‘The graveyard of the Earth’: inside City 40, Russia’s deadly nuclear secret
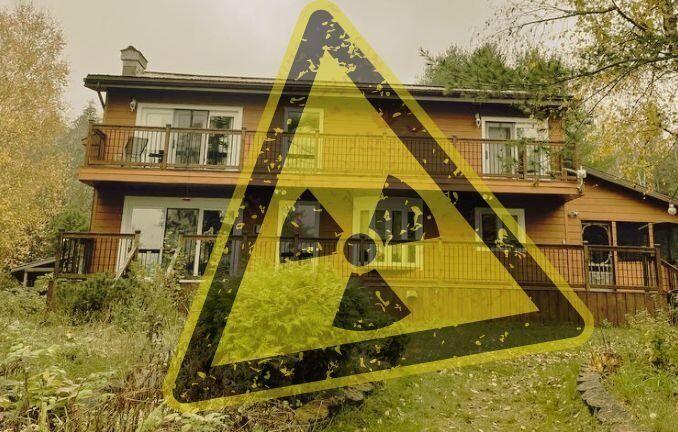
The city’s residents know the truth, however: that their water is contaminated, their mushrooms and berries are poisoned, and their children may be sick. Ozersk and the surrounding region is one of the most contaminated places on the planet, referred to by some as the “graveyard of the Earth”.
City 40’s inhabitants were told they were “the nuclear shield and saviours of the world”

From the late 1940s, people here started to get sick and die: the victims of long-term exposure to radiation.
‘The graveyard of the Earth’: inside City 40, Russia’s deadly nuclear secret, https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2016/jul/20/graveyard-earth-inside-city-40-ozersk-russia-deadly-secret-nuclear Samira Goetschel, Wed 20 Jul 2016 Ozersk, codenamed City 40, was the birthplace of the Soviet nuclear weapons programme. Now it is one of the most contaminated places on the planet – so why do so many residents still view it as a fenced-in paradise?
“Those in paradise were given a choice: happiness without freedom, or freedom without happiness. There was no third alternative.” (From the dystopian novel We, by Yevgeny Zamyatin, 1924)
Deep in the vast forests of Russia’s Ural mountains lies the forbidden city of Ozersk. Behind guarded gates and barbed wire fences stands a beautiful enigma – a hypnotic place that seems to exist in a different dimension.
Codenamed City 40, Ozersk was the birthplace of the Soviet nuclear weapons programme after the second world war. For decades, this city of 100,000 people did not appear on any maps, and its inhabitants’ identities were erased from the Soviet census.
Today, with its beautiful lakes, perfumed flowers and picturesque tree-lined streets, Ozersk resembles a suburban 1950s American town – like one of those too-perfect places depicted in The Twilight Zone.
Continue reading“Man-Made Hell On Earth”: A Canadian Doctor on His Medical Mission to Gaza

“I saw scenes that were horrific and I never want to see again,” said Yasser Khan, a surgeon from Toronto.
Jeremy Scahill, Intercepted, March 23 2024,
THROUGHOUT THE PAST five and a half months, Israel has waged a full-spectrum war against the civilian population of the Gaza Strip. The United States and other Western nations have supplied not only the weapons for this war of annihilation against the Palestinians, but also key political and diplomatic support.
The results of the actions of this coalition of the killing have been devastating. Conservative estimates hold that more than 31,000 Palestinians have been killed, including 13,000 children. More than 8,000 people remain missing, many of them believed to have died in the rubble of buildings destroyed in Israeli attacks. Famine conditions are now present in large swaths of the Gaza Strip. The fact that the International Court of Justice has found grounds to investigate Israel for plausible acts of genocide in Gaza has not deterred the U.S. and its allies from continuing to facilitate Israel’s war.
The massive scale of human destruction caused by the attacks would pose grave challenges to well-equipped hospitals. In Gaza, however, many health care facilities have been decimated by Israeli attacks or evacuated, while a few remain open but severely limited in the care and services they offer. Israeli forces have repeatedly laid siege to hospital facilities, killing hundreds of medical workers and taking captive scores of others, despite thousands of internally displaced Palestinians sheltering in the health care complexes. This week, Israel again launched raids on Al-Shifa Hospital, reportedly killing more than 140 people.
For months, doctors across Gaza have performed amputations and other high-risk procedures without anesthetics or proper operating rooms. Antibiotics are in short supply and often unavailable. Communicable diseases are spreading, as hundreds of thousands of Palestinians are forced to live in makeshift shelters with little access to toilets or basic sanitary supplies. Many new mothers are unable to breastfeed and infant formula shortages are common. Israel has repeatedly blocked or delayed aid shipments of vital medical supplies to Gaza. Basic preventative medical care is nearly nonexistent, and medical experts predict that malnutrition will condemn a new generation of young Palestinians to a life of developmental struggles.
The result of the onslaught against medical facilities is that there is only one fully functional hospital remaining in the territory, the European Hospital in Khan Younis. Dr. Yasser Khan, a Canadian ophthalmologist and plastic surgeon, just left Gaza where he spent 10 days at the hospital performing eye surgeries on victims of Israeli attacks. It was his second medical mission to Gaza since the war began last October.
What follows is a transcript of a lightly edited interview with Khan.
………………………Yasser Khan: Well, I’m from the greater Toronto area here in Canada, and I’ve been in practice for about 20 years. I’m an ophthalmologist, but I specialize in eyelid and facial plastic and reconstructive surgery.
So that’s my sub-specialty and that’s what I’ve been doing for about 20 years. And I’m a professor. I’ve been to over 45 different countries on a humanitarian basis where I’ve taught surgery, I’ve done surgery, I’ve established programs. And so I’ve been to many types of areas and zones in Africa, Asia, and South America…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
So that’s the kind of mass chaos that I encountered initially, and then I was told that every time there’s a bomb, give it about 15 minutes and the mass casualties come. That was the other thing that at the time shocked me: What we’d been seeing livestreamed on Instagram, on social media or whatever, I actually saw myself and it was worse than I can imagine. I saw scenes that were horrific that I’d never witnessed before and I never want to see again…………………………………………………….
It was quite demoralizing. You’ve gotta be on the ground to see how bad it is. In two months, things were not only the same in a bad way, but they’re much, much worse because now, two months later, Khan Younis has literally been destroyed as a city. It was an active, hustling, bustling city. The Nasser Hospital, as you know, it’s destroyed now. It’s basically a death zone. And there’s decomposing bodies in the hospital now. It’s been evacuated. And I will add one thing: As a health care worker, I know fully well that to build a major, fully functioning hospital takes years to perfect and build and process, right? So it’s a sheer tragedy that it’s destroyed in mere hours, so it’s really unfortunate…………………………………
So now [at European Gaza Hospital] instead of 20,000 people, there’s about 35,000 people seeking shelter in a hospital that’s already beyond capacity. And so now, both outside and inside, there’s a mass of people. There’s no place to move now in the hallways. The sterility of the hospital has significantly decreased. The European Gaza Hospital, all you have to do is go online and look at their pictures before. It was a beautiful, gorgeous hospital. Well-built, well-run, good quality control — and now it’s reduced to a place that is a mess. It’s a mess. There’s people cooking inside the hospital hallways, there’s the bathrooms, there’s people mixed in with the people who are sick, with major orthopedic injuries, post op. There’s no beds. So sometimes people go and just sleep in their little makeshift shelters. And so infection is, if you can imagine, infection is rampant. So if you don’t die the first time or if your leg or arm is not amputated the first time, it is for sure with infection. So then they have to amputate it to save your life. So it’s much, much worse.
The other thing I noticed was now, more so than even before, the health care workers and nurses and the doctors, they’re just burnt out. I mean, they’re just spent. They’ve witnessed so much in almost six months now. They’ve seen so much on a regular, hourly, daily basis. When I operate [at a hospital in Canada], typically speaking, I’ve got a few mostly elective lists, elective kind of not urgent problems that you gotta fix. And then there’s some trauma, or something that comes in that’s a bit more urgent once in a while, right? That’s my usual list. But [Palestinian medical workers], they are working on a daily basis on the most horrific, explosive trauma that you’ve ever seen. They’re doing sometimes 14, 15 amputations, mostly on children, per day, and they’ve been doing it for six months now.
The thing I try to emphasize to people is that it’s not only the actual medical trauma, it’s the other trauma associated with it in that these patients come in, if you’ve been involved in an explosive injury, and you come in injured, guaranteed you’ve lost loved ones. Guaranteed. So you’ve either lost a father, a mother, a child, all your children, all your family, your uncle, aunt, grandparents, your house, whatever. You’ve lost something. So every patient that comes in, not only is severely injured, is dealing with this trauma.
I had one girl who basically lost all her siblings, 8-year-old beautiful girl, lost her siblings. She came in for a leg fracture, was under the rubble for 12 hours. And her mother died, all her siblings gone. And all her family [were] gone, her aunts and uncles. As you know, it’s a generational killing, like slaughter. Generations. There’s about 2,000 families that have been erased now completely, are gone. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………
This has been a systematic, intentional attack on the health care system. The bizarre thing of all of this is that the Israeli politicians have not hidden it. They have said open statements about creating epidemics. There’s been tons of open statements about what they intend to do. So you can’t even make this stuff up. It’s bizarre how they have openly said this, right? But having said that, I think over 450 health care workers have been killed — doctors, nurses, paramedics, over 450 — when they’re not supposed to be a target, right? They’re protected by international law. Doctors have been kidnapped, specific doctors who are of unique specialties have been targeted and killed.
Doctors have been kidnapped, and, yes, they have been tortured. They dehumanize the doctors and health care workers when they capture them. We’ve seen pictures of them, so we know this happens, and it does indeed happen. A few of the doctors went through torture, and one doctor that came back, he’s a general surgeon, he came back, I was speaking to his wife, and he’s not the same anymore. He was tortured and he still has torture marks over his body, and he’s a general surgeon. That’s it, just a medical professional. The assistant director of the hospital was basically declothed and beat up in front of all the other hospital workers just to kind of insult and degrade him because he’s their boss. And they’re beating him up and kicking him and swearing at him, and everybody witnessed this, and they did it purposely in front of his workers. So, it’s a further dehumanization of a human being. These doctors when they come back, the few that are released, there’s still a lot that are under custody with the Israeli forces, they’re not the same anymore. For me, as a surgeon, it’s really heartbreaking for me to see that. As a surgeon, we have people’s lives in our hands and we heal. And then to see them mentally reduced to nothing is hard to take. Yeah. It’s hard to stomach……………………………………………………………………………………………
What I saw — I’m an eye surgeon, an eye plastic surgeon, and so I saw the classic, what I penned “the Gaza shrapnel face,” because in an explosive scenario, you don’t know what’s coming. When there’s an explosion, you don’t go like this [cover your face], you kind of actually, in fact, open your eyes. And so shrapnel’s everywhere. It’s a well-known fact that the Israeli forces are experimenting [with] weapons in Gaza to boost their weapon manufacturing industry. Because if a weapon is battle-tested, it’s more valuable, isn’t it? It’s got a higher value. So basically they’re using these weapons, these missiles that purposely, intently create these large shrapnel fragments that go everywhere. And they cause amputations that are unusual…………………………………………………………………………………….
And so I saw these facial injuries, I saw limbs of children just kind of hanging off, barely connected. I saw abdominal wounds where you had, of course, the intestines exposed. And the thing is that the emergency does not have room, so they’re all over the floor. So you have these massive trauma, and [the patients] are on the floor. And sometimes they get forgotten in the mass chaos………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. more https://theintercept.com/2024/03/23/intercepted-doctor-gaza-interview/?utm_medium=email&utm_source=The%20Intercept%20Newsletter
Canadian officials found radiation levels in these northern Ontario homes ‘well above’ the safe limit. Their response: ‘¯\_(ツ)_/¯’ .

Many residents might not be aware they are living atop radioactive infill, which came from nearby, closed-down uranium mines that helped develop atomic bombs during the Cold War.Toronto Star
The number of homes in Elliot Lake affected by buried radioactive waste could top 100 — twice as many as previously thought.
By Declan Keogh and Masih Khalatbari, Investigative Journalism Bureau, Thursday, March 21, 2024 https://www.thestar.com/news/investigations/canadian-officials-found-radiation-levels-in-these-northern-ontario-homes-well-above-the-safe-limit/article_6b68ad20-e605-11ee-9a2a-f72182db65b6.html
In January 2021, a senior official with Canada’s nuclear regulator asked a colleague to do a rough, “back-of-the-envelope” calculation on the amount of potentially deadly radiation that residents in Elliot Lake were exposed to in their homes.
The government had just received a complaint that long-forgotten radioactive mine waste was buried underneath some homes in the northern Ontario city. Ron Stenson, senior project officer at the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC), wanted to “confirm our assumption that 468 Bq/m3 is not an urgent health concern.”
He did not get the answer he wanted. A senior official with the commission’s radiation protection division replied that those levels of radon are “well above” the public radiation dose limit set by federal authorities.
Stenson’s response came 90 minutes later: “¯\_(ツ)_/¯.”
For too long, shrugging is all the Canadian government has done, as far as local homeowner Lisa Speck is concerned.
The government official’s email is “a true visual representation of the response we’ve received to date,” she says. “It accurately summarizes the respect we’ve been shown.”
Documents show 100+ homes affected
Documents obtained by the Investigative Journalism Bureau show the number of homes affected by buried radioactive waste could top 100 — twice as many as previously thought. Many of the residents might not be aware they are living atop radioactive infill, which came from nearby, closed-down uranium mines that helped develop atomic bombs during the Cold War.
And when faced with calls for action, civil servants make jokes.
Speck, part of a group of Elliot Lake homeowners fighting to get the radioactive mining waste removed from their properties, called the email exchange “disgusting” and “dismissive.”
Despite having spent billions of dollars to clean up similar radioactive waste in Port Hope, federal regulators deny they have any obligation to do the same in Elliot Lake, saying the waste buried beneath the properties is the homeowners’ responsibility.
CNSC declined an interview request. In a statement, the agency said it could not answer detailed questions from the IJB because of ongoing litigation, adding that it’s “dedicated to upholding the highest standards of safety in our work.” Stenson did no respond to a request for comment.
Lawyers representing impacted Elliot Lake homeowners filed an application to Federal Court for a judicial review last July in the hopes of forcing the reversal of the federal government’s position.
The government filed their response in federal court on March 4, reiterating the waste is outside their jurisdiction and stating that the Nuclear Safety and Control Act, which governs the CNSC, does not compel them to act upon demands from the homeowners.
It argues federal legislation does not give the public the right “to file complaints, request inspections, or demand orders be issued as against regulated entities.”
A screen grab from a January 2021 email sent by a senior project officer at the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC), after being told the levels of radon recorded at homes in Elliot Lake are “well above” the safe limits. Toronto Star illustration
Lawyers representing impacted Elliot Lake homeowners filed an application to Federal Court for a judicial review last July in the hopes of forcing the reversal of the federal government’s position.
The government filed their response in federal court on March 4, reiterating the waste is outside their jurisdiction and stating that the Nuclear Safety and Control Act, which governs the CNSC, does not compel them to act upon demands from the homeowners.
It argues federal legislation does not give the public the right “to file complaints, request inspections, or demand orders be issued as against regulated entities.”
Lawyers representing impacted Elliot Lake homeowners filed an application to Federal Court for a judicial review last July in the hopes of forcing the reversal of the federal government’s position.
The government filed their response in federal court on March 4, reiterating the waste is outside their jurisdiction and stating that the Nuclear Safety and Control Act, which governs the CNSC, does not compel them to act upon demands from the homeowners.
It argues federal legislation does not give the public the right “to file complaints, request inspections, or demand orders be issued as against regulated entities.”
At the crux of the federal government’s refusal to accept responsibility is a technicality: It says that it isn’t responsible for the regulation of naturally-occurring radioactive materials, only those that have been processed in some way. It says that the uranium rock dug up during mining “was never chemically processed” before being trucked to nearby Elliot Lake for use as backfill during the construction of homes. That, the government says, means it’s technically “not considered radioactive waste.”
‘Public perception of a coverup’
The government didn’t always view the radiation blight in Elliot Lake as someone else’s problem, internal documents suggest.
By the 1980s, the government had assumed some role alongside the mining companies that built most of the houses.
The Atomic Energy Control Board (AECB) — the predecessor of the CNSC — took responsibility for “about 1,900 private properties and public areas,” according to a 1998 internal report summarizing the ongoing radiation problems in Elliot Lake.
Despite discovering “contaminated materials in structures” as well as “excessive gamma radiation due to the presence of mine waste on private properties,” there had been “minimal effort” to remove the waste, the summary report noted.
Fans and venting had been previously installed in homes to funnel the dangerous gas outside. However, it was likely these remediation efforts had failed, the report stated, possibly because residents didn’t know how to maintain the systems — or that they even existed.
“There is no evidence to suggest that owners were made aware of corrections made, or that they must assume responsibility for maintenance,” the report states.
All of this, the report concluded, created a “public perception of a coverup.”
“The only way to remove the mine waste issue from public perception is to remove the contamination.”
Supplied
As of 1998, it was estimated up to 120 properties were potentially affected by radioactive contamination and, as a result, “increased radiation exposure is likely as is renewed public concern.”
The report also called for a citywide effort to test properties, monitor and remediate excess levels of radiation and clean up the “man-introduced contamination” once and for all. It’s unclear whether those calls were heeded.
At the time, it was assumed that cleanup efforts would be shared between the federal government and the mining companies, with the companies offering financial assistance to remediate the properties they once owned.
Billions spent on remediation in other Ontario communities
In 2001, the federal government signed a deal with the municipalities of Port Hope and Clarington to collect, transport and permanently store as much as 2 million cubic metres of low-level radioactive waste that had been distributed by a government-owned radium and uranium refinery between the 1930s and the 1980s.
The $2.6 billion remediation project, which involves digging up and removing soil around affected houses, the construction of permanent storage facilities and monitoring of radiation levels, is slated to be completed by the end of this year.
Despite the parallels to Elliot Lake, the federal government has said it is not responsible for the cleanup in the northern community because the radioactive contamination came from a private company, not a crown corporation.
In June 2023, lawyers for the residents sent a host of politicians including Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and executives of CNSC more than 3,000 pages of evidence and documentation. They called on the government and mining companies to remove the uranium waste in Elliot Lake.
Upon receiving the demands, Patrick Burton, director of CNSC’s uranium mines and mills division, asked two of his colleagues in radiation protection about the claims that residents were getting excess doses of radiation. He also told them to “buy a shovel and get a [travel authorization] for Elliot Lake,” adding a winking face emoji.
“Is that going to get a response?” replied one of his colleagues with a smiling face emoji.
When reached by the IJB, Burton directed questions about the email to CSNC. The agency did not offer further comment. When questioned by lawyers representing the Elliot Lake homeowners, Burton said it was supposed to be a joke among colleagues.
“The intention was never … for the homeowners to become aware of this exchange,” Burton said during his deposition.
Homeowner Speck says the joke was “rude” but says she would welcome the government’s shovels to clean up the uranium on her property.
“The statement sort of lends to the fact that he thinks it’s a small job. If it’s such a small job that he’s just going to go to buy a shovel and fix it … then just do that,” Speck says.
“Everyone in the community would expect better from a government official than to be joking about a matter that could potentially affect … or maybe has affected, a population of people.”
With files from the Toronto Star’s Marco Chown Oved. The Investigative Journalism Bureau is a non-profit newsroom based at the University of Toronto’s Dalla Lana School of Public Health.
Disadvantaged Canadian towns look at the $billions promised by nuclear waste hosting

Offended tribal elders formed the Committee for Future Generations and initiated what they called the 7,000 Generations Walk Against Nuclear Waste, which saw participants trudge nearly 1,000 kilometres from Pinehouse to the legislature in Regina.
No local DGR debate has been harder fought than the 30-month marathon of psychological and ground warfare that unfolded in Saugeen Shores, one of several contestant municipalities in Bruce County, between 2011 and 2014.
Inside the race for Canada’s nuclear waste: 11 towns vie to host deep burial site Canada’s nuclear waste will be deadly for 400,000 years. What town would like the honour of hosting it?CHARLES WILKINS TheGlobe and Mail Feb. 26 2015,
“……..There are 11 rural and wilderness municipalities vying for the DGR, survivors of an original roster of 22. The aspirants include veteran northern encampments such as Hornepayne, Ontario, where, as Brennain Lloyd of the environmental education group Northwatch describes it, there is “a really fierce desire” on the part of at least a few municipal administrators to “bring the nuke dump to town.”
And Schreiber, a struggling railway town on the north shore of Lake Superior. And Ignace, another struggler, in the boreal wilds to the west. And, to the east, Manitouwadge.
And Creighton, Saskatchewan, directly across the Manitoba border from Flin Flon (Creighton is a town described by a former resident as “having had its fiscal balls to the wall for half a century”).
And Blind River, Ontario, on the north shore of Lake Huron, where survival has for years depended on the uncertain flow of traffic along the Trans-Canada Highway.
And Elliot Lake, some 50 kilometres north of Lake Huron, where uranium mining was the sustaining industry during the 1950s and ’60s but which these days survives on the pensions of retirees who moved to the town to take advantage of discount housing left over from the boom years.
“What makes it all so attractive to competing municipalities is, of course, the money,” says Tony McQuail.
While billions of dollars will flow directly through the chosen town over a period of four or five decades, Lloyd suggests that most of the money is likely to end up in the pockets of big-city consultants and other outside beneficiaries.
Mainly, the price tag will buy decades’ worth of infrastructure and construction costs, as well as maintenance, monitoring and employment training. It will also pay for the transportation of the waste to the spanking new DGR, which will, by the time it opens, have been a reality for its “willing host” for a quarter of a century or more.
Finishing just the first phase of the preliminary assessment brings $400,000 of NWMO money to candidate towns, so they can “build sustainability and well-being.” It has been speculated that some towns had no intention of staying in the process beyond the early payout.
While some towns applied to participate of their own volition, others were, according to Lloyd of Northwatch, courted by the NWMO. “What bothers me most about the process,” says Lloyd, “is the ‘siloing’ that the NWMO practises on the municipal politicians they choose to target.
“They approach them not in the context of their communities, where the politicians are immediately answerable to their constituencies, but at municipal conferences and conventions where they’re away from home, isolated, perhaps a little unsure of themselves. They wine and dine them and soft-talk them about the unimaginable benefits that could accrue to their towns should they consider hosting the DGR.
“Then they fly them to Toronto and put them up in the best hotels and take them up to the Bruce Power site, or other nuclear generating stations, and show them what of course appears to be secure and flawless waste storage. The politicians are just snowed—they’re made to feel like important players. They take this dream of hope and prosperity and safe science back to their communities and in effect go to work for the NWMO.”
Other northern councils—at Ear Falls, at Nipigon, at Wawa—have been more divided over the DGR and so were eliminated early, or withdrew, from the process. Similarly, Brockton, near the site of Bruce Power, was cut late in 2014 after its residents elected a largely anti-DGR council. (The NWMO says Brockton’s assessment simply didn’t pan out.)
The aboriginal communities of Pinehouse and English River, Saskatchewan, were dropped from the process when community debate over land and water issues, as well as a growing distrust of the NWMO, became irresolvable.
While Pinehouse was still in the running, three community leaders, including a cousin of the mayor, received money from the NWMO. Offended tribal elders formed the Committee for Future Generations and initiated what they called the 7,000 Generations Walk Against Nuclear Waste, which saw participants trudge nearly 1,000 kilometres from Pinehouse to the legislature in Regina.
No local DGR debate has been harder fought than the 30-month marathon of psychological and ground warfare that unfolded in Saugeen Shores, one of several contestant municipalities in Bruce County, between 2011 and 2014………..http://www.theglobeandmail.com/report-on-business/rob-magazine/inside-the-race-for-canadas-nuclear-waste/article23178848/
‘We are the masters of the house’: Israeli channels air snuff videos featuring systematic torture of Palestinians

It’s hard to imagine the depths to which Israeli society has sunk. The official tells the Channel 13 reporter that “the feeling is one of pride.”
Israeli TV channels aired a number of reports showing the torture and humiliation of Palestinians in Israeli prisons. The videos are consumed by the Israeli public as entertainment, revealing the sadism of Israeli society.
BY JONATHAN OFIR , https://mondoweiss.net/2024/03/we-are-the-masters-of-the-house-israeli-channels-air-snuff-videos-featuring-systematic-torture-of-palestinians/
Over the past month, mainstream Israeli television channels have aired what can only be described as snuff films. They depict the systematic torture of Palestinians from Gaza in Israeli jails. Such videos have aired on at least three occasions — twice on Channel 14, and once on the public broadcaster, Channel 13. While Channel 14 is considered right-wing, so is about two-thirds of the Israeli public, and the more “mainstream” Channel 13 has shown no qualms about airing similar footage.
The broadcasts follow prison officials into detention centers to document the mistreatment of prisoners, which seems to be something that the officials — and apparently the viewers — find satisfying rather than revolting. The airing of these snuff films is a demonstration of societal sadism.
As Yumna Patel has recently reported, several rights groups have sounded the alarm over the widespread and systemic abuse that Palestinian prisoners face at the hands of the Israeli authorities. These groups’ calls have been unintentionally buttressed by Israeli soldiers’ unapologetic videos of themselves torturing or demeaning Palestinian detainees, which they boastfully post on social media. Now, it seems that the phenomenon has expanded to mainstream Israeli television.
The two aforementioned reports on Channel 14 (threads with subtitles can be found here and here) contained footage of actual interrogation sessions during which torture was used. The Channel 13 report did not, but it exposed some of the worst prison conditions to be broadcast to the public. These conditions include forcing prisoners to live in inhumane conditions and subjecting them to torture and harassment. Here’s the 11-minute video with translated subtitles.
‘The feeling is one of pride’
“Here, we see the cells in which the Nukhba terrorists are held,” the narrator says.
The “Nukhba” refers to elite Hamas-led fighters who carried out the October 7 attack. In the cell, viewers notice metal bunkbeds without mattresses, and instead of a toilet, there is just a hole in the floor. The room is almost completely dark throughout the day, and prisoners have their hands and legs chained together.
We hear attack dogs barking constantly as prisoners are made to kneel while bound and blindfolded, their heads touching the floor.
“This is how it should be,” a guard says. “This is how a Nukhba prisoner should be…what happened on October 7 will never return.”
In another scene, a guard shouts at prisoners as dogs continue to bark incessantly. “Heads down! Heads on the floor!” he yells.
“There are many prisoners here that I personally saw at the [October 7] events,” a prison official says, taking pride in humiliating them. “The difference is that this time, he is afraid, shaking, with his head on the floor…no Allahu Akbar, nothing. You won’t hear a squeak from him.”
“They have no mattresses,” says a warden shift commander. “They have nothing…we control them 100% — their food, their shackling, their sleep…[we] show them we are the masters of the house.” Even without knowing the background to that phrase, to hear him say it is chilling.
“Masters of the house” was the election slogan of Itamar Ben-Gvir, the Jewish Power leader and current Minister of National Security. Ben-Gvir declared war on Palestinian prisoners long before October 7, and this has included shutting down bakeries that supply bread to prisoners — described by Ben-Gvir as an “indulgence” — and drastically limiting prisoners’ water use. So now it’s become much worse.
While one is tempted to believe that all prisoners here are “Nukhba” members, it turns out that many of them aren’t even suspected of that. Rather, they were rounded up in Gaza after October 7, during mass arrests in which hundreds of Gazan men were stripped and paraded in a most sadistic demonstration of power. The mass arrests also included hundreds of women, including pregnant women detained with their babies. Israeli security officials told Haaretz that by their own estimate, “only 10 to 15 percent of the hundreds of the semi-naked and bound Gazan men arrested in the Strip during the recent days are Hamas members or those who identified with the organization.”
Back to the Channel 13 coverage, viewers can hear the nonstop blasting of the Zionist anthem, Am Israel Hai (“the people of Israel live”).
“The prison authorities claim that it is meant to boost the morale of the staff,” the narrator declares. “But it is clear that this is another part of the psychological warfare against the prisoners.”
Torture, in other words.
It’s hard to imagine the depths to which Israeli society has sunk. The official tells the Channel 13 reporter that “the feeling is one of pride.”
The reason such sadism has become formalized as a matter of policy is because this is what the Israeli public demands. The Israeli Democracy Institute released a survey last week showing that two-thirds of Jewish Israelis oppose “the transfer of humanitarian aid to Gaza residents at this time,” even if “via international bodies that are not linked to Hamas or to UNRWA.” For right-wing voters, the opposition to aid jumps from 68% to 80%.
This is not Israel’s Abu Ghraib moment, because when Abu Ghraib was revealed, most Americans were revolted. Israeli society, on the other hand, is thirsting for genocide. No wonder they consume such videos as entertainment on mainstream TV.
Thanks to Tali Shapiro, B.M.@ireallyhatyou, Hilel Biton-Rosen, and Dave Reed.
The last stammering of Jewish fascism

In Israel, the Jewish democratic opposition organized anti-Zionist demonstrations, which were not very well attended. Speakers emphasized the betrayal of the Prime Minister, who used the shock of October 7 not to save the hostages, but to realize his colonial dream.
Washington then decided to radically change its policy. Until then, it had considered that it could not afford to let Israel lose. It had therefore supported its crime. Now, it could no longer afford to let the Jewish fascists win. It’s important to understand that Washington didn’t change its mind when it saw the suffering of the Gazans, nor because of a sudden outburst of anti-fascism, but because of the threats of the “revisionist Zionists”. Its positions are dictated exclusively by its desire to maintain its domination of the world. It could not contemplate another defeat for its Israeli allies, this time after those in Syria and Ukraine. But it could even less envisage losing to the “revisionist Zionists”.
Victoria Nuland’s dismissal demonstrates the Biden Administration’s desire to clean up its own house, while doing the same for Israel.
https://www.voltairenet.org/article220564.html VOLTAIRE NETWORK | PARIS (FRANCE) | 12 MARCH 2024, by Thierry Meyssan
Anyone acting in good faith understands that murdering 30,000 innocent people has nothing to do with eliminating Hamas. Operation Iron Glaive appears for what it is: a cover to realize the old dream pursued by Jewish fascists from Jabotinsky to Netanyahu: to expel the Arab population from Palestine. From then on, this mass crime, committed for the first time live on television, turned the world’s political chessboard upside down. Feeling threatened, the Jewish supremacists themselves threatened the United States. Anxious to remain masters of the “free world”, the United States is preparing to topple the Jewish supremacists.
The Biden administration watched with bated breath as Israel reacted to the attack by the Palestinian Resistance, including Hamas, known as the “Flood of Al-Aqsa” (October 7). Operation Iron Glaive began with a massive pounding of Gaza City on a scale unprecedented anywhere in the world, including the World Wars. From October 27 onwards, this was followed by ground intervention, looting and the torture of thousands of Gazan civilians. In five months, 37,534 civilians were killed or disappeared, including 13,430 children and 8,900 women, 364 medical personnel and 132 journalists. [1].
At first, Washington reacted by unwaveringly supporting “Israel’s right to defend itself”, threatening to veto any ceasefire request and supplying as many bombs as necessary for the widespread destruction of the Palestinian enclave. It was unthinkable, in its eyes, to suffer yet another defeat, after those in Syria and Ukraine. However, Americans were watching the horrors live on their cell phones. Many high-ranking State Department officials wrote and spoke of their shame at supporting this butchery. Petitions were circulated. Prominent figures, both Jewish and Muslim, resigned.
In the midst of a presidential election campaign, Joe Biden’s team could no longer stain its hands with blood. It therefore began to put pressure on the Israeli war cabinet to negotiate the release of the hostages and conclude a ceasefire. However, Benjamin Netanyahu’s coalition refused, playing on the trauma of its citizens to ensure that peace would only return once Hamas had been eradicated. Washington eventually realized that the events of October 7 were merely a pretext for Jabotinsky’s followers to do what they had always wanted to do: expel the Arabs from Palestine. He became more insistent, stressing that the Palestinians had a right to live, that the colonization of their land was illegal under international law, and that the Israeli-Palestinian question would be resolved by a “two-state solution” (and not by the binational state envisaged by Resolution 181 of 1947).
Revisionist Zionists” (i.e., followers of Jabotinsky [2]) responded by organizing the “Conference for the Victory of Israel” [3] on January 28, 2024. Headlining the event was Rabbi Uzi Sharbaf, sentenced in Israel to life imprisonment for his racist crimes against Arabs, but pardoned by his friends. Sharbaf did not hesitate to proclaim himself heir to the Lehi and Stern groups who fought against the Allies alongside duce Benito Mussolini.
The message was perfectly received in Washington and London: this tiny group intended to impose its will on the Anglo-Saxons and would not hesitate to attack them if they tried to prevent ethnic cleansing.
The White House immediately issued a ban on fundraising and transfers to them [4]. This ban was extended to all Western banks under the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA).
In addition, on February 8, President Joe Biden signed a Memorandum on the conditions of US arms transfers [5]. Israel has until March 25 to guarantee in writing that it will not violate either International Humanitarian Law (but not International Law itself) or Human Rights (in the sense of the US Constitution).
For their part, the parliaments of the Netherlands and the United Kingdom have begun debating the possibility of ceasing arms trading with Israel.
In Israel, the Jewish democratic opposition organized anti-Zionist demonstrations, which were not very well attended. Speakers emphasized the betrayal of the Prime Minister, who used the shock of October 7 not to save the hostages, but to realize his colonial dream.
The “revisionist Zionists” then launched a media offensive against the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA). Since 1949, this UN agency has been providing education, food, healthcare and social services to 5.8 million stateless Palestinians in Palestine itself, as well as in Jordan, Lebanon and Syria. It has an annual budget of over $1 billion and employs over 30,000 people. Already in 2018, President Donald Trump had questioned the agency’s assistance to Palestinians and suspended US funding for it. His intention was to force the Palestinian factions back to the negotiating table. Five years on, the aim of the “revisionist Zionists” is very different. By attacking UNRWA, they intend to force Jordan, Lebanon and Syria to expel Palestinian refugees too. To this end, they accused 0.04% of its staff of having taken part in Operation Flood of Al-Aqsa, and blocked their bank accounts in Israel. UNRWA Director Philippe Lazzarini of Switzerland immediately suspended the 12 accused employees and ordered an internal investigation.
Of course, he never received the proof the Israelis claimed to have, but one donor after another, led by the United States and the European Union, suspended funding. Within days in Gaza, and weeks in Jordan, Lebanon and Syria, the United Nations aid system collapsed.
Continue readingThere is no such thing as a “nuclear waste-eating” reactor

Contrary to popular belief, the French nuclear industry is by no means “triumphant”, “the best in the world” or “at the cutting edge of technology”: in fact, EDF (bankrupt), Areva (renamed Orano after filing for bankruptcy) and CEA (subsidized by public money) are constantly making fools of themselves and leaving the French with astronomical bills.
A magic reactor killed by environmentalists?
By Stéphane Lhomme by beyondnuclearinternational, https://beyondnuclearinternational.org/2024/03/17/a-magic-reactor-killed-by-environmentalists/
On the contrary, a “nuclear waste-eating reactor” does not exist
Appearing as a guest on several TV channels (BFM, Cnews, etc.), a certain Fabien Bouglé managed to fool both viewers and journalists (most of whom are totally ignorant about nuclear power) with a series of fibs, each more enormous than the last. Here are a few clarifications.
There is no such thing as a “nuclear waste-eating” reactor
The smooth-talking Bouglé left his ignorant interlocutors stunned and bewildered as he talked about “waste-eating” reactors that would have already solved the radioactive waste issue if an infamous green lobby, “betraying France to Germany” (sic!), hadn’t “prevented” the advent of such reactors.
So, like throwing a log on the fire, all you have to do is put the radioactive waste produced by today’s power plants into a “magic” reactor, and the waste will disappear.
Mr. Bouglé finally divulged his “secret”: the so-called “waste-eating” reactors are simply… breeder reactors: a type of reactor that the global nuclear industry has failed to operate for 70 years, like Superphénix in France! And, even if it did work, it would in no way eliminate radioactive waste. What’s more, less than 1% of nuclear fuel (the most radioactive waste) could theoretically have its lifespan reduced, but without disappearing and while becoming even more radioactive! In the nuclear industry, as elsewhere, miracles do not exist.
The Astrid project was not “on the way to success” and was not “taken over by Bill Gates”
Despite its pretty name, the Astrid reactor project was nothing more than a little Superphénix: a sodium-cooled breeder reactor. Look at the “progress”: 40 years after the launch of Superphénix (1240 MW), the CEA wanted to make another attempt with a reactor half as powerful (600 MW), before giving up altogether.
Japan’s Monju fast-breeder reactor was definitively shut down after countless failures, a terrible fire and sodium leaks; Germany’s Kalkar fast-breeder reactor was never commissioned; and the USA has abandoned the sector. Only Russia manages to keep its BN800 hobbling along… but it doesn’t perform any of the miracles expected of it (producing “more fissile material than it consumes”, “eating” radioactive waste and other nonsense).
As for Bill Gates, he’s one of the dummies who, in recent years, have announced various types of miraculous reactors, always claiming to be able to produce electricity “cheaply, safely and with little waste” (blah blah blah). Beginning in 2006, Bill Gates and his company Terrapower first tried to make a “travelling wave” reactor work, then a “molten salt” one, both abandoned after wasting billions. Now Gates is dreaming of developing… a sodium-cooled fast-neutron reactor: back to Superphénix and 70 years of failure for the global nuclear industry.

France’s nuclear woes are caused by… France’s nuclear woes!
The “evil anti-nuclear environmentalists” and the so-called “traitors in the pay of Germany” denounced by Inspector Bouglé have nothing to do with the disasters of French nuclear power: EDF, Areva (now Orano) and the CEA are doing just fine on their own! For example:
- Industrial and financial disasters at the EPR sites in Finland, Flamanville and England: 15 to 20 years (instead of four and a half) to build a reactor costing 20 billion Euros instead of 3 billion, and with serious defects.
- The unprecedented scandal of the thousands of defective parts (including the famous Flamanville EPR vessel) produced by Areva in its Le Creusot plants.
- Catastrophic and ruinous flops at the Iter (fusion) and RJH reactor sites.
- Stress corrosion (up to 32 reactors out of 56 shut down at the same time in 2022)
And so on.
Contrary to popular belief, the French nuclear industry is by no means “triumphant”, “the best in the world” or “at the cutting edge of technology”: in fact, EDF (bankrupt), Areva (renamed Orano after filing for bankruptcy) and CEA (subsidized by public money) are constantly making fools of themselves and leaving the French with astronomical bills.
The Fessenheim closure is not the cause of electricity shortages in France and imports from Germany
Mr. Bouglé claims that France was an exporter to Germany before the closure of Fessenheim and that it has suddenly become an importer because of the plant’s closure in 2020. He’s talking nonsense.
In reality, there are exchanges (in both directions) between the two countries throughout the year. When the balance sheet is drawn up on December 31, France is still an importer from Germany (*), and has been for over 25 years (**), long before Fessenheim was shut down.
This phenomenon is mainly due to the absurd choice of electric heating, developed on a massive scale in France to “justify” nuclear power: as soon as it gets cold, electricity consumption is such that it far exceeds the capacity of the French nuclear fleet, even when it’s working properly!
It’s also worth noting the ridiculous claim that life was wonderful in France with 58 reactors, and that it has suddenly gone into crisis with “only” 56 reactors, which in reality is an insane number. For the record, during the stress corrosion crisis, France was saved by importing massive amounts of electricity from neighboring countries, which have only a few reactors, if any at all.
(*) Of course, we can criticize the fact that a significant proportion of Germany’s electricity is generated by coal-fired power plants (even if the share of renewables is increasing exponentially), but the fact is that it’s this “dirty” electricity that heats France every winter, and French nuclear enthusiasts don’t go so far as to refuse this electricity and stay in the cold and dark!
(**) Except, very narrowly, in 2011: following the Fukushima disaster, Germany immediately shut down 8 reactors. But by 2012, France was once again a net importer from Germany.
The joke about waste-eating reactors
Let’s start by noting that nuclear reactors continually produce insane quantities of radioactive waste of various kinds, from nuclear fuel to the tools and clothing used in power plants, which are contaminated… and can’t be “eaten”!
But let’s concentrate on the most radioactive, the spent fuel that comes out of the reactor core after use.
Spent fuel comprises four types of element: plutonium, uranium, fission products and minor actinides. Note that the vast majority of radioactivity is contained in these last two categories.
To attempt reuse this waste fuel, separation work must already be carried out in a gigantic plant such as La Hague. These operations require huge amounts of electricity and using large quantities of terribly corrosive and dangerous chemicals: a far cry from the “clean” energy that could “save the planet”.
– Plutonium
Listening to Mr. Bouglé, the uninformed viewer (and the ignorant journalist) think that all they have to do is recover this fuel and put it in the so-called “waste-eating reactor”, which will make this waste disappear… while producing electricity! Jackpot, bravo and thanks for everything. But Santa Claus doesn’t exist, and it’s all poppycock. And here’s why.
It is used by the military for their atomic weapons. Some of this plutonium can be recovered to make fuel (known as “mox”) for use in today’s power plants, which exacerbates the consequences of an accident when it occurs. Various studies show that this option reduces only slightly the amount of uranium needed from mining. But in no case is this plutonium “eaten” or “incinerated”; it is almost entirely recovered after use.
– Uranium
The uranium resulting from these separation operations, known as “reprocessed uranium”, can theoretically be reused in place of mined uranium, but in reality, this option poses a number of technical problems. EDF has been trying to use it for years in its Cruas power plant (Ardèche), after re-enrichment… in Russia (thanks Putin!). But this remains very marginal, and in no case is this uranium “eaten” or “incinerated”; it is almost entirely recovered after use.
– Fission products
There’s nothing we can do with them, except vitrify them and store them for millennia!
– Minor actinides
These are the only elements of radioactive waste that could theoretically have their lifespan reduced in breeder reactors… while becoming even more radioactive! But even if such a “feat” were to happen (provided we finally manage to operate breeder reactors properly), minor actinides would not be “eaten”, “incinerated” or “disintegrated”. In fact, they are vitrified like fission products and have to be stored for millennia.
Conclusion
Of course, there is no technology that can “eat” nuclear waste. At most, it is theoretically possible (but not in practice) to degrade a tiny fraction of it, and even then, at the cost of new radioactive and chemical contamination and very high energy consumption.
Once and for all, let’s remember that there will never be a nuclear miracle, be it with magic reactors, or by replacing uranium with thorium (the thorium sector is also that of fast-breeder reactors!), or with fusion, or by calling old projects that have never worked “4th generation” or “SMR”.
Stéphane Lhomme is Director of the Nuclear Observatory.
Why the US is trying to imprison Assange: Report from inside the Court

But even if what the United States is saying were true, these documents were not published first by Assange. John Young, the owner of a website called cryptome.org testified to the court that he was the one who published the documents first, and the United States never prosecuted him or asked him to take them down.
Extraditions for political offenses are forbidden under Article 4 of the US-UK Extradition Treaty 2003
The Extradition Act, which is the implementation of the US-UK treaty inside British law, is missing this section. This is likely due to the fact it was passed at the height of the “War on Terror” in 2003, giving the Americans carte blanche to snatch people, drag them to the US and throw them in dungeons
Richard Medhurst Al Mayadeen English, 7 Mar 2024, https://english.almayadeen.net/articles/analysis/why-the-us-is-trying-to-imprison-assange–report-from-inside
Richard Medhurst is a British journalist who has covered Julian Assange’s extradition case from inside the court since 2020. In this article, he explains what took place in the latest hearings, why the United States is trying to extradite the WikiLeaks founder, and why everyone should care.
Julian Assange is an Australian journalist in the United Kingdom, and the founder of WikiLeaks. He published documents that were given to him by a US soldier called Chelsea Manning, which showed US war crimes in Iraq, Afghanistan, and much more.
The United States want to extradite Assange from the UK to America, and put him on trial for publishing these classified documents. They are threatening him with 175 years in prison.
The reason this case is so serious is because it essentially makes journalism illegal.
The United States claims Assange asked Manning for classified documents and that this is a crime. It’s not.
The US alleges that Assange having classified documents in his possession and publishing them is a crime. It’s not.
Asking for classified documents; protecting sources, these are things journalists do every single day around the world.
But because these files were so embarrassing to the United States and exposed the brutality of their war crimes, they are threatening Assange with almost two centuries in prison; and to do it, they are accusing him of being a “spy” and a “hacker”, charging him with 17 counts under the “Espionage Act”, and with one count of “Conspiracy to Commit Computer Intrusion”.
The goal of this indictment is to make an example out of Assange, and make other journalists afraid to publish things that the public has a right to know.
If extradited, Assange would be placed in the worst prison conditions imaginable, “Special Administrative Measures” (or SAMs): A strict regime of solitary confinement, no contact with other prisoners allowed, and barely any contact with your family. SAMs are internationally recognized as torture. Julian would be sent to the worst prison in America, ADX Florence, a super-maximum security facility in Colorado.
On January 4, 2021, British judge Vanessa Baraitser blocked Assange’s extradition because US prison conditions would be so oppressive in his current state as to drive him to suicide.
Nevertheless, despite blocking the extradition on health grounds, she agreed with all the political and trumped-up charges.
I have attended all of Assange’s court hearings and saw the smears against him debunked by dozens of expert witnesses. But the judge still chose to side with the United States. She chose to essentially criminalize journalism, even drawing dangerous equivalences between the US Espionage Act and Britain’s Official Secrets Act (OSA).
After this, the United States went to the English High Court to appeal her ruling and won by providing empty promises that they would supposedly treat Assange well– even though the United States has a history of violating extradition assurances. I exposed this when I published classified documents from David Mendoza’s extradition from Spain to the US, a case previously cited in court by Julian’s lawyers.
After the US succeeded in overturning the lower court’s ruling in Dec 2021, there was only one thing left: A signature from the Home Secretary, who allowed the extradition to go ahead.
The above is everything that took place between 2020 and 2024, which brings us to the latest hearings at the Royal Courts of Justice in February 2024.
Point 1: To appeal the ruling of the lower court from Jan 4, 2021.
Assange’s lawyers argued that the judge was correct to block Assange’s extradition on health grounds, but she was wrong to agree with all the political charges (equating him with a “hacker” and a “spy”).
They’re saying very plainly: This case is undemocratic, it criminalizes journalism, and doesn’t take into account the fact that the documents Assange published expose enormous US war crimes that the public had the right to know about.
(See for example the “Collateral Murder” video published by Julian Assange’s WikiLeaks: Footage from a US gunship crew laughing as they slaughter Iraqi civilians, among them children and reporters).
Another claim made by the United States is that Assange “harmed informants” by publishing unredacted cables. Ironically, this was proven false by the United States’ own military when they court-martialed Chelsea Manning (the soldier that gave the files to Assange). The US military couldn’t find a single example of anyone having been harmed by the disclosures.
The assertion by the United States that Julian Assange simply published all these documents without censoring or redacting names simply isn’t true: I listened to many journalists tell the court how they spent countless hours meticulously redacting names with Assange.
Assange’s lawyers are also arguing that the judge in the lower court failed to undertake a balancing act. She blindly accepted the United States’ premise that the lives of informants– who weren’t even harmed– are more important than the people killed and tortured by the United States. This is tantamount to saying: The United States should be allowed to continue committing these war crimes in secret; that it’s somehow okay for them to butcher people in Iraq and Afghanistan, and the public have no right to know.
But even if what the United States is saying were true, these documents were not published first by Assange. John Young, the owner of a website called cryptome.org testified to the court that he was the one who published the documents first, and the United States never prosecuted him or asked him to take them down.
This demonstrates that the whole case against Assange is selective, political, and has nothing to do with the law.
Assange’s lawyers are also arguing that the judge in the lower court failed to undertake a balancing act. She blindly accepted the United States’ premise that the lives of informants– who weren’t even harmed– are more important than the people killed and tortured by the United States. This is tantamount to saying: The United States should be allowed to continue committing these war crimes in secret; that it’s somehow okay for them to butcher people in Iraq and Afghanistan, and the public have no right to know.
But even if what the United States is saying were true, these documents were not published first by Assange. John Young, the owner of a website called cryptome.org testified to the court that he was the one who published the documents first, and the United States never prosecuted him or asked him to take them down.
This demonstrates that the whole case against Assange is selective, political, and has nothing to do with the law.
The Espionage Act that Assange is being charged under was created during World War I, in 1917. It has always been used as a political tool against dissidents such as Eugene Debs, or whistleblowers like Daniel Ellsberg and Edward Snowden, who exposed the true extent of the US war in Vietnam, and NSA mass surveillance.
If you’re charged under the Espionage Act, you’re also forbidden from arguing a public interest defense. This means that even if you expose colossal government crimes, you still go to prison.
Point 2: The Home Secretary was wrong to allow the extradition
This constitutes the second part of Assange’s appeal: It is illegal in Britain to extradite someone to another country, knowing they could face the death penalty.
If the Home Secretary, who has the final say on extraditions, is aware of such a risk, they are compelled to bar the extradition.
It is inconceivable that Priti Patel was unaware of who Julian Assange is, and the likelihood he would be killed in the United States. Once in US jurisdiction, the US could pile on additional charges, or simply execute him, as espionage is a capital offense.
Even without a specific death sentence, at 52 years old, even a 30-year bid is akin to a death sentence.
The hollow assurances given by the United States do not preclude the death penalty. And on top of that, the Home Secretary didn’t even bother asking for assurances that would.
So how could the Home Secretary agree to send Assange to a foreign country that so clearly wants to see him dead?
Mike Pompeo, who back then was head of the CIA, and then-president Donald Trump, launched this legal case against Julian Assange. In the past, Donald Trump had called for Assange to be given the death penalty, while Mike Pompeo proclaimed Assange “has no First Amendment rights”. After WikiLeaks published a trove of CIA documents, dubbed the Vault 7 files, Mike Pompeo declared war on WikiLeaks by publicly labeling it a “non-state hostile intelligence service”
All these political denunciations of WikiLeaks and Assange were then followed up with threats against him and his family. As we heard in court in 2020 from protected witnesses, the CIA had drawn up plans to potentially kidnap or assassinate Julian.
The United States is accusing Julian Assange of “espionage”. Normally, this is where the case should be thrown out, because espionage is considered a textbook political offense. And it is forbidden to extradite someone for a political offense under the US-UK Extradition Treaty, Art 4.
Customary extradition treaties have always forbidden extradition for political offenses such as “espionage” and “treason”. And this line of defense has been used before in court to successfully block extraditions.
- Extraditions for political offenses are forbidden under Article 4 of the US-UK Extradition Treaty 2003
Here is where the problem arises:
The Extradition Act, which is the implementation of the US-UK treaty inside British law, is missing this section. This is likely due to the fact it was passed at the height of the “War on Terror” in 2003, giving the Americans carte blanche to snatch people, drag them to the US and throw them in dungeons.
At the time of its passage, many criticized the Extradition Treaty as being extremely one-sided in favor of the United States.
No matter how you look at Assange’s case, it is unfair and illegal.
The United States wants to prosecute Julian Assange under US law, but at the same time deny him any protections under US law, such as free speech. If Assange has no First Amendment rights as a foreign national, then how can he be punished as a foreign national – who is not even in the US? This is such a flagrant double standard, and selective application of the law.
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR) is incorporated into British law through the Human Rights Act. Upon examination, it is clear that Julian’s rights are being flagrantly violated
Article 5 protects one from arbitrary detention.
Because this is a political case, it would be a violation of the Extradition Treaty to send Julian to America. Therefore, he has no reason to be in prison right now, and is therefore being arbitrarily detained in violation of his Article 5 rights.
Article 6 guarantees the right to a fair trial.
We know the United States spied on Assange’s conversations with his lawyers when he was inside the Ecuadorian embassy; stole his electronic devices; and collected medical and legal records.
In 2020, I sat in court with Fidel Narvaez, the former Consul to the Ecuadorian embassy in London. We listened to the submissions of two protected witnesses who confirmed they had spied on Assange because the security company they worked for, UC Global, had been contracted by the CIA to do so. They also discussed plans to potentially kidnap and poison Julian Assange and harvest DNA from his baby.
To spy on someone’s privileged conversations with their lawyers, and to use tainted evidence in court is scandalous beyond words, and violates the fundamentals of due process in any jurisdiction. Any judge would have thrown this case out from day one.
We also know Assange will not get a fair trial in America because the jury will be selected from a pool of people who work for the CIA, NSA, or have friends and family working in the intelligence community. These are the very same people whose crimes Julian Assange exposed.
The court in Virginia that issued the charges and would hold this trial is used specifically for this reason; because the jury is biased and the government knows it can’t lose. It is already 100% guaranteed that he will get convicted and go to prison.
Additionally, the United States could use secret evidence against Julian Assange, that he wouldn’t even be allowed to view due to it being “classified”.
Article 7 protects one from being punished retroactively. The case against Julian Assange is unprecedented: No publisher in America has ever been prosecuted, let alone convicted for publishing classified documents.
This case criminalizes journalism, and therefore violates Article 10, which guarantees freedom of expression.
Assange’s lawyers went over the ECHR repeatedly because it is incorporated into British law, meaning the court is obliged to follow it. Not only that, but this was their way of hinting to the judges: If you don’t give us permission to appeal, we will go to the European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) in Strasbourg, and that court will look upon your decision unfavorably.
(The United Kingdom is a founding and current member of the European Council, which is separate from the European Union).
Assange’s lawyer, Mark Summers, argued very clearly: The Strasbourg court will see that a) these US war crimes were real; b) they were happening on the ground at the time, and; c) by publishing these documents Assange altered the United States’ behavior: The helicopter massacres like in the “Collateral Murder” video stopped, and the Iraq war came to an end.
Assange’s team put together a very compelling defense during this week’s hearing.
Continue readingNuclear industry wants Canada to lift ban on reprocessing plutonium, despite proliferation risks


The CANDU Owners Group is far from neutral or independent…………… First, Canadian Nuclear Laboratories is a private company owned by a consortium of multi-national companies: AtkinsRéalis (formerly SNC Lavalin), Fluor, and Jacobs. ……...has overseas members, including utilities from China, Pakistan, India, South Korea, Argentina, and Romania. The first three countries are nuclear weapons states that either possess reprocessing plants for military purposes (India and Pakistan) or reportedly divert plutonium extracted from commercial spent fuel for military purposes (China), while South Korea and Argentina have for decades flirted with the idea of reprocessing.
Bulletin, By Gordon Edwards, Susan O’Donnell | March 11, 2024
Plutonium is “the stuff out of which atomic bombs are made.” Plutonium can also be used as a nuclear fuel. Reprocessing is any technology that extracts plutonium from used nuclear fuel. In Canada, the nuclear industry seems determined to close the nuclear fuel cycle by pushing for a policy to permit reprocessing—thereby seeking to lift a 45-year-old ban.
In 1977, Canada tacitly banned commercial reprocessing of used nuclear fuel, following the lead of the Carter administration, which explicitly opposed reprocessing because of the possibility it could lead to increased proliferation of nuclear weapons around the world.[1] That unwritten policy in Canada has held sway ever since.[2] New documents obtained through Canada’s Access to Information Act reveal that, behind closed doors, the nuclear industry has been crafting a policy framework that, if adopted, would overturn the ban and legitimize the extraction of plutonium from Canada’s used commercial nuclear fuel.
For over two years, documents show that the Canadian government has held a series of private meetings with industry representatives on this subject, keeping such activities secret from the public and from parliament. This raises questions about the extent to which nuclear promoters may be unduly influencing public policymaking on such sensitive nuclear issues as reprocessing in Canada.[3] But, given the stakes for the whole society and even the entire planet, the public must have a say about nuclear policy decisions…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Before the ban. Dreams of a plutonium-fueled economy were spawned in 1943-44 by British, French, and Canadian scientists working at a secret wartime laboratory in Montreal, which was part of the Anglo-American Project to build the first atomic bombs. Canada’s first heavy-water reactors were designed by the Montreal team, in part, to produce plutonium for weapons. The team also had hopes that after the war, plutonium might become a dream fuel for the future. They envisioned a “breeder reactor” that could produce more plutonium than it uses, thereby extending nuclear fuel supplies.
For 20 years after the war, Canada sold uranium and plutonium for US bombs. Two reprocessing plants were operated at Chalk River Nuclear Laboratories in Ontario. In addition, all the pilot work on plutonium separation needed to design Britain’s Windscale reprocessing plant was carried out at Chalk River.
After the ban. Although the 1977 ban scuppered AECL’s hopes for commercial reprocessing, plutonium remained the holy grail. In the decades that followed, AECL researchers studying the geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste clandestinely carried out reprocessing experiments at the Whiteshell Nuclear Research Establishment in Manitoba. Instead of burying used nuclear fuel bundles, the scientists anticipated burying solidified post-reprocessing waste. Meanwhile, AECL scientists at Chalk River fabricated three tonnes of mixed-oxide fuel (MOX) in glove boxes, using plutonium obtained from CANDU fuel reprocessed overseas. In 1996, Prime Minister Jean Chrétien volunteered to import weapons-grade plutonium from dismantled US and Soviet warheads to fuel CANDU reactors. Facing fierce public opposition in Canada, the project never came to pass.
But the dream of a plutonium economy remained. In 2011, a sprawling mural on three walls of the Saskatoon Airport depicted the nuclear fuel chain, from mining uranium to the reprocessing of used fuel to recover “potential energy” before disposing of the leftovers. Although the word plutonium appeared nowhere, reprocessing was presented as the inevitable final step in this vision of a virtuous nuclear fuel cycle. The mural was commissioned by Cameco, the giant Canadian multi-national corporation that helped make the central Canadian province of Saskatchewan into the “Saudi Arabia of uranium.” At the time, Cameco co-owned the largest operating nuclear power station in the world, the eight-reactor Bruce complex beside Lake Huron bordering the United States.
Despite such hopes, it became fashionable to publicly downplay reprocessing as expensive and therefore economically unlikely.[5] But the technology stayed on the books as a possibility, especially in case future generations would want to extract plutonium from used nuclear fuel for re-use before disposing of the remaining radioactive waste.
Back to the future? New Brunswick has one 660-megawatt-electric CANDU reactor at Point Lepreau on the Bay of Fundy in eastern Canada. The plant has been operating for over 40 years. In March 2018, two start-up companies—UK-based Moltex Energy and US-based ARC Clean Technology—offered to build “advanced” (fast) reactors on the same site.
The Moltex design is a 300-megawatt-electric molten salt reactor called “Stable Salt Wasteburner.” It is to be fueled with plutonium and other transuranic elements extracted from CANDU used fuel already stored on that site. Accordingly, the Moltex proposal requires a reprocessing plant in tandem with the reactor. The ARC design is a 100-megawatt-electric liquid sodium-cooled reactor, inspired by the second Experimental Breeder Reactor (EBR-2) operated by the Argonne National Laboratory in Idaho between 1964 and 1994. Although the ARC-100 does not require reprocessing at the outset, its optimal performance requires that the used fuel be recycled, likely through reprocessing.
From the beginning, Moltex claimed its proposed molten salt reactor would “recycle” CANDU used fuel and “burn” it in its molten salt reactor. Moltex claims that this would virtually eliminate the need for a deep geologic repository by turning a million-year disposal problem into a roughly 300-year storage problem. This claim has been flatly rebuffed.[6] Only later did the public learn that the Moltex technology requires reprocessing CANDU used fuel to extract plutonium using an innovative process called “pyroprocessing.” (In pyroprocessing, used fuel is converted to a metal and immersed in molten salt, then the plutonium and other transuranic elements are recovered by passing a current through the salt and collecting the desired products on electrodes.)
ARC Clean Technology maintains that its reactor design is proven by the 30-year operating experience of the EBR-2 reactor, despite differences in size and fuel enrichment.[7] The company, however, says nothing about the intimate connection between breeder reactors and plutonium, nor does it mention the chequered history of liquid sodium-cooled reactors globally—including the Fermi Unit 1 reactor’s partial meltdown near Detroit, the commercial failure of France’s Superphénix, the conversion of a German breeder reactor into an amusement park, or the dismal performance of Japan’s Monju reactor.
For either of the proposed New Brunswick reactors to operate as intended, Canada would need to lift its 45-year-old ban on commercial reprocessing of used nuclear fuel.
Testing the limits. The first sign that Canada’s reprocessing ban might be lifted came in 2019, when the federal government’s Impact Assessment Act exempted specified projects from environmental assessment. The exemption included any reprocessing plant with a production capacity of up to 100 metric tons (of used nuclear fuel) annually—just above the reprocessing capacity required for the Moltex project.[8]
Public calls to explicitly ban reprocessing started shortly after March 2021, when the federal government gave 50.5 million Canadian dollars in funding for Moltex’s project. This project clearly requires reprocessing: Without the plutonium produced by CANDU reactors to fuel its proposed molten salt reactor, the Moltex project can go nowhere.
In addition, Moltex hopes to eventually export the technology or the fuel, or both. Many Canadians are alarmed at the prospect of normalizing the use of recycled plutonium as a nuclear fuel in Canada and abroad.
In 2021, in response to a recommendation by the International Atomic Energy Agency, the Canadian government conducted public consultations to develop a modernized policy on commercial radioactive waste management and decommissioning. Over 100 citizens groups participated, and many called for an explicit ban on reprocessing.
Public attention to the issue of reprocessing grew after nine US nonproliferation experts sent an open letter to Prime Minister Justin Trudeau in May 2021. The letter expressed concern that by funding a spent fuel reprocessing and plutonium extraction project, Canada would “undermine the global nuclear weapons nonproliferation regime that Canada has done so much to strengthen.” …………………..
A second letter sent to Trudeau in July 2021 refuted “misleading claims” that Moltex posted on-line in rebuttal to the first letter. Moltex’s rebuttal claims were quickly taken down. And a third letter authored by one of the US nonproliferation experts was sent in November 2021. None of the government responses to these three letters addressed the core issue, which is the request for an independent review of the proliferation implications of Canada’s funding of reprocessing.
The federal government released its draft policy for radioactive waste management and decommissioning in March 2022, hinting that reprocessing might be permitted in the future. Public interest groups made their opposition to that suggestion very clear. A national steering group coordinated by Nuclear Waste Watch, a Canada-based network of public interest organizations, released an alternative policy proposal that explicitly banned reprocessing. The Council of Canadians, a national advocacy group, sent out an action alert that generated 7,400 letters calling for the explicit prohibition of reprocessing.
The Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission, tasked with the job of licensing Moltex’s proposed reactor, declared that a policy framework for reprocessing is necessary and that such a policy must come from the federal government.[9] Moltex’s Chief Executive Officer, Rory O’Sullivan, observed that Canada was chosen by Moltex because the country had no explicit policy on reprocessing: “Moltex would likely not have come to Canada if a reprocessing policy had been mandated at the time.”
In November 2021, Canada’s Ministry of Natural Resources—the lead federal department on nuclear issues—issued an internal memo entitled “Policy Development on Reprocessing” that refers to a series of planned meetings on reprocessing with industry representatives starting December 1, 2021.[10] The CANDU Owners Group—a nonprofit corporation assembling utilities operating CANDU reactors, Canadian Nuclear Laboratories, and nuclear suppliers—was singled out by the ministry to prepare a policy paper on reprocessing.[11]
The CANDU Owners Group is far from neutral or independent.
First, Canadian Nuclear Laboratories is a private company owned by a consortium of multi-national companies: AtkinsRéalis (formerly SNC Lavalin), Fluor, and Jacobs. The company is currently constructing a government-funded facility with hot cells at Chalk River to conduct research, including on reprocessing and plutonium extraction. Canadian Nuclear Laboratories operates under a “government-owned contractor operated” agreement with Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, the same publicly owned corporation that pushed for commercial reprocessing in the late 1970s.
The CANDU Owners Group also has overseas members, including utilities from China, Pakistan, India, South Korea, Argentina, and Romania. The first three countries are nuclear weapons states that either possess reprocessing plants for military purposes (India and Pakistan) or reportedly divert plutonium extracted from commercial spent fuel for military purposes (China), while South Korea and Argentina have for decades flirted with the idea of reprocessing.
By all evidence, the government of Canada is currently enlisting private entities that favor reprocessing to assist in the development of an industry-friendly policy on reprocessing. And the government does this without involving the public, parliament, or outside experts—all of whom have expressed a keen interest—and repeatedly asked to participate—in plutonium policy discussions. In the process, misleading information about reprocessing is being forwarded to government officials with no other voices to correct the record.[12]
In the most recent move, a dozen US nonproliferation experts wrote again to Prime Minister Trudeau on September 22, 2023, after the release of documents obtained through an access to information request. In their letter, the experts reiterated their concerns that the Canadian government is funding a project that would lead to increase the availability—and therefore potential proliferation—of weapons-usable plutonium for civilian purposes in Canada and beyond.
Democratic deficit. Despite all these developments, there has been no public discussion or parliamentary deliberation about the implications of introducing civilian reprocessing into Canada’s nuclear fuel cycle. Absence of transparency and public debate means the democratic process is being ignored. Yet, the issue is of great public importance because of the taxpayer money invested, proliferation risks involved, and the long-term societal implications of the security measures needed to safeguard nuclear weapons usable materials.
This makes one wonder why it took a group of concerned citizens and an access to information request to find out that, behind closed doors, the nuclear industry has been drafting its own policy to permit commercial reprocessing, expecting its adoption by the government of Canada against all objective criteria of democracy.
n 1976, British nuclear physicist Brian Flowers authored a Royal Commission report to the UK parliament. He wrote: “We regard the future implications of a plutonium economy as so serious that we should not wish to become committed to this course unless it is clear that the issues have been fully appreciated and weighed; in view of their nature we believe this can be assured only in the light of wide public understanding.”
The same precept should apply to nuclear policy in today’s Canada.
Notes…………………………………………………………………. https://thebulletin.org/2024/03/nuclear-industry-wants-canada-to-lift-ban-on-reprocessing-plutonium-despite-proliferation-risks/
Cold turkeys: The demise of nuclear power

Jim Green, Mar 12, 2024, https://reneweconomy.com.au/cold-turkeys-the-demise-of-nuclear-power-in-australias-aukus-partner-countries/
When announcing the AUKUS agreement in 2021, then Prime Minister (and secret energy minister) Scott Morrison said: “Let me be clear: Australia is not seeking to establish … a civil nuclear capability.” He also said that “a civil nuclear energy industry is not a requirement for us to go through the submarine program.”
However, Coalition Senators argued in a report last year that Australia’s “national security” would be put at risk by retaining federal legislation banning nuclear power and that the “decision to purchase nuclear submarines makes it imperative for Australia to drop its ban on nuclear energy.”
So, let’s see how nuclear power is faring in our AUKUS partners, the UK and the US.

This is a story about conventional, large reactors. All that needs to be said about ‘small modular reactors’ in the UK and the US is that none exist and none are under construction.
This is a story about conventional, large reactors. All that needs to be said about ‘small modular reactors’ in the UK and the US is that none exist and none are under construction.
The UK

The last power reactor start-up in the UK was 29 years ago — Sizewell B in 1995.
Over the past decade, several proposed new nuclear power plants have been abandoned (Moorside, Wylfa, Oldbury) and the only project to reach the construction stage is Hinkley Point C, comprising two French-designed EPR reactors.
In the late 2000s, the estimated construction cost for one EPR reactor in the UK was £2 billion (A$3.9 billion). When construction of two EPR reactors at Hinkley Point commenced in 2018 and 2019, the cost estimate for the two reactors was £19.6 billion.
The current cost estimate for the two reactors has ballooned to £46 billion (A$89 billion) or £23 billion (A$44.5 billion) per reactor. That is 11.5 times higher than the estimate in the late 2000s. Further cost overruns are certain. This is an example of the Golden Rule of Nuclear Economics: Add a Zero to Nuclear Industry Estimates.
The UK National Audit Office estimates that taxpayer subsidies for Hinkley Point — primarily in the form of a guaranteed payment of £92.50 (A$180) per megawatt-hour (2012 prices), indexed for inflation, for 35 years — could amount to £30 billion (A$58 billion) while other credible estimates put the figure as high as £48.3 billion (A$94 billion).
Delays

The delays associated with Hinkley Point have been as shocking as the cost overruns. In 2007, French utility EDF boasted that Britons would be using electricity from an EPR reactor at Hinkley Point to cook their Christmas turkeys in 2017. In 2008, the UK government said the reactors would be complete “well before 2020”.
But construction of the two reactors didn’t even begin until 2018 and 2019, respectively, at which time completion was expected in 2026. Now, completion is expected in 2030 or 2031.
Undoubtedly there will be further delays and if the reactors are completed, it will be more than a quarter of a century after the 2007 EDF boast that Britons would finally be using electricity from Hinkley Point to cook their Christmas turkeys.
Construction will take well over 10 years; planning and construction over 25 years. Yet in Australia, the Coalition argues that Australians could be cooking Christmas turkeys with nuclear power 10 years from now.
‘Something of a crisis’
Nuclear industry lobbyist Tim Yeo said in 2017 that the UK’s nuclear power program faced “something of a crisis”. The following year, Toshiba abandoned the planned Moorside nuclear power project near Sellafield despite generous offers of government support — a “crushing blow” according to Yeo.
Then in 2019, Hitachi abandoned the planned Wylfa reactor project in Wales after the estimated cost of the twin-reactor project had risen by 50 percent.
Hitachi abandoned the project despite an offer from the UK government to take a one-third equity stake in the project; to consider providing all of the required debt financing; and to consider providing a guarantee of a generous minimum payment per unit of electricity.
Long gone was the 2006 assertion from then UK industry secretary Alistair Darling that the private sector would have to “initiate, fund, construct and operate” nuclear power plants.
The UK Nuclear Free Local Authorities noted that Hitachi joined a growing list of companies and utilities backing out of the UK nuclear new-build program:
“Let’s not forget that Hitachi are not the first energy utility to come to the conclusion that new nuclear build in the UK is not a particularly viable prospect. The German utilities RWE Npower and E-on previously tried to develop the site before they sold it on Hitachi in order to protect their own vulnerable energy market share in the UK and Germany.
“British Gas owner Centrica pulled out of supporting Hinkley Point C, as did GDF Suez and Iberdrola at Moorside, before Toshiba almost collapsed after unwise new nuclear investments in the United States forced it to pull out of the Sellafield Moorside development just a couple of months ago.”
Sizewell C

The UK government hopes to progress the Sizewell C project in Suffolk, comprising two EPR reactors, and is once again offering very generous support including taking an equity stake in the project and using a ‘regulated asset base‘ model which foists financial risks onto taxpayers and could result in taxpayers paying billions for failed projects — as it has in the US.
If recent experience is any guide, the government will struggle to find corporations or utilities willing to invest in Sizewell regardless of generous government support.
(The same could be said for plans for small modular reactors or mid-sized reactors envisaged by Rolls-Royce — it is doubtful whether private finance can be secured despite generous taxpayer subsidies.)
Many reactors have been permanently shut down in the UK: the IAEA lists 36 such reactors. Since the Sizewell B reactor startup in 1995, there have been 24 permanent reactors shut-downs and zero startups.
Repeat: since the last reactor startup in the UK, there have been 24 shut-downs!
The capacity of the nine remaining reactors (5.9 gigawatts — GW) is less than half of the peak of 13 GW in the late 1990s. Nuclear power’s contribution to electricity supply has fallen from 22 percent in the early 2000s to 14.2 percent.
Meanwhile, the UK government reports that renewable power sources accounted for 44.5 percent of total UK generation in the third quarter of 2023, a higher share than fossil fuels and around three times more than nuclear’s share.
What to make of the conservative UK government’s goal of quadrupling nuclear capacity to 24 GW by 2050? It is deeply implausible. The facts speak for themselves. Two dozen reactor shutdowns and zero startups since 1995.
The Hinkley Point project has been extremely slow and extremely expensive. The Sizewell C project is uncertain. Other proposals — including proposals for small modular reactors — are even more uncertain and distant.
Unsurprisingly, the extraordinary cost overruns and delays associated with Hinkley Point have complicated plans to advance the proposed Sizewell C project.
In 2010, the UK government announced that Sizewell was one of the locations slated for new reactors. Fourteen years later, construction is some years away and it remains uncertain if the project will reach the construction stage. EDF and the UK government are seeking to raise a further £20 billion from new investors. All reasonable offers considered.
France

The Sizewell C project is equally complicated across the channel due to EDF’s massive debts and its plan to replace the EPR design with an EPR2 design, about which little is known except that safety will be sacrificed on the altar of economics. EDF’s debt as of early 2023 was €64.5 billion (A$107 billion) and it was fully nationalised later in 2023 due to its crushing debts.
In addition to its adventures across the channel, EDF has a “colossal maintenance and investment programme to fund” in France as the Financial Times noted in October 2021.
As in the UK, there has not been a single reactor startup in France since the last millennium. The only current reactor construction project is one EPR reactor under construction at Flamanville. The current cost estimate of €19.1 billion (A$31.6 billion) is nearly six times higher than the original estimate of €3.3 billion (A$5.5 billion).
Construction of the Flamanville reactor began in 2007 and it remains incomplete 17 years later. Planning plus construction have taken over a quarter of a century. Yet the Coalition argues that Australians could be cooking Christmas turkeys with nuclear power 10 years from now.
France’s nuclear industry was in its “worst situation ever“, a former EDF director said in 2016 — and the situation has worsened since then. Another former EDF director said in early 2024 that the French nuclear industry is “on a slow descent to hell” and he has “fierce doubts about EDF’s ability to build more reactors.”
The US

The V.C. Summer project in South Carolina (two AP1000 reactors) was abandoned in 2017 after the expenditure of around US$9 billion (A$13.6 billion). Construction began in 2013 and the project was abandoned in 2017.
The project was initially estimated to cost US$11.5 billion; when it was abandoned, the estimate was US$25 billion (A$38 billion).
Largely as a result of the V.C. Summer disaster, Westinghouse filed for bankruptcy in 2017 and its parent company Toshiba only avoided bankruptcy by selling its most profitable assets. Both companies decided that they would no longer take on the huge risks associated with reactor construction projects. A year earlier, Westinghouse said its goal was to win overseas orders for at least 45 AP1000 reactors by 2030.
Criminal investigations and prosecutions related to the V.C. Summer project are ongoing: the fiasco is known as the ‘nukegate’ scandal.
Vogtle

With the abandonment of the V.C. Summer project in South Carolina, the only remaining reactor construction project in the US was the Vogtle project in Georgia (two AP1000 reactors).
Construction of the Vogtle reactors began in 2013 and the expected completion dates of 2016 and 2017 were pushed back seven years to 2023 and 2024. In 2014, Westinghouse claimed a three-year construction schedule for AP1000 reactors but the Vogtle reactors took 10 and 11 years to complete.
The first licence application for the Vogtle project was submitted in 2006 so planning and construction took 17 years in addition to the time spent before the 2006 application.
The latest cost estimate for the Vogtle project is $34 billion (A$51 billion), more than twice the estimate when construction began (US$14–15.5 billion). The project only survived because of multi-billion-dollar taxpayer bailouts.
In 2006, Westinghouse said it could build an AP1000 reactor for as little as US$1.4 billion (A$2.1 billion) — 12 times lower than the latest Vogtle estimate of US$17 billion (A$25.5 billion) per reactor. Another example of the Golden Rule of Nuclear Economics: Add a Zero to Nuclear Industry Estimates.
Corruption scandals

In 2005, the US Nuclear Energy Institute claimed that Westinghouse’s estimate of US$1,365 per kilowatt “has a solid analytical basis, has been peer-reviewed, and reflects a rigorous design, engineering and constructability assessment.”
In fact, the estimate was out by an order of magnitude and the Institute’s involvement in a raft of corruption scandals has been exposed. No doubt the Dutton Coalition would happily parrot whatever lies the Institute chose to feed them, and no doubt the Murdoch/Sky/AFR echo-chamber would happily amplify those lies.
During the ill-fated ‘nuclear renaissance’, the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission received applications to build 31 reactors, but only the Vogtle and V.C. Summer projects reached the construction stage and only the twin-reactor Vogtle project was completed. Two out of 31 ain’t bad. Well it is, actually.
Thirteen reactors have been permanently shut down since 2013 with many more closures in the pipeline. The US has one of the oldest reactor fleets in the world with a mean age of 42.1 years. The mean age of the 29 reactors closed worldwide from 2018‒2022 was 43.5 years.
Around 20 unprofitable, ageing reactors have been saved by nuclear bailout funding but their future is precarious. In addition to the V.C. Summer corruption scandal, nuclear bailout programs are mired in corruption scandals (see here, here, here and here and if you’re still not convinced see here, here, and here).
Dr. Jim Green is the national nuclear campaigner with Friends of the Earth Australia and a member of the Nuclear Consulting Group.
After Ukraine, US readies ‘transnational kill chain’ for Taiwan proxy war

It effectively prepares Taiwan to be used as the spear tip and trigger of a multinational war offensive against China.
This discussion includes preparations for a nuclear first strike on China.
The question in Washington regarding war with China is not if, but when–and how.
The US plans on using proxies for war against China: Taiwan, Korea, Japan (JAKUS), Philippines, and Australia (AUKUS).
fight could involve a nuclear first strike. Palestine has shown what it will try to get away with: brazen genocide with the whole world watching.
The issue is no longer war or peace in Ukraine. Deputy Secretary of State Kurt Campbell sees Ukraine as a “unified field” of war with China. He revels in the possibility of a “magnificent symphony of death” in Asia.
The coda, of course, will be a deafening fermata of silence across the entire planet. Unless we stop this insane march to war.
K.J.Noh, 1 Mar 24, https://geopoliticaleconomy.com/2024/03/01/ukraine-us-kill-chain-taiwan-war/
Washington approved the dangerous sale of the Link 16 communications system to Taiwan. This is the final link of what the US military calls a “transnational coalition kill chain” against China, and signals a commitment to kinetic war.
In many traditions, when you paint or sculpt a Buddha, the eyes are the very last to be painted. It’s only after the eyes have been completed that the sculpture is fully alive and empowered.
The United States has approved a $75 million weapons package to Taiwan province, involving the sale of the Link 16 communications system.
The acquisition of Link 16 is analogous to “painting the eyes on the Buddha”: a last touch, it makes Taiwan’s military systems and weapons platforms live and far-seeing.
It confers deadly powers, or more prosaically, in the words of the US military, it completes Taiwan as the final, lethal link of what the US Naval Institute calls a “transnational coalition kill chain”, for war against China.
What exactly is Link 16? It is a key system in the US military communications arsenal. Specifically, it’s the jam-resistant tactical data network for coordinating NATO weapons systems for joint operations in war.
If this sale is completed, it signals serious, granular, and single-minded commitment to kinetic war. It would signal that the Biden administration is as serious and unwavering in its desire to provoke and wage large-scale war with China over Taiwan as it was with Russia over Ukraine, which also saw the implementation of this system.
More important than any single weapons platform, this system allows the Taiwan/ROC military to integrate and coordinate all its warfighting platforms with US, NATO, Japanese, Korean, Australian militaries in combined arms warfare.
The deadliest link
Link 16 would be the deadliest piece of technology yet to be transferred, because it allows sea, air, and land forces to be coordinated with others for lethal effect.
It permits, for example, strategic nuclear/stealth bombers (US B-1B Lancers, B-2 Spirits) to coordinate with electronic warfare and surveillance platforms (EA Growlers, Prowlers, EP-3s), fighters and bombers (F-16,F-22, F-35s) as well as conduct joint arms warfare with US, French, British carrier battle groups, Japanese SDF destroyers, and South Korean Hyun Moo missile destroyers, as well as THAAD and Patriot radars and missile batteries.
It also allows coordination with low-earth orbit satellites and other Space Force assets.
In other words, Link 16 supplies a brain and nervous system to the various deadly limbs and arms that the Taiwan authorities have been acquiring and preparing on the prompting of the US. It ensures interoperability and US control.
It effectively prepares Taiwan to be used as the spear tip and trigger of a multinational war offensive against China.
To give a shoe-on-the-other-foot analogy, this would be like China giving separatists in a US territory or state (e.g. Hawaii, Guam, Puerto Rico, Texas) not just arms and training – already a belligerent act of war, which the US is currently doing – but connecting insurgent militaries directly to the PLA’s surveillance, reconnaissance, and command/control systems.
This coordinates and completes, to borrow the words of the US Naval Institute (USNI), the final link in a “transnational coalition kill chain” for war.
Offsetting peace, sowing dragon’s teeth
The current US doctrine of war against China is based on distributed, dispersed, diffused, network-centric warfare to be conducted along the myriad islands of the archipelagic states encircling China in the Pacific.
These are the “island chains” upon which the US has encircled and sown dragon’s teeth: tens of thousands of troops armed with mobile attack platforms and missiles.
This is to be coordinated with subsurface warfare, automated/autonomous warfare, and longer-range stand-off weapons and attacks.
Powerful think tanks like CSBA, CNAS, CSIS, RAND and the Pentagon have been working out the doctrine, details, logistics, and appropriations for this concept intensively for over a decade while advocating intensely for it.
The sale of link 16 to Taiwan realizes and completes a key portion of this, binding the Chinese island as the keystone of this “multinational kill chain”.
This doctrine of dispersion is based on a “rock-paper-scissors” concept that networked diffusion “offsets” (Chinese) precision.
China’s capacity to defend itself and its littoral perimeter with precision missiles can be undermined with diffuse, distributed attacks from all across the island chains.
Note that this diffusion and dispersion of attack platforms across the entire Pacific gives the lie to the claim that this is some inherently deterrent strategy to defend Taiwan island. Diffusion is clearly offensive, designed to overrun and overwhelm defenses: like Ukraine, this is not to deter war, but to enable it.
This thus signals that aggressive total war against China is being prepared, in granular, lethal fashion on tactical and operational levels.
On the strategic level, currently, at the CFR, CNAS, and other influential think tanks in Washington, the talk is all about “protracted warfare” with China, about pre-positioning systems and munitions for war, about ramping up to an industrial war footing for the inescapable necessity of war with China.
This discussion includes preparations for a nuclear first strike on China.
The US senses that the clock is running rapidly down on its power. If war is inevitable, then it is anxious to start war sooner rather than later.
RAND warned in 2016 that 2025 was the outside window for the US to prevail in war with China. The “Minihan window” also hints at 2025. The “Davidson window” is 2027.
The question in Washington regarding war with China is not if, but when–and how.
Link 16 makes “how” easier, and brings “when” closer.
But the US is still engaged in Ukraine. Can it wage a two-front war?
The current administration has hardline Russophobes who want to continue to bleed Russia out in Ukraine. It wants protracted war with Russia. It firmly believes it can wage ambidextrous, multi-front war.
Many US officials also believe that war with Ukraine and war with China are connected. They see Russia and China as a single axis of “revisionist powers” (i.e., official enemies) conspiring against the US to undermine its so-called “rules-based order” (i.e., US hegemony).
Furthermore, if the US abandons Ukraine, this could weaken the Taiwan authorities’ resolve and willingness to wage war on behalf of Washington.
Earlier in the war, when Russian gains in Ukraine were uncertain, Bi-khim Louise Hsiao (Taiwan’s current vice-president elect) gloated publicly and prominently that Ukraine’s victories were a message to China, as well as proof-of-concept of an effective doctrine for waging and winning war against China. As such, the Taiwan authorities were and are a major supporter of the Ukraine proxy war.
But the converse also holds true. Based on the same premise, if the US abandons and loses Ukraine, it sends a clear message to the people on Taiwan island that they will be the next to be used and abandoned; that their US-imposed war and war doctrine (light, distributed, asymmetrical combined arms warfare) for fighting China is a recipe for catastrophic loss.
The US plans on using proxies for war against China: Taiwan, Korea, Japan (JAKUS), Philippines, and Australia (AUKUS). Thus it cannot signal too overtly its perfidious, unreliable, and instrumental mindset.
Washington has to keep up the pretense. It cannot be seen to overtly lose in or abandon Ukraine. It needs a “decent interval”, or a plausible pretext to cut and run.
Still, the US is stretched thin. For example, it is relying on Korean munitions to Ukraine, and South Korea has provided more munitions than all of the EU combined.
Moreover, the US is currently at war with itself. The fracturing of its body politic can only be unified with a common war against a common enemy. Russia is not that enemy for the US. China is. The Republicans want war with China now.
Eli Ratner and Elbridge Colby have been fretting for years about the need to husband weaponry, arms, and munitions in order to wage war against China.
Since the outbreak of Ukraine, Ratner has been working hard to pull India into the US defense industry’s supply chain, and claims to have been successful.
South Korea’s considerable military-industrial complex is being pulled into sub-contracting for US war with China.
Since many of its major Chaebol corporations got their start as subcontractors for the war in Vietnam (for example, Hyundai was a subcontractor for Halliburton/Brown & Root), the Korean economy is simply reverting back to its corporate-martial roots.
South Korea’s economy is currently tanking due to US-forced sanctions on China. Major Korean electronic firms have lost 60 to 80% of their profits due to US-imposed chip sanctions.
Under those conditions, military manufacturing and/or subcontracting looks to be the only way forward.
In this way, the US is forcing a war economy onto its vassals.
The business of the US is war
Continue readingIsrael Didn’t Even Try to Defend the Legality of Its Occupation to World Court

Israel’s system is “an even more extreme form of the apartheid” than South Africa’s was, South African ambassador said.
By Marjorie Cohn , TRUTHOUT, March 6, 2024
or six days, more than 50 countries, the League of Arab States, the African Union and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation presented testimony to the International Court of Justice (ICJ, or World Court) about the legality of Israel’s occupation of Palestinian territory. The overwhelming majority of them, largely from the Global South, told the court that the occupation was illegal.
The historic hearing, which took place February 19-26, was held in response to the United Nations General Assembly’s December 30, 2022, request for an advisory opinion on the following questions:
(a) What are the legal consequences arising from the ongoing violation by Israel of the right of the Palestinian people to self-determination, from its prolonged occupation, settlement and annexation of the Palestinian territory occupied since 1967, including measures aimed at altering the demographic composition, character and status of the Holy City of Jerusalem, and from its adoption of related discriminatory legislation and measures?
(b) How do the policies and practices of Israel … affect the legal status of the occupation, and what are the legal consequences that arise for all States and the United Nations from this status?
The General Assembly asked the ICJ to discuss these issues with reference to international law, including the UN Charter; international humanitarian law; international human rights law; resolutions of the Security Council, General Assembly and Human Rights Council; and the 2004 advisory opinion of the ICJ finding that Israel’s wall on Palestinian land violated international law.
Israel regularly thumbs its nose at the World Court. It ignored the court’s ruling that the wall was illegal and refuses to implement the ICJ’s provisional order to refrain from committing genocidal acts and ensure humanitarian aid to Gaza.
Before the hearing, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu blasted the court: “Israel does not recognize the legitimacy of the proceedings of the international court in The Hague regarding ‘the legality of the occupation’ — which are an effort designed to infringe on Israel’s right to defend itself against existential threats,” he said. “The proceedings in The Hague are part of the Palestinian attempt to dictate the results of the diplomatic settlement without negotiations.”
Although Israel didn’t appear at the hearing, it submitted a five-page statement which called the General Assembly’s questions “a clear distortion of the history and present reality of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.” Israel didn’t even attempt to defend the legality of the occupation, focusing instead on why the ICJ should not issue an advisory opinion.
Israel complained that the ICJ “is asked simply to presume Israeli violations of international law — to accept, as given, plainly biased and flawed assertions directed against Israel alone.” Although consent of the parties is not required for the ICJ to render advisory opinions, Israel protested that it had “not given its consent to judicial settlement of its dispute with the Palestinian side.”
A handful of countries — including the U.S., Canada, U.K., Fiji, Hungary, Italy and Zambia — sided with Israel. Only Fiji argued that the occupation was lawful. The U.S. contended that an occupation can be neither lawful nor unlawful; it is rather governed exclusively by international humanitarian law, which only deals with acts by the occupying power, and doesn’t examine the legality of the occupation itself.
“The court should not find that Israel is legally obligated to immediately and unconditionally withdraw from occupied territory,” said Richard Visek from the U.S. State Department, urging the court to consider Israel’s “legitimate security needs.” Visek defended Israel in the ICJ the day after the U.S. vetoed a Security Council resolution demanding an immediate ceasefire in Gaza for the fourth time.
Israeli Genocide Is “Result of Decades of Impunity”
“The genocide underway in Gaza is the result of decades of impunity and inaction. Ending Israel’s impunity is a moral, political and legal imperative,” Palestine’s Foreign Minister Riyad al-Maliki told the court……………………………………………………………………………………………
Israel’s Occupation of Palestinian Territory Is Illegal
It is a peremptory norm of international law that territory cannot be acquired by force. In 1967, Israel launched a “preemptive” war against Egypt, Jordan and Syria, and seized the West Bank, Gaza, Jerusalem, the Golan Heights and the Sinai Peninsula. Israel has occupied those Palestinian territories ever since.
Visek from the U.S. State Department told the ICJ that Israel was defending itself in the 1967 war. But it was Israel that initiated the war. Rossa Fanning, Ireland’s attorney general, called it “the war [Israel] launched,” thus, an act of aggression. Wilde noted that Israel “claimed to be acting in self-defence, anticipating a non-immediately imminent attack,” but “even assuming, arguendo, its claim of a feared attack, States cannot lawfully use force in non-immediately imminent anticipatory self-defence.” Article 51 of the UN Charter forbids a state from using military force except in self-defense after an armed attack by another state.
…………………………………………………………….Israel asserts that it has not occupied the Gaza Strip since 2005, when it withdrew its military forces and settlements. But it continues to exercise military control over Gaza by continuous military operations in and against Gaza.
……………………….Gaza and its population remain under effective Israeli control and are, therefore, occupied. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Apartheid “Goes Hand-in-Hand” With Violation of Right to Self-Determination
Israel maintains a system of apartheid in the occupied Palestinian territory, as confirmed by Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch and Israeli human rights group B’Tselem. Vusimuzi Madonsela, South Africa’s ambassador to the Netherlands, called Israel’s apartheid system “an even more extreme form of the apartheid that was institutionalized against Black people in my country.”
In the West Bank, Israel preserves its separation wall, segregated roads, checkpoints and restrictive permit requirements. While Israelis are subject to a civil legal system, Palestinians are controlled by a military system. They can be held indefinitely with no charges or due process in administrative detention and can be convicted based on secret evidence………………………………………………….
Israeli Settlements Constitute Illegal Annexation
More than 700,000 Israeli settlers — 10 percent of the nearly 7 million people in Israel — have been transferred into the occupied Palestinian territories, “continuously terrorizing and forcibly displacing Palestinians from even more of their territory and engaging in pogroms against them,” Shoman from Belize stated.
This constitutes a “disguised form of annexation,” Ireland’s Fanning said. “The prohibition on the acquisition of territory by force is firmly established in customary international law. Using force to occupy and maintain such occupation for the purposes of territorial acquisition or annexing an occupied territory by force in whole or in part, is each illegal.”
Israel’s policy of settling its civilians in occupied Palestinian territory and displacing the local population violates international humanitarian law, as the ICJ has ruled. Article 49 of the Fourth Geneva Convention says: “The Occupying Power shall not deport or transfer parts of its own civilian population into the territory it occupies.”
Legal Consequences for All States and the UN
“Israel must dismantle the physical, legal and policy regime of discrimination and oppression … evacuate Israeli settlers from Palestinian territories, permit Palestinians to return to their country and property, and lift the siege and blockade of Gaza,” Webb from Belize told the ICJ. “These consequences, taken collectively, mean that Israel must immediately, unconditionally, and totally withdraw from the entire Palestinian territory.”
…………………………………………………………………………………… The ICJ will likely issue its advisory opinion in about six months. https://truthout.org/articles/israel-didnt-even-try-to-defend-the-legality-of-its-occupation-to-world-court/
The horrors of nuclear weapons testing

I think that enough time has gone by that the longer-term dangers of nuclear weapons, such as radioactive fallout, have largely disappeared from the public consciousness—much to the agony and despair of those afflicted to this day.
Radioactive fallout and its long-term effects—things that the average person today does not really appreciate—would be the result from any future nuclear weapons explosion that touched the Earth’s surface. Fallout does not just affect the target, but also the surrounding areas—which could be as far as hundreds of miles away. And the effects could last for years, if not decades thereafter.
Bulletin By Walter Pincus, March 7, 2024
There has been talk in the national security community lately about the so-called “merits” of resuming underground or even atmospheric nuclear weapons tests. I think this would be a grave mistake for many reasons—chief among them is that it forgets the horrific health effects that resulted from some previous nuclear tests.
To be clear, since 1963, atmospheric tests of nuclear weapons have been banned, as have tests in outer space and under water. And underground explosive tests have been banned ever since the 1996 Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, or CTBT. (Technically speaking, while the United States and China have signed the CTBT, neither has ratified it. Russia did both sign and ratify the treaty but on November 2, 2023 Russia announced it had rescinded its ratification. All three countries, however, have so far abided by the CTBT treaty.)
Meanwhile, sub-critical nuclear tests—which use tiny amounts of plutonium but do not create self-sustaining, exponentially-growing, nuclear chain reactions—have continued to this day, in laboratories or in specially constructed underground tunnels. The US is building new tunnels for sub-critical tests at the Nevada Nuclear Test Site where they are expected to help in designing the new, US W93 nuclear warhead now under development.
Presumably, then, what we are referring to when we talk about the possible resumption of nuclear testing is not the latter sub-critical testing, but some version of atmospheric, outer space, underwater, or underground explosives testing.
And here things get tricky.
Because I think that enough time has gone by that the longer-term dangers of nuclear weapons, such as radioactive fallout, have largely disappeared from the public consciousness—much to the agony and despair of those afflicted to this day.
I believe that the more people understand and even can visualize the immediate and long-term dangers of nuclear weapons use, the less likely it is that they may be used. Several nuclear scientists have told me they have memories of specific past nuclear atmospheric tests, most memorably two who were involved in the Manhattan Project—Harold Agnew and Hans Bethe.
Agnew photographed the Hiroshima mushroom cloud from the US aircraft that followed the Enola Gay that dropped the atomic bomb. Agnew almost always brought up the effect that had on him when we met.
For his part, Bethe, at 88—on the 50th anniversary of the birth of the atomic bomb—wrote: “I feel the most intense relief that these weapons have not been used since World War II, mixed with horror that tens of thousands of such weapons have been built since that time—one hundred times more than any of us at Los Alamos could ever imagine.”
In an interview years earlier at Cornell University where he was teaching, Bethe had told me something similar—and at 91, I have never forgotten those words.
The closer you are to nuclear weapons, the more you are aware of the dangers if they were to be used again. However, I believe, most people today have forgotten, if they ever knew, what a single nuclear weapon could do.
Seeing is believing. But believing in this case should make you work to oppose their use, as can be seen in a very rough sort of timeline of my own life…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
It was in February 1966, well after the 1963 atmospheric test ban treaty, that I first wrote about the impact of nuclear weapons. It was a rather flip, three-paragraph note in The Reporter Magazine, which no longer exists. The story concerned a law that had passed Congress the previous month, a measure which required the US Government to pay $11,000 to each of the 82 men, women and children—or their survivors—who had been on Rongelap Atoll in the Marshall Islands in the central Pacific on March 1, 1954 when the United States detonated Test Bravo from a tower on an artificial island built within Bikini Atoll, more than 120 miles west of Rongelap.
Bravo was the first US test of a deliverable thermonuclear bomb and was expected to have a six-megaton yield, the equivalent of six million tons of TNT. In fact, the explosion was more than double that—15 megatons—and one thousand times more powerful than the atomic bomb that destroyed Hiroshima.
Thanks in good part to thousands of documents on nuclear weapons declassified and released during the Clinton Administration, I was able to describe details about the Bravo explosion two years ago in my book, Blown To Hell: America’s Deadly Betrayal of the Marshall Islanders, as follows:
In a few seconds the fireball, recorded at one hundred million degrees, had spread nearly three miles in diameter, then quickly spread to ten miles. The sandspit and nearby reef where Bravo had stood, along with coral island areas, were vaporized down almost two hundred feet into the sea, creating a crater about one mile in diameter.
It was estimated that three hundred million tons of vaporized sand, coral and water shot up into the air as the fireball rose, and one-hundred-mile-an-hour winds created by the blast pulled additional debris up into the fireball. Within one minute, the fireball had gone up forty-five thousand feet with a stem four miles wide filled with radioactive debris. It continued to zoom upward, shooting through the troposphere and into the stratosphere within five minutes.
Later data showed the cloud bottom was at fifty-five thousand feet, the secondary mushroom cloud bottom was at one-hundred-fourteen thousand feet, and the upper cloud hit one-hundred-thirty thousand feet.
Ten minutes after detonation the mushroom cloud had widened and measured seventy-five miles across just below the stratosphere.
Original projections had predicted Bravo radioactive fallout would emanate from a fifteen-mile-wide cylinder that could stretch into the stratosphere. Instead, it turned out to be a one-hundred-mile-wide cloud where “debris was carried up and dispersed over a much larger area than was thought possible,” wrote Dr. William Ogle, the test’s task force commander of the scientific group that dealt with radioactivity.
Radioactive fallout and its long-term effects—things that the average person today does not really appreciate—would be the result from any future nuclear weapons explosion that touched the Earth’s surface. Fallout does not just affect the target, but also the surrounding areas—which could be as far as hundreds of miles away. And the effects could last for years, if not decades thereafter. These effects are worth spelling out in detail, using what happened downwind of the test as an example.
That March 1, 1954 morning, the Japanese fishing boat Lucky Dragon, with a crew of 23 aboard, was trawling its nets 90 miles east-northeast of Bikini. A crewman at the stern rail saw a whitish flare in the west that briefly lit up the clouds and the water. It grew in size, turned to yellow-red, then orange. After a few minutes, the colors faded and shortly thereafter the ship was rocked by the blast of an explosion.
The Lucky Dragon’s captain and the fishing master, who had read ship warnings before they left port, realized they might have strayed into a nuclear test area. They quickly decided to haul in their fishing nets and head back to Japan, almost 2,500 miles away.
It was another two or three hours before a fine white dust began to come down on the boat. With a light rain, the radioactive dust continued to settle on crewmen and the fish on the deck as they worked for another two hours to bring in their lines.
On Rongelap about 30 miles further east, at about 11:30 a.m., a similar powdery, radioactive ash began falling in the area. It stuck to the Marshallese people’s skin, hair, and eyes; many walked barefoot and the powder stuck to their toes; it fell on fish drying on wooden racks that would be eaten that night. Rain briefly fell as the fallout continued into afternoon, dissolving the powdery ash on roofs and carrying it down drains into water barrels that provided drinking water to each household.
On parts of Rongelap Island, where most people lived, the almost five hours of fallout led to drifts of up to one-inch or more high on the ground, on roofs, and along the beach. People recalled that when the moon broke through the clouds that night, it looked like patches of snow on the ground.
It would be two days before the Marshallese were evacuated from Rongelap and taken to the Kwajalein Navy Base by a US Navy destroyer. By then, most of the Rongelapese people had suffered from acute radiation exposure and nausea; some had experienced skin lesions as well.
Since the Bravo test was highly classified, a decision was made in Washington to keep the fallout incident secret, although the Atomic Agency Commission (AEC) had released a statement on March 1, 1954 that a nuclear test had taken place in the Marshall Islands Pacific Proving Ground. That had generated a small front page story in the March 2, 1954, edition of The New York Times. It was not until March 11, 1954, that the AEC admitted people “unexpectedly exposed to some radioactivity” had been moved to Kwajalein “according to a plan as a precautionary measure.”
Two weeks passed before the Lucky Dragon returned to its home port in Japan. It was only then that on March 16, 1954, the first story appeared in the Japanese Yomiuri Shimbun newspaper of what had happened to the boat’s crew and their fish—not what happened to the Marshallese. That story immediately triggered initial worldwide attention to the dangers of fallout from nuclear weapons.
However, it was not until President Eisenhower’s March 31, 1954 press conference that AEC Chairman Lewis Strauss, who had just returned from observing post-Bravo nuclear tests, admitted publicly that the Bravo test was “in the megaton range” and “the yield was about double that of the calculated estimate.” ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The early part of the 1955 report described the blast and heat effects of early atomic bombs detonated in the air, before discussing fallout from Bravo and other detonations. “In the air explosion, where the fireball does not touch the earth’s surface, the radioactivity produced in the bomb condenses only on solid particles from the bomb casing itself and the dust which happens to be in the air. In the absence of materials drawn up from the surface, these substances will condense with the vapors from the bomb and air dust to form only the smallest particles. These minute substances may settle to the surface over a very wide area—probably spreading around the world—over a period of days or even months. By the time they have reached the earth’s surface, the major part of their radioactivity has dissipated harmlessly in the atmosphere and the residual contamination is widely dispersed.”
The report then turned to what fallout would occur if the fireball hit the ground. “If however the weapon is detonated on the surface or close enough so that the fireball touches the surface, then large amounts of material will be drawn up into the bomb cloud. Many of the particles thus formed are heavy enough to descend rapidly while still intensely radioactive. The result is a comparatively localized area of extreme radioactive contamination, and a much larger area of some hazard. Instead of wafting down slowly over a vast area, the larger and heavier particles fall rapidly before there has been an opportunity for them to decay harmlessly in the atmosphere and before the winds have had an opportunity to scatter them.”
It described the Bravo fallout as looking like snow “because of calcium carbonate from coral,” and then noted its “adhesive” quality thanks to moisture picked up in the atmosphere as it descended. In the end it contaminated “a cigar-shaped area extending approximately 220 statute miles downwind, up to 40 miles wide,” from Bikini. It “seriously threatened the lives of nearly all persons in the area who did not take protective measures,” the report said.
The report then talked about radioactive strontium in fallout as having a long, average lifetime of nearly 30 years, noting it could enter the human body either by inhaling or swallowing. Deposited directly on edible plants, the strontium could be eaten by a human or animal. While rainfall or human washing of the plants would remove most of the radioactive material, radioactive strontium deposited directly on the soil or in the ocean, lakes, or rivers could be taken up by plants, animals, or fish. There it would lodge in their tissue where it could later be eaten by humans…………….
The other radioactive element in fallout described specifically as a threat in the report was radioactive iodine. Even though the average life of radioactive iodine was only 11.5 days, it was described as a serious hazard because, if inhaled, it concentrated in the thyroid gland where it could damage cells, depending on dosage………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Back on Rongelap, despite some cleanup, there are few in residence. A study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in July 2019, done by researchers from Columbia University, found that levels of plutonium and cesium in the soil on Rongelap and other Marshall Island atolls were “significantly higher” than levels that resulted from fallout existing from the July 1986 Chernobyl nuclear power accident—which occurred 28 years after US nuclear tests had ended in the Marshalls.
The Rongelap Marshallese as well as the Japanese seamen who were exposed to fallout on March 1, 1954, can be seen as surrogates for anyone caught in a future nuclear war. Rongelap Atoll, as well as Bikini Atoll, for the most part still cannot be inhabited despite attempts to decontaminate them. Think of what today’s cities would be like if hit by a thermonuclear weapon whose fireball struck the ground and created radioactive fallout.
Within weeks it will be 70 years since the Bravo test. The more the US public and the world are reminded of that test and the resulting Rongelap story, the more they should work to deter any potential use of nuclear weapons. https://thebulletin.org/premium/2024-03/the-horrors-of-nuclear-weapons-testing/?utm_source=Newsletter&utm_medium=Email&utm_campaign=ThursdayNewsletter03072024&utm_content=NuclearRisk_NuclearTestingHorrors_03072024
Oppenheimer feared nuclear annihilation – and only a chance pause by a Soviet submariner kept it from happening in 1962
on October 27, 1962, a nuclear war was averted not because President Kennedy and Premier Khrushchev were doing their best to avoid war (they were), but because Capt. Vasily Arkhipov had been randomly assigned to submarine B-59.”
This is but one of countless examples where global and military history has been dramatically altered by chance and luck. On Oct. 27, 1962, the world was extremely lucky. The question that Robert Oppenheimer would surely ask is, will we be so lucky the next time?
March 7, 2024, https://theconversation.com/oppenheimer-feared-nuclear-annihilation-and-only-a-chance-pause-by-a-soviet-submariner-kept-it-from-happening-in-1962-223148 Mark Robert Rank, Professor of Social Welfare, Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis
History has often been shaped by chance and luck.
One of the blockbuster films of the past year, “Oppenheimer,” tells the dramatic story of the development of the atomic bomb and the physicist who headed those efforts, J. Robert Oppenheimer. But despite the Manhattan Project’s success depicted in the film, in his latter years, Oppenheimer became increasingly worried about a nuclear holocaust resulting from the proliferation of these weapons.
Over the past 80 years, the threat of such nuclear annihilation was perhaps never greater than during the Cuban missile crisis of 1962.
President John F. Kennedy’s secretary of state, Dean Acheson, said that nuclear war was averted during that crisis by “just plain dumb luck.” As I detail in my forthcoming book, “The Random Factor,” nowhere was the influence of chance and luck more evident than on Oct. 27, 1962.
Russian missiles next door
To set the stage, a cold war of hostilities between the U.S. and the communist Soviet Union began almost immediately following World War II, resulting in a nuclear arms race between the two during the 1950s and continuing through the 1980s.
As a part of the Cold War, the U.S. was extremely concerned about countries falling under the Soviet communist influence and umbrella. That fear was magnified in the case of Cuba.
Tensions between the U.S. and Cuba had dramatically escalated following the failed 1961 U.S. attempt to overthrow revolutionary leader Fidel Castro and his communist ruling party. Known as the Bay of Pigs invasion, its failure proved to be a major embarrassment for the Kennedy administration and a warning to the Castro regime.
In May 1962, Castro and Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev agreed to secretly deploy strategic nuclear missiles in Cuba, with the intention of providing a strong deterrent to any potential U.S. invasion in the future. The Russian missiles and equipment would be disassembled and shipped aboard freighters bound for Havana, then be reassembled on-site.
On Oct. 14, a high-flying U.S. U-2 spy plane photographed the construction of a missile launch site in western Cuba. This marked the beginning of the 13 days in October known as the Cuban missile crisis.
After heated deliberations with his cabinet and advisers, Kennedy decided on a naval blockade surrounding Cuba to prevent further Soviet ships from passing through. In addition, Kennedy demanded removal of all missiles and equipment already in Cuba.
This began a standoff between the U.S. and Russia. Ultimately, the missiles were disassembled and removed from Cuba. In exchange, the U.S. removed its Jupiter ballistic missiles from bases in Turkey and Italy.
But one utterly random – and utterly crucial – aspect of this resolution was not known until years later through the memoirs of, and interviews with, Soviet sailors.
Continue readingUS Refuses to Assure UK Judges That Assange Won’t Be Executed If He’s Extradited

UK law prohibits extradition to a country that may impose capital punishment.
By Marjorie Cohn , TRUTHOUT, February 27, 2024
n February 20 and 21, as nearly 1,000 supporters of Julian Assange gathered outside the London courthouse, a two-judge panel of the High Court of Justice presided over a “permission hearing.” Assange’s lawyers asked the judges to allow them to appeal the home secretary’s extradition order and raise issues that the district court judge had rejected without full consideration.
The High Court panel, Dame Victoria Sharp and Justice Jeremy Johnson, were concerned that the U.S. government could execute Assange if he is extradited to the United States, a penalty outlawed in the U.K. Although Assange faces 175 years in prison for the charges alleged in the indictment, there is nothing to prevent the U.S. from adding additional offenses which would carry the death penalty.
The Trump Administration Indicted Assange for Exposing U.S. War Crimes
Assange is charged with 17 counts of alleged violations of the Espionage Act, based on obtaining, receiving, possessing and publishing national defense information. He is accused of “recruit[ing] sources” and “soliciting” confidential documents just by maintaining the WikiLeaks website that stated it accepted such materials. Assange is also charged with one count of “conspiracy to commit computer intrusion” with intent to “facilitate [whistleblower Chelsea] Manning’s acquisition and transmission of classified information related to the national defence of the United States.”
The basis for the indictment, Assange’s lawyers told the panel, is WikiLeaks’s “exposure of criminality on the part of the U.S. government on an unprecedented scale.” Assange is charged for revealing war crimes committed by the United States in Iraq, Afghanistan and Guantánamo Bay. The indictment has nothing to do with Hillary Clinton and the 2016 election or Swedish allegations of sexual misconduct, which have been dropped.
WikiLeaks revealed the “Iraq War Logs” — 400,000 field reports including 15,000 unreported deaths of Iraqi civilians, as well the as systematic rape, torture and murder after U.S. forces handed over detainees to a notorious Iraqi torture squad. The revelations also included the “Afghan War Diary” — 90,000 reports of more civilian casualties by coalition forces than the U.S. military had reported.
In addition, WikiLeaks revealed the “Guantánamo Files,” 779 secret reports with evidence that 150 innocent people had been held at Guantánamo Bay for years, and 800 men and boys had been tortured and abused, in violation of the Geneva Conventions and the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment.
WikiLeaks also revealed the notorious 2007 “Collateral Murder Video,” in which a U.S. Army Apache attack helicopter targeted and killed 11 unarmed civilians in Baghdad, including two Reuters journalists and a man who came to rescue the wounded. Two children were injured. The video contains evidence of war crimes prohibited by the Geneva Conventions.
And WikiLeaks exposed “Cablegate” — 251,000 confidential U.S. State Department cables that “disclosed corruption, diplomatic scandals and spy affairs on an international scale.” According to The New York Times, they told “the unvarnished story of how the government makes its biggest decisions, the decisions that cost the country most heavily in lives and money.”
“These were the most important revelations of criminal U.S. state behavior in history,” Assange attorney Mark Summers argued to the High Court panel.
Assange’s Appellate Issues
Assange is asking the U.K. High Court to review issues of treaty obligations, human rights violations and political persecution.
The U.S.-U.K. Extradition Treaty would allow the U.S. to amend or add charges which could expose Assange to the death penalty, a punishment prohibited in the U.K. In response to questioning by one of the judges, the prosecutor admitted that the U.S. had not provided assurances that Assange would not be subject to the death penalty if extradited.
Article 4(1) of the extradition treaty does not allow extradition for political offenses. Espionage is the “quintessential” political offense, Assange attorney Edward Fitzgerald told the panel. “The gravamen (and defining legal characteristic) of each of the charges is thus an alleged intention to obtain or disclose US state secrets in a manner that was damaging to the security of the US state,” which makes them political offenses, Assange’s lawyers wrote. The defense claimed it was an abuse of process for the United States to pursue extradition of Assange for a political offense……………………………………………………………………………….
“The Most Important Revelation Since Abu Ghraib”
The Collateral Murder video is “the most important revelation since Abu Ghraib,” Summers told the panel. “The cables Assange published disclosed extrajudicial assassinations, rendition, torture, dark prisons and drone killings.” Summers said the Guantánamo Files revealed a “colossal criminal act.” The defense pointed out that WikiLeaks’s revelations actually saved lives. After WikiLeaks published evidence of Iraqi torture centers established by the U.S., the Iraqi government refused President Barack Obama’s request to grant immunity to U.S. troops who committed criminal and civil offenses there. As a result, Obama had to withdraw U.S. forces from Iraq.
The Obama administration, which prosecuted more whistleblowers under the Espionage Act than all prior U.S. administrations combined, considered prosecuting Assange, but feared it would violate the First Amendment. The administration was unable to distinguish what WikiLeaks did from what The New York Times and The Guardian did since they also published documents that Chelsea Manning had leaked.
But the Trump administration did indict Julian Assange. The U.K. arrested Assange and has held him in Belmarsh Prison for nearly five years pending a decision on whether he should be extradited to the U.S. to stand trial.
In January 2021, following a three-week hearing, Baraitser denied extradition after finding that Assange’s mental health was so frail there was a “substantial risk” of suicide if he was extradited to the U.S. because of the harsh conditions of confinement in which he would be held. But she rejected all other legal objections to extradition that Assange had raised.
U.S. “Assurances” That Assange Will Be Treated Humanely
After Baraitser had already ruled, the U.S. came forward with diplomatic “assurances” that Assange would be treated humanely if extradited to the United States. The Biden administration assured the court that Assange: (1) would not be subject to onerous Special Administrative Measures (SAMs) that would keep him in extreme isolation and monitor his confidential communications with his attorneys; (2) would not be housed at the notorious ADX Florence maximum security prison in Colorado; (3) would receive psychological and clinical treatment in custody; and (4) could serve any custodial sentence in Australia.
But the U.S. said the assurances wouldn’t apply if Assange committed a “future act” that “met the test” for the SAMs. That unspecified contingency would be based on a subjective determination of prison authorities with no judicial review.
Although the United States has reneged on nearly identical assurances in the past, the High Court accepted them at face value, saying it was satisfied that the U.S. was acting in good faith, and in December 2021, the High Court reversed Baraitser’s denial of extradition.
However, in a 2023 decision, the U.K. Supreme Court unanimously held that the court has an independent duty to determine the validity of assurances,
writing, “The government’s assessment of whether there is such a risk is an important element of that evidence, but the court is bound to consider the question in the light of the evidence as a whole and to reach its own conclusion.”
In June 2023, a single High Court judge, Jonathan Swift, refused Assange permission to appeal in a cursory three-page ruling. The hearing on February 20 and 21 was an effort by Assange’s legal team to reverse that decision so that the High Court will entertain his appeal.
Assange Redacted Names of Informants to Protect Them
…………………… Several witnesses testified at the 2020 extradition hearing that Assange took great care to ensure that the names were redacted. Other outlets published the unredacted cables before WikiLeaks with no adverse consequences.
………………….Moreover, Brig. Gen. Robert Carr testified at Manning’s court martial that no one was harmed by the WikiLeaks releases. Summers told the panel that Baraitser never balanced the public interest in the disclosures against the fact that no harm came from them.
Conviction of Assange Would Chill Investigate Journalists From Exposing Government Secrets
In November 2022, The New York Times, The Guardian, Le Monde, DER SPIEGEL and El País signed a joint open letter calling on the Biden administration to drop the Espionage Act charges against Assange. They wrote, “Publishing is not a crime,” noting that Assange is the first publisher to be charged under the Espionage Act for revealing government secrets.
The indictment would punish conduct that national security journalists routinely engage in, including cultivating and communicating confidentially with sources and soliciting information from them, shielding their identities from disclosure, and publishing classified information. If Assange is prosecuted and convicted, it will discourage journalists both in the U.S. and abroad from publishing evidence of government wrongdoing.
No publisher has ever been prosecuted under the Espionage Act for disclosing government secrets. The U.S. government has never prosecuted a publisher for publishing classified information, which constitutes an essential tool of investigative journalism.
But rather than dropping Trump’s prosecution of Assange consistent with the position of the Obama-Biden administration, Joe Biden has zealously pursued extradition and prosecution.
Pending House Resolution Would Call for Dismissal of All Charges Against Assange.
On December 13, 2023, House Resolution 934 was introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives by Rep. Paul A. Gosar (R-Arizona), with cosponsors from both political parties. It would express “the sense of the House of Representatives that regular journalistic activities are protected under the First Amendment, and that the United States ought to drop all charges against and attempts to extradite Julian Assange.” The resolution states that the WikiLeaks disclosures “promoted public transparency through the exposure of the hiring of child prostitutes by Defence Department contractors, friendly fire incidents, human rights abuses, civilian killings, and United States use of psychological warfare.”
…………… The conviction of Assange under the Espionage Act, the resolution continues, “would set a precedent allowing the United States to prosecute and imprison journalists for First Amendment protected activities, including the obtainment and publication of information, something that occurs on a regular basis.”
…………..
At the conclusion of the two-day hearing, the High Court panel set a due date of March 4 for further written submissions from the parties. If the court agrees to review at least one of Assange’s appellate issues, there will be a full hearing. Meanwhile, Assange, who is in poor physical and emotional health, remains in prison.
If the High Court denies his right to appeal, Assange can ask the European Court of Human Rights to hear his case. If that court finds “exceptional circumstances” and an “imminent risk of irreparable harm,” it can order provisional measures, including a stay of execution while the case is pending in the European court. But there is a danger that the U.K. could immediately extradite Assange to the United States before the European Court of Human Rights has a chance to consider Assange’s petition.
-
Archives
- March 2026 (109)
- February 2026 (268)
- January 2026 (308)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (376)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS




