need to communicate and quickly come to agreements. For example, in 2019, a European Space Agency satellite had to perform an emergency manoeuvre to avoid colliding with a communications satellite after an agreement with the operator could not be reached.
More than 100,000 new spacecraft could be launched into orbit by 2030, compared to the approximately 8,000 we have now. As more satellites are launched, the orbit becomes more crowded, increasing the risk of collisions. Each collision creates millions more pieces of debris, which can then collide with other debris or satellites, creating even more shrapnel. Eventually, this will reach a point where one crash sets off a chain reaction, causing our orbit to become so dense with shrapnel that it becomes unusable. The existing space infrastructure would eventually be destroyed and future activities in space could become impossible.
Space is the final frontier, and with countries and companies racing to stake their claim, we must consider what kind of future we want to create. If we continue on the current trajectory, we risk sacrificing Earth’s orbits and the opportunities they offer to society now and in the future. Importantly, we must regulate space launches more strictly and ensure that satellites and other spacecraft are disposed of responsibly, while also investing in technologies for tracking and removing orbital debris. By coming together as a global community to treat Earth’s orbits as a precious common good, we can safeguard our future in space before it is too late. #nuclear #antinuclear #nuclearfree #NoNukes
Nuclear companies sign up for space technology missions
WNN, 20 October 2023
With nuclear technology set to underpin new developments in space travel, NASA has awarded Ultra Safe Nuclear Corporation a contract to manufacture and test fuel and develop the design of a nuclear thermal propulsion engine for near-term missions. Separately, Space Nuclear Power Corporation has partnered with Lockheed Martin Corporation and BWX Technologies for the US Space Force/Air Force’s JETSON nuclear electric propulsion demonstration project, while Framatome has announced the creation of a new brand, Framatome Space.
……………………………………………………………………..The JETSON – Joint Emergent Technology Supplying On-orbit Nuclear Power – nuclear electric propulsion demonstration project was launched in January when the US Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL)/Space Vehicle Directorate issued solicitations to industry for high and low-power spacecraft concepts and designs using nuclear fission, rather than solar panels, for propulsion. On 3 October, the AFRL awarded Lockheed Martin, Westinghouse Government Services and Intuitive Machines LLC separate contracts totalling over USD53 million to develop the technologies and spacecraft concepts.
………………………………………………………………………………The JETSON – Joint Emergent Technology Supplying On-orbit Nuclear Power – nuclear electric propulsion demonstration project was launched in January when the US Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL)/Space Vehicle Directorate issued solicitations to industry for high and low-power spacecraft concepts and designs using nuclear fission, rather than solar panels, for propulsion. On 3 October, the AFRL awarded Lockheed Martin, Westinghouse Government Services and Intuitive Machines LLC separate contracts totalling over USD53 million to develop the technologies and spacecraft concepts.
………………………….Framatome joins space race

Framatome has announced the creation of Framatome Space, which it said is putting the French company’s 65 years of nuclear and industrial expertise at the service of the space industry. The company is already supporting the French Alternative Energies & Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) and Ariane Group with a feasibility study on an nuclear thermal propulsion engine and earlier this year announced plans with USNC to form a joint venture to manufacture TRISO particles on a commercial scale………………………………………………………… https://www.world-nuclear-news.org/Articles/Nuclear-companies-sign-up-for-space-technology-mis #nuclear #antinuclear #nuclearfree #NoNukes
Burned-up space junk pollutes Earth’s upper atmosphere, NASA planes find
Space.com, By Tereza Pultarova, 19 Oct 23
Chemicals created by fiery satellite re-entries could affect Earth’s climate.
Scientists have long thought that the burning up of space junk in Earth’s atmosphere creates air pollution that can affect the planet’s climate. Now, for the first time, they’ve managed to detect the presence of these pollutants in the air high above our planet.
A team of researchers flew high-altitude NASA aircraft over Alaska and the U.S. mainland to sample the chemical composition of the thin air in the stratosphere, the second-lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere, which extends from about 6 miles to 30 miles (10 to 50 kilometers) above the planet’s surface.
The planes, NASA’s WB-57 and ER-2 aircraft, allowed the researchers to reach altitudes of up to 11.8 miles (19 km), which is about five miles (9 km) above the cruising altitude of commercial airliners.
Sensitive sensors in the nosecones of the planes analyzed the chemical compounds diluted in the thin, pristine stratospheric air, which is out of reach of Earth-based air pollution sources. The researchers found traces of lithium, aluminum, copper and lead in the sampled air. The detected concentrations of these compounds were much higher than what could be caused by natural sources, such as the evaporation of cosmic dust and meteorites upon their encounter with the atmosphere. In fact, the concentrations of these pollutants reflected the ratio of chemical compounds present in alloys used in satellite manufacturing, the researchers said in a statement.
“We are finding this human-made material in what we consider a pristine area of the atmosphere,” Dan Cziczo, a professor of Earth, atmospheric, and planetary sciences at Purdue University in Indiana and one of the authors of the study, said in the statement. “And if something is changing in the stratosphere — this stable region of the atmosphere — that deserves a closer look.”
In recent years, scientists have been sounding alarm bells about the possible effects of the rising number of rocket launches and satellite re-entries on the upper layers of Earth’s atmosphere. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The study was published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on Monday (Oct. 16). https://www.space.com/air-pollution-reentering-space-junk-detected #nuclear #antinuclear #nuclearfree #NoNukes
Star Wars? Learned professor speaks of threat to peace in space

https://www.nuclearpolicy.info/news/star-wars-learned-professor-speaks-of-threat-to-peace-in-space/ 6 Oct 23 #nuclear #antinuclear #nuclear-free #NoNukes
Space-based weapons and nuclear-powered space vehicles might seem the stuff of Science Fiction but many of the leading militaries in the world now have ‘Space Commands’, an armed service dedicated ‘dominance’ in the world of space. Representatives from the UK/Ireland Nuclear Free Local Authorities heard today about the threat to peace now being posed by the increasing militarisation of space.
Professor Emeritus Dave Webb was the guest speaker at the October meeting of the NFLA Steering Committee. Dave is the former Chair of the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament and is now the Convenor of the Global Network Against Weapons and Nuclear Power in Space. Established in 1992, the network is an international body of academics and activists opposed to the militarisation and the use of nuclear power in space.
In 1999, the United Nations General Assembly declared that October 4-10 every year would be designated as ‘World Space Week’ to ‘celebrate the contributions of space science and technology to the betterment of the human condition’; in response the Global Network designates 7-14 October as ‘Keep Space for Peace Week’.
Despite being signatories to the Outer Space Treaty of 1967 which prohibits nuclear weapons in space; limits the use of the Moon and all other celestial bodies to peaceful purposes; establishes that space shall be freely explored and used by all nations; and precludes any country from claiming sovereignty over outer space or any celestial body, many of the world’s leading powers have established new military commands to establish a presence in space.
With communications, navigation, command-and-control, surveillance, espionage, and the detection of threats being reliant on signals beamed from space, each of the world’s major powers wants to be able to ensure that its satellites remain safe from electronic interference, sabotage, or destruction, whilst over time being able to develop the capability to destroy those of their adversaries in time of war.
As militarisation continues, tensions between the powers engaged in this space race will increase and so war will become more likely. This year’s theme for ‘Keep Space for Peace Week’ reflects one such source of tension – the increasingly crowded skies above our Earth.
Professor Webb explains: “This year we are highlighting the danger posed to peace by our crowded Low Earth Orbit.
“In 1985 – 1988, there were about 5,000 – 6,000 objects in orbit, there are now about 27,000 and this figure is increasing rapidly. Elon Musk’s Space X has launched about 12,000 satellites and various other companies are now planning 71,000 more.
“The United States being especially aggressive in working to secure as many of the remaining slots as possible, seeking to freeze out its rivals generating resentment. The Global Network is currently engaged in legal action in the US to pressure the Federal Communications Commission to follow the law and conduct environmental impacts assessments before approving any further launches,
6th October 2023
Star Wars? Learned professor speaks of threat to peace in space
Space-based weapons and nuclear-powered space vehicles might seem the stuff of Science Fiction but many of the leading militaries in the world now have ‘Space Commands’, an armed service dedicated ‘dominance’ in the world of space. Representatives from the UK/Ireland Nuclear Free Local Authorities heard today about the threat to peace now being posed by the increasing militarisation of space.
Professor Emeritus Dave Webb was the guest speaker at the October meeting of the NFLA Steering Committee. Dave is the former Chair of the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament and is now the Convenor of the Global Network Against Weapons and Nuclear Power in Space. Established in 1992, the network is an international body of academics and activists opposed to the militarisation and the use of nuclear power in space.
In 1999, the United Nations General Assembly declared that October 4-10 every year would be designated as ‘World Space Week’ to ‘celebrate the contributions of space science and technology to the betterment of the human condition’; in response the Global Network designates 7-14 October as ‘Keep Space for Peace Week’.
Despite being signatories to the Outer Space Treaty of 1967 which prohibits nuclear weapons in space; limits the use of the Moon and all other celestial bodies to peaceful purposes; establishes that space shall be freely explored and used by all nations; and precludes any country from claiming sovereignty over outer space or any celestial body, many of the world’s leading powers have established new military commands to establish a presence in space.
With communications, navigation, command-and-control, surveillance, espionage, and the detection of threats being reliant on signals beamed from space, each of the world’s major powers wants to be able to ensure that its satellites remain safe from electronic interference, sabotage, or destruction, whilst over time being able to develop the capability to destroy those of their adversaries in time of war.
As militarisation continues, tensions between the powers engaged in this space race will increase and so war will become more likely. This year’s theme for ‘Keep Space for Peace Week’ reflects one such source of tension – the increasingly crowded skies above our Earth.
Professor Webb explains: “This year we are highlighting the danger posed to peace by our crowded Low Earth Orbit.
“In 1985 – 1988, there were about 5,000 – 6,000 objects in orbit, there are now about 27,000 and this figure is increasing rapidly. Elon Musk’s Space X has launched about 12,000 satellites and various other companies are now planning 71,000 more.
“The United States being especially aggressive in working to secure as many of the remaining slots as possible, seeking to freeze out its rivals generating resentment. The Global Network is currently engaged in legal action in the US to pressure the Federal Communications Commission to follow the law and conduct environmental impacts assessments before approving any further launches,
“NASA scientists have warned that growing space debris could lead to likely-cascading collisions in orbit, however accidental. This ‘Kessler Syndrome’ could lead to military tensions as collisions would often involve space vehicles of competing nations, and retaliation and further escalation might result.”
In readiness for possible future warfighting in space, the UK Government has also established a Space Command as the fourth branch of the armed forces, with a mission to ‘protect and defend UK and allied interests in, from, and to space’.
UK government funding is also backing research at the Universities of Bangor and Southampton to develop nuclear propulsion systems for the next generation of rockets and Rolls Royce has received a grant to develop a nuclear power plant for deployment at a future crewed moon-base. In addition, seven space ports are in development in the UK, five in Scotland, one in Snowdonia, and one at Newquay.
The NFLAs have real worries about the use of the space ports for military purposes and the deployment of nuclear power in space.
NFLA Steering Committee Chair, Councillor Lawrence O’Neill explained: “With new space ports, UK Space Command will be looking to deploy more military spy satellites to further its mission, but over time a new generation of military space vehicles may be developed with the capacity to carry conventional or non-conventional weapons. Although this might seem fanciful, this pattern has been followed with drones.
“At first these unmanned aerial vehicles were used for surveillance, but they have since been developed into formidable weapons platforms bristling with missiles, with strikes guided by anonymous remote operators located thousands of miles from the battlefield; coupled with AI, they would be more formidable still as a robot never tires nor has second thoughts. Who is to say that space vehicles will not be developed in a same pattern, if left unchecked?”
The NFLAs are also concerned that a British manned moon base might be usurped for military, rather than altruistic scientific, purposes, and that any use of nuclear power there will lead to the contamination of space and the lunar surface, and pose a real of radioactive contamination if an explosion took place on Earth.
Cllr O’Neill concluded: “Any failed launch or re-entry of a nuclear-powered space vehicle could, if an explosion occurred, lead to the dispersal of radioactive contamination into our atmosphere. This fear was one of the reasons cited by the advisory body CORWM, the Committee on Radioactive Waste Management, for not recommending to government any plan to blast radioactive waste into space.
“These are the many reasons why it is so important that we Keep Space for Peace.”
-
Archives
- March 2026 (38)
- February 2026 (268)
- January 2026 (308)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (376)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS