Japan starts 5th ocean discharge of Fukushima nuclear-tainted wastewater despite opposition

(Xinhua) Web editor: Zhang Kaiwei, Liang Jun, April 19, 2024
TOKYO, April 19 (Xinhua) — Japan on Friday started the fifth-round of release of nuclear-contaminated wastewater from the crippled Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant into the Pacific Ocean.
Despite opposition among local fishermen, residents as well as backlash from the international community, Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), the plant’s operator, started discharging the radioactive wastewater in the morning, the first round in fiscal 2024.
Similar to the previous four rounds, about 7,800 tons of the wastewater, which still contains tritium, a radioactive substance, will be discharged until May 7.
TEPCO analyzed the water stored in the tank scheduled for release, and found that the concentrations of all radioactive substances other than tritium were below the national release standards, while the concentration of tritium that cannot be removed will be diluted with seawater, Japanese newspaper Asahi Shimbun reported.
TEPCO will measure the concentration of radioactive substances such as tritium in the surrounding waters every day during the period to investigate the effects of the release, it added.
The Fukushima nuclear-contaminated water release began in August 2023, and a total of about 31,200 tons of the water was released in four rounds in fiscal 2023, which ended in March.
In fiscal 2024, TEPCO plans to discharge a total of 54,600 tons of contaminated water in seven rounds, which contains approximately 14 trillion becquerels of tritium.
Coral bleaching: Fourth global mass stress episode underway – US scientists

Coral around the world is turning white and even dying as recent record
ocean heat takes a devastating toll. It has triggered the fourth global
mass coral bleaching event, according to the US National Oceanic and
Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
Bleaching happens when coral gets
stressed and turns white because the water it lives in is too hot. Coral
sustains ocean life, fishing, and creates trillions of dollars of revenue
annually.
Ocean heat records have been falling for months but this is the
first global evidence of how this episode is affecting sea life. The US
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) confirmed the mass
stress in all oceans (the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Ocean) after weeks
of receiving reports from scientists globally. The bleached coral can look
beautiful in pictures but scientists that dive to examine the reefs say
that up close the coral is clearly ill and decaying.
BBC 15th April 2024
Not content with nuclear wastes to the seas, the nuclear lobby now wants floating nuclear power – (for the environment! they say).

New association for maritime nuclear created
OFFSHORE ENERGY , April 3, 2024, by Naida Hakirevic Prevljak
A global group of companies with a common interest in developing nuclear energy solutions for the maritime sector have launched Nuclear Energy Maritime Organization (NEMO).
To be headquartered in London, NEMO will officially start activities in the second quarter of 2024.
By bringing together stakeholders with relevant expertise, NEMO aims to assist nuclear and maritime regulators in the development of appropriate standards and rules for the deployment, operation and decommissioning of floating nuclear power………………………………
Advanced nuclear technologies deployed at sea can reduce environmental impact, enhance social responsibility, and increase economic competitiveness. NEMO aims to provide a platform for its members to network and facilitate a functional connection between regulators to foster development and exchange best practices.
NEMO’s inaugural members are South Korean shipbuilder HD KSOE, the UK-based classification society Lloyd’s Register, American manufacturing and engineering company BWXT Advanced Technologies, American nuclear innovation company TerraPower, Japanese shipbuilder and ship repairer Onomichi Dockyard, American nuclear reactor designer and vendor Westinghouse Electric Company, Anglo-American maritime nuclear innovation company CORE POWER (UK), Fincantieri subsidiary VARD Group, French classification society Bureau Veritas, Italian classification society RINA, and Korean developer, consultant serving nuclear supply chain JEIL Partners.
……………………………………. The organization plans to hold regular events, workshops, webinars, and publications for its members and the wider public. The organization also intends to collaborate with other industry associations, government bodies, academic institutions, and civil society organizations to advance the cause of floating nuclear power.
In related news, Korean industry majors, led by shipping companies HMM and Sinokor, forged an alliance last year to develop nuclear-powered ships.
Under the agreement, the partners aim to develop and demonstrate how small modular nuclear reactors can be used to propel ships. The project will also investigate the development of relevant marine system interface and propulsion technology as well as the production of hydrogen using molten salt reactors (MSR). https://www.offshore-energy.biz/new-association-for-maritime-nuclear-created/
Japan confirms experts met in China to ease concerns over discharge of treated radioactive water
Japan said Sunday its experts have held talks with their Chinese
counterparts to try to assuage Beijing´s concerns over the discharge of
treated radioactive wastewater from the wrecked Fukushima Daiichi nuclear
power plant into the sea. The discharges have been opposed by fishing
groups and neighboring countries especially China, which banned all imports
of Japanese seafood. China´s move has largely affected Japanese scallop
growers and exporters to China. During the talks held Saturday in the
northeastern Chinese city of Dalian, Japanese officials provided
“science-based” explanation of how the discharges have been safely carried
out as planned, according to the Japanese Foreign Ministry.
Daily Mail 31st March 2024
Japan finishes first-year ocean discharge of nuclear-tainted wastewater amid backlash

“All fishermen are against ocean dumping. The contaminated water has flowed into what we fishermen call ‘the sea of treasure’, and the process will last for at least 30 years,“
“There is no good reason to dump radioactive materials into the ocean. There is no reason to just dilute them and flush them away,“
https://thesun.my/world/japan-finishes-first-year-ocean-discharge-of-nuclear-tainted-wastewater-amid-backlash-PD12227910 18 Mar 24,
TOKYO: Despite opposition and concern from at home and abroad, Japan’s crippled Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant has finished its initial year of discharging nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean, according to the plant’s operator, said Xinhua.
As per the initial plan, approximately 31,200 tons of wastewater, containing radioactive tritium, was released into the ocean since the discharge started in August 2023, with each round of discharge carried out for about two weeks. Earlier this week, International Atomic Energy Agency Director-General Rafael Grossi emphasised continued efforts in monitoring Japan’s ocean discharge of nuclear-contaminated wastewater from the crippled plant, following his first visit to Fukushima prefecture since the discharge started.
Stressing that the discharge marks merely the initial phase of a long process, Grossi said that “much effort will be required in the lengthy process ahead,“ and reiterated the organisation’s stance on maintaining vigilance throughout the process.
While the Japanese government and TEPCO have asserted the safety and necessity of the discharge, concerns have been raised by neighbouring countries and local stakeholders regarding environmental impacts.
“All fishermen are against ocean dumping. The contaminated water has flowed into what we fishermen call ‘the sea of treasure’, and the process will last for at least 30 years,“ said Haruo Ono, a fisherman in the town of Shinchi in Fukushima.
“There is no good reason to dump radioactive materials into the ocean. There is no reason to just dilute them and flush them away,“ said the man in his 70s.
“Is it really necessary, in the first place, to dump what has been stored in tanks into the sea? How can we say it’s ‘safe’ when the discharged water clearly consists of harmful radioactive substances? I think the government and TEPCO must provide a solid answer,“ said Chiyo Oda, a resident of Fukushima’s Iwaki city.
Concerns were fuelled among the Japanese public over the recent leakage of contaminated water from pipes at the Fukushima plant. – Bernama, Xinhua
Fourth discharge of treated Fukushima water completed

The release of the fourth batch of treated radioactive water from the
crippled Fukushima No. 1 nuclear power plant into the sea concluded Sunday,
with the next round possibly starting next month, the plant’s operator
said.
Japan Times 17th March 2024
https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2024/03/17/japan/fourth-fukushima-water-release-completed
Concerns and complaints continue as fourth Fukushima wastewater discharge completed

Concerns and complaints from home and abroad remain while Japan’s crippled Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant has finished its first year of discharging nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean.
The plant completed its fourth and final round of discharge for the current fiscal year, which ends in March, Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) said on Sunday.
As per the initial plan, approximately 31,200 tonnes of wastewater containing radioactive tritium has been released into the ocean since August 2023, with each discharge running for about two weeks.
Earlier this week, International Atomic Energy Agency Director-General Rafael Grossi emphasized continued efforts to monitor the discharging process.
Stressing that the discharge marks merely the initial phase of a long process, Grossi said that “much effort will be required in the lengthy process ahead,” and reiterated the organization’s stance on maintaining vigilance throughout the process.
While the Japanese government and TEPCO have asserted the safety and necessity of the process, there are still concerns from other countries and local stakeholders regarding environmental impacts.
Sophia from the U.S. complained that the release of nuclear-contaminated water into the sea made her fear for the future.
Najee Johnson, a college student from Canada, suggested the Japanese government find a different plan because it could pollute our ocean and harm our sea life.
Haruo Ono, a fisherman in the town of Shinchi in Fukushima, said “All fishermen are against ocean dumping. The contaminated water has flowed into what we fishermen call ‘the sea of treasure’, and the process will last for at least 30 years.”
“Is it really necessary, in the first place, to dump what has been stored in tanks into the sea? How can we say it’s ‘safe’ when the discharged water clearly consists of harmful radioactive substances? I think the government and TEPCO must provide a solid answer,” said Chiyo Oda, a resident of Fukushima’s Iwaki city.
The recent leakage of contaminated water from pipes at the Fukushima plant also fueled concerns among the Japanese public.
Besides, the promised fund of more than 100 billion yen (around $670 million) to compensate and support local fishermen and fishing industry remains doubtful as a court ruling last December relieved the government of responsibility to pay damages to Fukushima evacuees.
A Tokyo court ruled that only the operator of the tsunami-wrecked Fukushima nuclear power plant has to pay damages to the evacuees, relieving the government of responsibility. Plaintiffs criticized the ruling as belittling their suffering and the severity of the disaster. The court also slashed the amount by ordering the TEPCO to pay a total of 23.5 million yen to 44 of the 47 plaintiffs.
The ruling backpedaled from an earlier decision in March 2018, when the Tokyo District Court held both the government and TEPCO accountable for the disaster, which the ruling said could have been prevented if they both took better precautionary measures, ordering both to pay 59 million yen in damages.
Radioactive waste, baby bottles and Spam: the deep ocean has become a dumping ground

The ocean’s depths are not some remote alien realm, but are in fact intimately entangled with every other part of the planet. We should treat them that way
by James Bradley. Guardian 12 Mar…….
“…………………………………………………………………………………………..The ocean’s depths have also been used as the final resting place for large amounts of nuclear material.
A 2019 study found at least 18,000 radioactive objects scattered across the bottom of the Arctic Ocean, many of them dumped there by the Soviet Union. These objects include vessels such as the K-27, the 110-metre nuclear submarine powered by an experimental liquid-metal-cooled reactor, which was scuttled in 1982 with its reactor still on board (when the explosive charges that were supposed to sink the K-27 failed to fully detonate, it had to be rammed with a tug); the wreck of the K-141 Kursk, which sank in the Barents Sea in 2000 during a naval exercise, killing all 118 on board and bearing its reactor and fuel to the bottom; and the K-159 attack submarine, which sank while being towed near Murmansk in 2003 with 800kg of spent uranium fuel on board. The head of Norway’s Nuclear Safety Authority says it is only a matter of time before these objects begin to release their toxic legacy into the water; others have called the situation a “Chornobyl in slow motion on the sea floor”.
While the Soviet Union dumped more nuclear waste on the sea floor than any other country, it was certainly not alone. Between 1948 and 1982, the British government consigned almost 70,000 tonnes of nuclear waste to the ocean’s depths, and the US, Switzerland, Japan and the Netherlands are just a few of the nations that have used the ocean to dispose of radioactive material, albeit in much smaller quantities. And while international treaties now prohibit the dumping of radioactive material at sea, the British government is exploring plans to dispose of up to 750,000 cubic metres of nuclear waste, including more than 100 tonnes of plutonium, beneath the sea floor off Cumbria. British officials argue this sort of geological disposal offers a way of keeping waste stable and secure over hundreds of thousands of years, although incidents such as the 2014 leak of radioactive material at a waste disposal facility half a kilometre beneath salt beds in New Mexico suggests that like many of the assurances offered by the nuclear industry, this claim should be approached with great caution.
The dumping of nuclear waste in the ocean is only one part of a far larger story of carelessness and greed. Human waste in the form of plastics and other objects is everywhere in the deep ocean, a fact that is made brutally apparent by the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology’s Deep-sea Debris Database, which documents the presence of tyres, fishing nets, sports bags, mannequins, beach balls and baby’s bottles spread across the sea floor at depths of many thousands of metres. In some regions, the number of such objects exceeds 300/sq km.
This tide of garbage has even reached the deepest and most remote parts of the ocean: …………………………………………………………………………………….
Possibly more disturbing, though, is the growing accumulation of microplastics in the ocean depths………………………………………………..
Nor is plastic the only thing that drifts downwards. In 2019 Chinese scientists discovered radioactive carbon-14 from the detonation of nuclear bombs in the 1940s and 50s in the bodies of amphipods living at the bottom of the Mariana Trench, borne into the deep not by ocean circulation, but in the rain of organic matter from above. More recent studies have found radioactive caesium from the Fukushima nuclear disaster in sediment more than 7,000 metres down in the Japan Trench……………………………………………………….. more https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2024/mar/12/radioactive-waste-baby-bottles-and-spam-the-deep-ocean-has-become-a-dumping-ground
Could Fukushima’s radioactive water pose lasting threat to humans and the environment?

studies have highlighted how tritium can be absorbed into sediments and soils, raising concerns about its potential transfer to the water cycle and the food web.
research showing that fish have transported radioactive particles generated by the Fukushima incident far and wide. Like a number of other nuclear accidents before it, that makes what happened at Fukushima a global concern.”
by Alan Williams, University of Plymouth, https://phys.org/news/2024-03-fukushima-radioactive-pose-threat-humans.html
The meltdown of Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi power plant, caused by the devastating earthquake and tsunami of March 2011, represents the most severe nuclear power accident of the 21st century so far.
However, a new study highlights how the decision by the Japanese government to begin releasing the radioactive water stored within it—a decision approved by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)—has generated scientific and public debate, given its potential to cause environmental harm for decades to come.
Writing in the journal Environmental Science and Technology, researchers say the water cannot be stored indefinitely due to the ongoing risk of earthquakes and tsunamis in the region.
But they say not enough is known about the long-term impacts of tritium—the primary radionuclide present, with a half-life of 12.6 years—to ascertain if the release of more than one million tons of water can be considered safe or not.
As a result, they have called for assurances that regular monitoring will be carried out in different components of the region’s ecosystem to examine any impacts the release might be having on the environment.
They have also suggested more evidence is needed about the future effects of tritium in the presence of multiple and emerging stressors, such as hypoxia, rising ocean temperatures, and microplastics, given that environmental contamination can occur in many combinations.
The study was carried out at the University of Plymouth, where researchers have been examining the environmental impacts of radioactive material for almost three decades.
“The Japanese tsunami of 2011 was devastating for people living along this whole coastline. The presence of a nuclear power plant within the region left a lasting threat, and this study highlights some of the complex challenges that need managing and scientific questions that still need addressing.”
“Being in a region prone to earthquakes and tsunamis, there is an obvious danger in simply storing radioactive water there indefinitely. But based on our research, not enough is known about the impacts of tritium on both environmental and human health to say that releasing the water into the ocean is completely safe,” says Awadhesh Jha, professor in genetic toxicology and ecotoxicology and corresponding author on the research.
The new study includes a review of existing literature on the behavior of tritium in the environment and studies that have assessed its impact on individual species.
That includes studies that have highlighted how tritium can be absorbed into sediments and soils, raising concerns about its potential transfer to the water cycle and the food web.
There has also been research showing that tritium can cause DNA damage to certain fish species, which could impact their physical and reproductive fitness and—ultimately—the genetic diversity of a population.
However, the researchers say there is little data available on the distribution, behavior, and potential effects of tritiated water and organically-bound tritium, and therefore assessing the broad risks is almost impossible.
They also say the Fukushima situation cannot be compared with the Chornobyl accident, as some authorities have attempted to do, given the differing geographical locations of the two plants and the fact the long-term environmental impacts of Chornobyl are still being debated.
“Through our study, we have found research showing that fish have transported radioactive particles generated by the Fukushima incident far and wide. Like a number of other nuclear accidents before it, that makes what happened at Fukushima a global concern.”
“As such, we urgently need global research into the impacts of tritium—and how they might be managed—especially with the nuclear power industry set to expand significantly. If it does indeed expand, the construction of nuclear power plants, especially in coastal regions, should also take into account worst-case scenarios of flooding, earthquakes, and tsunamis as part of a fundamental goal to minimize radioactive discharges to the environment,” says Professor Jha.
New Research from Antarctica Affirms the Threat of the ‘DoomsdayGlacier,’ but Funding to Keep Studying It Is Running Out.
In a worst case scenario, rising global temperatures and marine heatwaves could melt enough of the Thwaites Glacier and other Antarctic ice to raise sea levels 10 feet by the early 2100s.

Inside Climate News, By Bob Berwyn, February 26, 2024
“………………………………………………………….. It took a whole day of sailing just to monitor and map the front of the Thwaites Glacier’s floating shelf, he said, with ice cliffs in some places towering several hundred feet above the water, marking the abrupt edge of an ice expanse about the size of Nebraska and averaging between 2,500 and 4,000 feet thick. If all the ice melts, it would raise average global sea level about 2 feet.
The sediment samples Kirkham and other scientists collected four years ago provided the data for a study published Monday in the Proceedings of the National Academies of Sciences that affirms one of the most serious concerns about Antarctica—that an irreversible meltdown of some of the frozen continent’s ice masses has already started.
“You just can’t ignore what’s happening on this glacier,” said lead author Rachel Clark, a University of Houston ice researcher who also works with the International Thwaites Glacier Collaboration, a team that has been trying to figure out just how fast the vulnerable ice will melt. But, she said the new study is important because it shows that the melting is not just random or limited to one glacier.
“It is part of a larger context of a changing climate,” she said.
Not Just Thwaites
After analyzing the chemistry and other characteristics of seafloor sediment grains from various depths and different locations near the floating edge of the glacier, the team’s members were able to show that the glacier had been relatively stable for nearly 10,000 years, since the end of the last ice age, but that it started to retreat in the mid-1940s.
Shifts in regional winds and associated changes in ocean currents are pushing more relatively warm water toward Antarctica’s frozen fringe, melting the ice and loosening it from rocky seafloor anchor points that have held the floating part of the glacier in place for thousands of years. As the ice melts away from the pinning points, it can float to sea and disintegrate faster, allowing the glacier behind it to accelerate toward the ocean. In the last 30 years, the amount of ice flowing out to sea from the Thwaites and Pine Island glacial areas and their associated floating ice shelves has doubled.
……………………………………the Thwaites Glacier, and the neighboring Pine Island Glacier, have kept retreating since the 1940s. …………………..
While the Thwaites Glacier has been identified as being among the most vulnerable to pinning point loss, a similar pattern of melting and retreat in many other Antarctic glaciers and ice shelves at least since the 1970s was documented in a separate study published Feb. 21 in Nature.
………………………………………………………… “We already seem to have pushed the climate and ice sheet system past certain irreversible thresholds, and need to observe and understand more about Thwaites, not less,” said Pam Pearson, founder and director of the International Cryosphere Climate Initiative. “Pleas of ignorance will be little comfort to future generations displaced by Antarctic sea-level rise that we could have stopped had we only acted in time.” https://insideclimatenews.org/news/26022024/new-research-from-antarctica-affirms-threat-of-doomsday-glacier-but-funding-is-running-out/
Release of fourth batch of Fukushima treated radioactive water begins

Japan Times, 28 Feb 24
The operator of the crippled Fukushima No. 1 nuclear power plant on Wednesday started releasing a fourth batch of treated radioactive water into the sea, in what will be the last discharge for the fiscal year ending March.
As in previous rounds, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings (Tepco) will discharge 7,800 metric tons of treated water over about 17 days, having confirmed that the radioactivity level of the latest batch of water meets the standards set by the government and the utility.
China, which opposes the water release, has banned Japanese seafood imports since the first discharge in late August. The two countries have engaged in informal discussions to resolve the matter, but no substantial progress has been made……………………….. more https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2024/02/28/japan/society/fukushima-radioactive-water-fourth-release/
China is ‘unlikely’ to lift import ban on Japanese seafood as dumping continues

predatory species higher up in the food chain have a greater chance of experiencing bioaccumulation and biomagnification of radioactive substances. As time goes on and more nuclear-contaminated water is discharged, the negative effects will only increase
By GT staff Feb 25, 2024 , https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202402/1307658.shtml
Half a year after Japan opened Pandora’s box by dumping nuclear-contaminated wastewater from the crippled Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the ocean, Japanese media are discussing the possibility of bilateral talks for getting China to revoke its import ban on Japanese marine products, in an apparent attempt to test the waters.
In response, Chinese experts told the Global Times on Sunday that, in the short term, it is unlikely that China will revoke the ban as there are currently no conditions for a withdrawal.
Meanwhile, a Kyodo News survey on Friday showed that most Japanese fishery groups have been affected by the discharge, with many feeling the impact through China’s import ban on Japanese seafood.
The survey found that 29 out of 36 respondents among the members of the National Federation of Fisheries Cooperative Associations said they “had felt” or “had somewhat felt” negative effects, including financial damage due to the contaminated water dumping, overwhelmingly due to the subsequent import ban by China.
Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Mao Ning said at a regular press conference that the precautionary measures taken by China and some other countries in response to Japan’s move are aimed at protecting food safety and people’s health.
“These measures are entirely legitimate, reasonable and necessary,” Mao said.
Chang Yen-chiang, director of the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea Research Institute of Dalian Maritime University, revealed several main factors why China is less likely to revoke the ban in the short run.
There is no halt in the ocean discharge, that is, the Japanese side has not withdrawn from their erroneous actions, he said.
Currently, half a year has passed since the dumping began, meaning that under the influence of ocean currents, the impact of Japan’s nuclear-contaminated water discharge on East Asia may just be starting, and further impacts need to be assessed, Chang said.
In addition, predatory species higher up in the food chain have a greater chance of experiencing bioaccumulation and biomagnification of radioactive substances. As time goes on and more nuclear-contaminated water is discharged, the negative effects will only increase, Chang said. “Under these circumstances, how could the ban be lifted?” the expert asked.
TEPCO – operator of the Daiichi plant – plans to release a total of about 54,600 tons of nuclear-contaminated water on seven occasions in the 2024 fiscal year, more than double the amount of 2023, according to media reports.
Chang called on Japan to consider solving the Fukushima nuclear power plant issue on a fundamental level, such as focusing on research on how to handle the burnt-out nuclear reactors. Otherwise, radioactive substances will continue to be produced endlessly, and the discharge of nuclear contamination could last for over 100 years, making the situation increasingly worse.
Japanese media have reported on a series of scandals concerning leaks occurring during the contaminated water discharge process, which led to soil contamination around the nuclear power plant.
Most recently, 1.5 metric tons of highly radioactive water escaped in early February during valve checks at a treatment machine designed to remove cesium and strontium from the contaminated water, according to TEPCO.
According to Japanese experts studying the soil, the radiation levels in Fukushima soil are much higher compared to other areas.
“We should be more vigilant toward crops and plants grown in this contaminated soil. China should increase radioactive testing of Japanese agricultural products and cosmetics imports,” Chang stated.
China is ‘unlikely’ to lift import ban on Japanese seafood as dumping continues
By GT staff reportersPublished: Feb 25, 2024 09:50 PM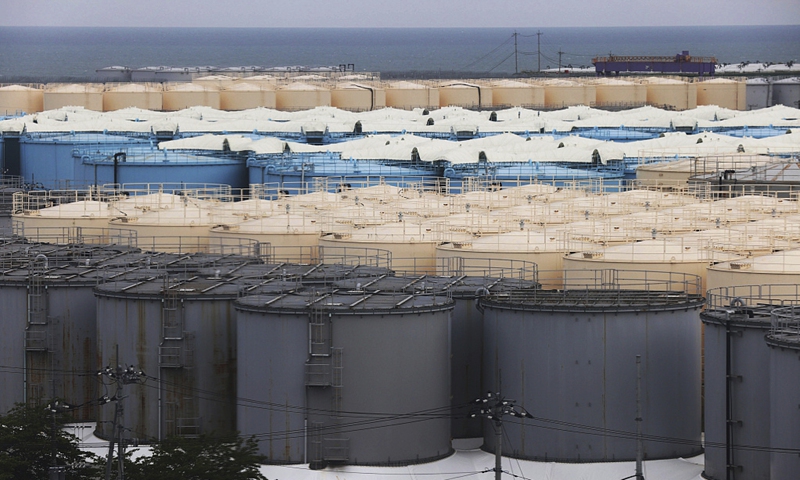
Water tanks near Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant in Okuma town of Fukushima prefecture on May 26, 2023 Photo: VCG
Half a year after Japan opened Pandora’s box by dumping nuclear-contaminated wastewater from the crippled Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the ocean, Japanese media are discussing the possibility of bilateral talks for getting China to revoke its import ban on Japanese marine products, in an apparent attempt to test the waters.
In response, Chinese experts told the Global Times on Sunday that, in the short term, it is unlikely that China will revoke the ban as there are currently no conditions for a withdrawal.
Meanwhile, a Kyodo News survey on Friday showed that most Japanese fishery groups have been affected by the discharge, with many feeling the impact through China’s import ban on Japanese seafood.
The survey found that 29 out of 36 respondents among the members of the National Federation of Fisheries Cooperative Associations said they “had felt” or “had somewhat felt” negative effects, including financial damage due to the contaminated water dumping, overwhelmingly due to the subsequent import ban by China.
Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Mao Ning said at a regular press conference that the precautionary measures taken by China and some other countries in response to Japan’s move are aimed at protecting food safety and people’s health.
“These measures are entirely legitimate, reasonable and necessary,” Mao said.
Chang Yen-chiang, director of the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea Research Institute of Dalian Maritime University, revealed several main factors why China is less likely to revoke the ban in the short run.
There is no halt in the ocean discharge, that is, the Japanese side has not withdrawn from their erroneous actions, he said.
Currently, half a year has passed since the dumping began, meaning that under the influence of ocean currents, the impact of Japan’s nuclear-contaminated water discharge on East Asia may just be starting, and further impacts need to be assessed, Chang said.
In addition, predatory species higher up in the food chain have a greater chance of experiencing bioaccumulation and biomagnification of radioactive substances. As time goes on and more nuclear-contaminated water is discharged, the negative effects will only increase, Chang said. “Under these circumstances, how could the ban be lifted?” the expert asked.
TEPCO – operator of the Daiichi plant – plans to release a total of about 54,600 tons of nuclear-contaminated water on seven occasions in the 2024 fiscal year, more than double the amount of 2023, according to media reports.
Chang called on Japan to consider solving the Fukushima nuclear power plant issue on a fundamental level, such as focusing on research on how to handle the burnt-out nuclear reactors. Otherwise, radioactive substances will continue to be produced endlessly, and the discharge of nuclear contamination could last for over 100 years, making the situation increasingly worse.
Japanese media have reported on a series of scandals concerning leaks occurring during the contaminated water discharge process, which led to soil contamination around the nuclear power plant.
Most recently, 1.5 metric tons of highly radioactive water escaped in early February during valve checks at a treatment machine designed to remove cesium and strontium from the contaminated water, according to TEPCO.
According to Japanese experts studying the soil, the radiation levels in Fukushima soil are much higher compared to other areas.
“We should be more vigilant toward crops and plants grown in this contaminated soil. China should increase radioactive testing of Japanese agricultural products and cosmetics imports,” Chang stated.
As Japanese industries, including fisheries and cosmetics, have been affected, Japanese media continues to report news about bilateral talks aimed at getting China to revoke its import ban on Japanese marine products, trying to test the reaction from China.
The Asahi Shimbun revealed Friday that nuclear experts from Japan and China started talks in January regarding contaminated water. The report noted that the Chinese side has still shown no signs of ending its import ban.
The Kyodo News reported on Thursday that when Chinese Ambassador to Japan Wu Jianghao met with the leader of the Social Democratic Party, Mizuho Fukushima, in January, China’s import suspension was also discussed, but there were no conditions for lifting the ban at present.
Antarctica sea ice reaches alarming low for third year in a row

The extent of ice floating around the continent has contracted to below 2m sq km for three years in a row, indicating an ‘abrupt critical transition’
Graham Readfearn, 25 Feb 24 https://www.theguardian.com/world/2024/feb/24/antarctica-sea-ice-reaches-alarming-low-for-third-year-in-a-row
For the third year in a row, sea ice coverage around Antarctica has dropped below 2m sq km – a threshold which before 2022 had not been breached since satellite measurements started in 1979.
The latest data from the US National Snow and Ice Data Center confirms the past three years have been the three lowest on record for the amount of sea ice floating around the continent.
Scientists said another exceptionally low year was further evidence of a “regime shift”, with new research indicating the continent’s sea ice has undergone an “abrupt critical transition”.
Antarctica’s sea ice reaches its lowest extent at the height of the continent’s summer in February each year.
On 18 February the five-day average of sea ice cover fell to 1.99m sq km and on 21 February was at 1.98m sq km. The record low was 1.78m sq km, set in February 2023.
Whether the current level represents this year’s minimum won’t be known for another week or two.
Antarctica sea ice reaches alarming low for third year in a row
The extent of ice floating around the continent has contracted to below 2m sq km for three years in a row, indicating an ‘abrupt critical transition’
Graham Readfearn @readfearnSun 25 Feb 2024
For the third year in a row, sea ice coverage around Antarctica has dropped below 2m sq km – a threshold which before 2022 had not been breached since satellite measurements started in 1979.
The latest data from the US National Snow and Ice Data Center confirms the past three years have been the three lowest on record for the amount of sea ice floating around the continent.
Scientists said another exceptionally low year was further evidence of a “regime shift”, with new research indicating the continent’s sea ice has undergone an “abrupt critical transition”.
Antarctica’s sea ice reaches its lowest extent at the height of the continent’s summer in February each year.
On 18 February the five-day average of sea ice cover fell to 1.99m sq km and on 21 February was at 1.98m sq km. The record low was 1.78m sq km, set in February 2023.
Whether the current level represents this year’s minimum won’t be known for another week or two.
“But we’re confident the three lowest years on record will be the last three years,” said Will Hobbs, a sea ice scientist at the University of Tasmania.
Antarctica’s sea ice reaches its peak each September, but last year’s maximum extent was the lowest on record, easily beating the previous record by about 1m sq km. Scientists were shocked at how much less ice regrew last year, falling well outside anything seen before.
Coverage appeared to recover slightly in December as the refreeze progressed, but then fell away again to the current levels.
There are no reliable measurements of how thick Antarctic sea ice is, but Ariaan Purich, a climate scientist specialising in Antarctica and the Southern Ocean at Monash University, said it was possible the ice that did regrow was thinner than usual.
“It seems plausible, and thinner sea ice could melt back more quickly,” she said.
Scientists are still investigating what is causing the decline in sea ice,, but they are concerned global heating could be playing a role – in particular by warming the Southern Ocean that encircles the continent.
Sea ice reflects solar radiation, meaning less ice can lead to more ocean warming.
Walt Meier, senior research scientist at the National Snow and Ice Data Center, said that since most of the ice melts completely each summer “much of the ice is only 1-2 metres [thick]” – and even less near the ice edge.
“With the very low maximum last September, the ice was probably thinner on average in many areas, but it’s hard to say how much of an effect it has had on the rate of melt and the approaching minimum,” he said.
Antarctica’s ecosystems are tied to the sea ice, from the formation of phytoplankton that can remove carbon from the atmosphere to the breeding sites of penguins.
Purich led research last year that said the continent’s sea ice could have undergone a “regime shift” that was probably driven by warming of the subsurface ocean about 100 metres down.
Research led by Hobbs and colleagues at the Australian Antarctic Program Partnership and other institutions has added evidence to support this claim.
In a paper published this month in the Journal of Climate scientists examined changes in the extent of sea ice and where it was forming each year.
Looking at two periods – 1979 to 2006 and 2007 to 2022 – the researchers found the amount of sea ice had become much more variable, or erratic, in the later period.
This change could not be explained by changes in the atmosphere – mostly winds – which have previously dictated most of the year-to-year variability of the ice.
The study concludes an “abrupt critical transition” has occurred in Antarctica, but Hobbs said they could not say why.
“We don’t know what the driver of change is. It could be ocean warming or a change in ocean salinity,” he said. But it was also possible the change was a natural shift.
Scientists have warned the loss of sea ice is just one of several major changes being observed in Antarctica that is likely to have global consequences – in particular, its loss is exposing more of the continent to the ocean, accelerating the loss of ice on the land, which can push up global sea levels.
Scientists have been increasingly vocal in calling for governments to take the Antarctic changes more seriously and have lamented the comparative lack of data from on and around the continent.
Hobbs said: “What we need is sustained measurements of ocean temperature and salinity underneath the sea ice. We need improvements in our climate models. And we need time.”
Atlantic Ocean circulation nearing ‘devastating’ tipping point, study finds

Collapse in system of currents that helps regulate global climate would be at such speed that adaptation would be impossible
Jonathan Watts, 12 Feb 24,
https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2024/feb/09/atlantic-ocean-circulation-nearing-devastating-tipping-point-study-finds
The circulation of the Atlantic Ocean is heading towards a tipping point that is “bad news for the climate system and humanity”, a study has found.
The scientists behind the research said they were shocked at the forecast speed of collapse once the point is reached, although they said it was not yet possible to predict how soon that would happen.
Using computer models and past data, the researchers developed an early warning indicator for the breakdown of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (Amoc), a vast system of ocean currents that is a key component in global climate regulation.
They found Amoc is already on track towards an abrupt shift, which has not happened for more than 10,000 years and would have dire implications for large parts of the world.
Amoc, which encompasses part of the Gulf Stream and other powerful currents, is a marine conveyer belt that carries heat, carbon and nutrients from the tropics towards the Arctic Circle, where it cools and sinks into the deep ocean. This churning helps to distribute energy around the Earth and modulates the impact of human-caused global heating.
But the system is being eroded by the faster-than-expected melt-off of Greenland’s glaciers and Arctic ice sheets, which pours freshwater into the sea and obstructs the sinking of saltier, warmer water from the south.
Amoc has declined 15% since 1950 and is in its weakest state in more than a millennium, according to previous research that prompted speculation about an approaching collapse.
Until now there has been no consensus about how severe this will be. One study last year, based on changes in sea surface temperatures, suggested the tipping point could happen between 2025 and 2095. However, the UK Met Office said large, rapid changes in Amoc were “very unlikely” in the 21st century.
The new paper, published in Science Advances, has broken new ground by looking for warning signs in the salinity levels at the southern extent of the Atlantic Ocean between Cape Town and Buenos Aires. Simulating changes over a period of 2,000 years on computer models of the global climate, it found a slow decline can lead to a sudden collapse over less than 100 years, with calamitous consequences.
The paper said the results provided a “clear answer” about whether such an abrupt shift was possible: “This is bad news for the climate system and humanity as up till now one could think that Amoc tipping was only a theoretical concept and tipping would disappear as soon as the full climate system, with all its additional feedbacks, was considered.”
It also mapped some of the consequences of Amoc collapse. Sea levels in the Atlantic would rise by a metre in some regions, inundating many coastal cities. The wet and dry seasons in the Amazon would flip, potentially pushing the already weakened rainforest past its own tipping point. Temperatures around the world would fluctuate far more erratically. The southern hemisphere would become warmer. Europe would cool dramatically and have less rainfall. While this might sound appealing compared with the current heating trend, the changes would hit 10 times faster than now, making adaptation almost impossible.
“What surprised us was the rate at which tipping occurs,” said the paper’s lead author, René van Westen, of Utrecht University. “It will be devastating.”
He said there was not yet enough data to say whether this would occur in the next year or in the coming century, but when it happens, the changes are irreversible on human timescales.
In the meantime, the direction of travel is undoubtedly in an alarming direction.
“We are moving towards it. That is kind of scary,” van Westen said. “We need to take climate change much more seriously.”
Fijian youths condemn Japan’s discharge of radioactive water
Global Stringer, 22-Jan-2024, https://news.cgtn.com/news/2024-01-22/We-Talk-Fijian-youths-condemn-Japan-s-discharge-of-radioactive-water-1qz4wGtqnkc/p.html
The fourth round of discharge of nuclear-contaminated water from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant will begin in late February 2024, with a total release of 7,800 tonnes, local media reported on December 18. Japan has so far completed three rounds of nuclear discharge, sending more than 23,000 tonnes of nuclear wastewater into the Pacific Ocean in less than three months.
CGTN Stringer took to the streets of Fiji and asked many local college students for their opinions on this matter. The students expressed their strong opposition, noting that the islanders depend on the sea for a living. The discharge of nuclear-contaminated water into the sea will pollute the Pacific Ocean and destroy coral groups. It will seriously affect the living resources of the islanders, endanger the health of the people of the island country, and cause immeasurable damage to ecosystems.
-
Archives
- April 2024 (333)
- March 2024 (335)
- February 2024 (345)
- January 2024 (375)
- December 2023 (333)
- November 2023 (342)
- October 2023 (366)
- September 2023 (353)
- August 2023 (356)
- July 2023 (363)
- June 2023 (324)
- May 2023 (344)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS


