Space tourists and crew suffer high radiation risks – regulation is needed to protect them.
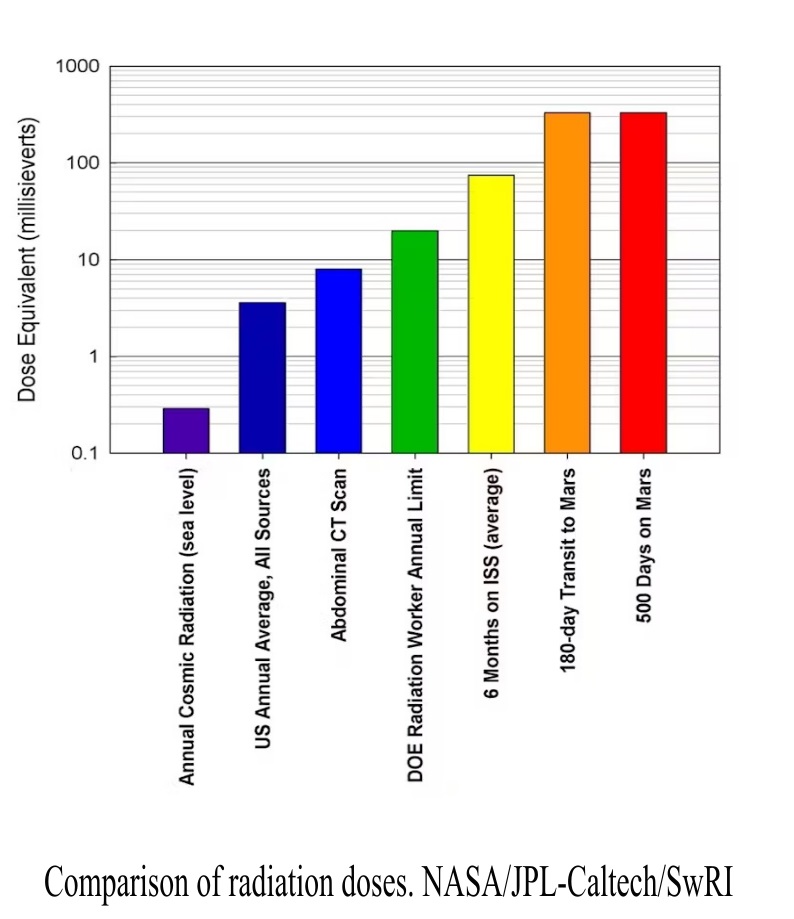
exposure to elevated levels of ionising radiation, such as those possible during space weather events, can potentially cause damage to DNA. The risk of space travel therefore ranges from a minor increase in health defects to serious health implications such as cancers.
The space tourism industry is currently not fully aware of the radiation risks, we discovered. It is instead relying on incomplete “informed consent” for non-crew participants.
The Conversation, March 19, 2024 , Chris Rees, Postgraduate Researcher of Space Risk Engineering, University of Surrey
In a decade or two, journeys into space could become as normal [really?]as transatlantic flights. In particular, the number of humans travelling into space with the help of commercial companies, such as Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin, will increase significantly.
But such travel comes with huge radiation risks. Sudden changes in space weather, such as solar flares, for example, could have significant health implications for crew and passengers. Now our recent paper, from the University of Surrey, Foot Anstey LLP Space and Satellite Team, has found that current legislation and regulation don’t do enough to protect space tourists and crew.
Changes in space weather could expose space tourists to radiation doses in excess of the recommended maximum 1 millisievert (mSv) yearly uptake for a member of the public and 20mSv yearly for those working with radiation. Research at the University of Surrey shows that during an extreme space weather event, flight participants could receive doses in excess of 100mSv.
Current legislation and regulation focusing on potential radiation exposure for space tourists is limited and largely untested. There is a heavy focus on conventional non-radiation risk and wider safety, with guidance stemming from regulation of normal commercial flights. However, these are significantly different to space tourism enterprises.
Similarly, the law around space flights and their associated risk liability is complex. Space law incorporates a mix of international law (such as international agreements, treaties and conventions), domestic legislation and guidance.
Cancer risk
Exposure to low levels of background natural radiation is part of everyday life. Most people are not aware of this exposure and the potential risks to our health. For example, an 0.08mSv effective dose from a commercial flight from the UK to the US.
However, exposure to elevated levels of ionising radiation, such as those possible during space weather events, can potentially cause damage to DNA. The risk of space travel therefore ranges from a minor increase in health defects to serious health implications such as cancers.
There has been significant risk assessment of radiation exposure on Earth; for example in the nuclear industry. This is unlike the space tourism industry, which is still in its infancy.
Previous research has focused on the potential risk assessment for astronauts from radiation exposure and long duration missions outside low-Earth orbit. But this does not consider risks for those on short trips to space as tourists. Thus, there is still significant work to be done to assess the unique risk for space tourist flights and the supporting guidance and regulation.
Any existing regulation, such as the UK Air Navigation Order and Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) space flight regulations, that is applicable to potential space flights focuses on crew, rather than paying passengers.
The space tourism industry is currently not fully aware of the radiation risks, we discovered. It is instead relying on incomplete “informed consent” for non-crew participants. The current regulation for the industry therefore places the risk burden firmly on the space tourist. We argue more legislation and regulation are needed.
Our recommendations
We made a series of recommendations in our report. But they are advisory. They are intended for the industry and regulators to consider as the space tourism sector continues to develop, particularly the FAA and the UK Civil Aviation Authority (CAA)………………………………… more https://theconversation.com/space-tourists-and-crew-suffer-high-radiation-risks-regulation-is-needed-to-protect-them-225693
US and Japan seek UN resolution calling on all nations to ban nuclear weapons in outer space
The United States and Japan are sponsoring a U.N. Security Council resolution calling on nations not to deploy or develop nuclear weapons in space
ByEDITH M. LEDERER Associated Press, March 19, 2024,
UNITED NATIONS — The United States and Japan are sponsoring a U.N. Security Council resolution calling on all nations not to deploy or develop nuclear weapons in space, the U.S. ambassador announced Monday.
Linda Thomas-Greenfield told a U.N. Security Council meeting that “any placement of nuclear weapons into orbit around the Earth would be unprecedented, dangerous, and unacceptable.”
The announcement that the U.S. and Japan had circulated a resolution follows White House confirmation last month that Russia has obtained a “troubling” anti-satellite weapon capability, although such a weapon is not operational yet.
Russian President Vladimir Putin declared later that Moscow has no intention of deploying nuclear weapons in space, claiming that the country has only developed space capabilities similar to those of the U.S.
The Outer Space Treaty ratified by about 114 countries including the United States and Russia prohibits the deployment of “nuclear weapons or any other kinds of weapons of mass destruction” in orbit or the stationing of “weapons in outer space in any other manner.”
Japan’s Foreign Minister Yoko Kamikawa, who chaired the council meeting, said that even during “the confrontational environment” of the Cold War, the rivals agreed to ensure that outer space remained peaceful. That prohibition on putting any weapons of mass destruction into orbit must be upheld today, she said.
Thomas-Greenfield said all parties to the treaty must commit to the ban on nuclear and other destructive weapons, “and we must urge all member states who are not yet party to it to accede to it without delay.”
She said the United States looks forward to engaging with the other members of the 15-nation Security Council “to forge consensus around this text.”…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
more https://abcnews.go.com/US/wireStory/us-japan-seek-resolution-calling-nations-ban-nuclear-108261129
La Hague reprocessing plant: expansion and continued operation until at least 2100

Last week, the Élysée Palace confirmed that the French reprocessing
plant at La Hague is to be expanded. Extensive investments are planned in
this context. There have already been plans since 2020 to build another
storage pool on the plant site.
At La Hague, there is still radioactive
waste from Germany, which may be returned this year. It was actually just a
side note: The Conseil de Politique Nucléaire (Nuclear Policy Council),
which was founded in 2023 and met at the Elysée Palace last Monday,
confirmed the prospect of major investments at La Hague in order to extend
the lifespan of the facilities until at least 2100.
Corresponding press
reports were confirmed by the Elysée Palace on Tuesday: The Council had
“confirmed the major guidelines of French policy on the nuclear fuel cycle,
which combines reprocessing, reuse of spent fuel and closing the cycle”,
the La Hague site would “be the subject of major investment”. No specific
timetables or amounts were mentioned in this context.
GRS 12th March 2024
There is no such thing as a “nuclear waste-eating” reactor

Contrary to popular belief, the French nuclear industry is by no means “triumphant”, “the best in the world” or “at the cutting edge of technology”: in fact, EDF (bankrupt), Areva (renamed Orano after filing for bankruptcy) and CEA (subsidized by public money) are constantly making fools of themselves and leaving the French with astronomical bills.
A magic reactor killed by environmentalists?
By Stéphane Lhomme by beyondnuclearinternational, https://beyondnuclearinternational.org/2024/03/17/a-magic-reactor-killed-by-environmentalists/
On the contrary, a “nuclear waste-eating reactor” does not exist
Appearing as a guest on several TV channels (BFM, Cnews, etc.), a certain Fabien Bouglé managed to fool both viewers and journalists (most of whom are totally ignorant about nuclear power) with a series of fibs, each more enormous than the last. Here are a few clarifications.
There is no such thing as a “nuclear waste-eating” reactor
The smooth-talking Bouglé left his ignorant interlocutors stunned and bewildered as he talked about “waste-eating” reactors that would have already solved the radioactive waste issue if an infamous green lobby, “betraying France to Germany” (sic!), hadn’t “prevented” the advent of such reactors.
So, like throwing a log on the fire, all you have to do is put the radioactive waste produced by today’s power plants into a “magic” reactor, and the waste will disappear.
Mr. Bouglé finally divulged his “secret”: the so-called “waste-eating” reactors are simply… breeder reactors: a type of reactor that the global nuclear industry has failed to operate for 70 years, like Superphénix in France! And, even if it did work, it would in no way eliminate radioactive waste. What’s more, less than 1% of nuclear fuel (the most radioactive waste) could theoretically have its lifespan reduced, but without disappearing and while becoming even more radioactive! In the nuclear industry, as elsewhere, miracles do not exist.
The Astrid project was not “on the way to success” and was not “taken over by Bill Gates”
Despite its pretty name, the Astrid reactor project was nothing more than a little Superphénix: a sodium-cooled breeder reactor. Look at the “progress”: 40 years after the launch of Superphénix (1240 MW), the CEA wanted to make another attempt with a reactor half as powerful (600 MW), before giving up altogether.
Japan’s Monju fast-breeder reactor was definitively shut down after countless failures, a terrible fire and sodium leaks; Germany’s Kalkar fast-breeder reactor was never commissioned; and the USA has abandoned the sector. Only Russia manages to keep its BN800 hobbling along… but it doesn’t perform any of the miracles expected of it (producing “more fissile material than it consumes”, “eating” radioactive waste and other nonsense).
As for Bill Gates, he’s one of the dummies who, in recent years, have announced various types of miraculous reactors, always claiming to be able to produce electricity “cheaply, safely and with little waste” (blah blah blah). Beginning in 2006, Bill Gates and his company Terrapower first tried to make a “travelling wave” reactor work, then a “molten salt” one, both abandoned after wasting billions. Now Gates is dreaming of developing… a sodium-cooled fast-neutron reactor: back to Superphénix and 70 years of failure for the global nuclear industry.

France’s nuclear woes are caused by… France’s nuclear woes!
The “evil anti-nuclear environmentalists” and the so-called “traitors in the pay of Germany” denounced by Inspector Bouglé have nothing to do with the disasters of French nuclear power: EDF, Areva (now Orano) and the CEA are doing just fine on their own! For example:
- Industrial and financial disasters at the EPR sites in Finland, Flamanville and England: 15 to 20 years (instead of four and a half) to build a reactor costing 20 billion Euros instead of 3 billion, and with serious defects.
- The unprecedented scandal of the thousands of defective parts (including the famous Flamanville EPR vessel) produced by Areva in its Le Creusot plants.
- Catastrophic and ruinous flops at the Iter (fusion) and RJH reactor sites.
- Stress corrosion (up to 32 reactors out of 56 shut down at the same time in 2022)
And so on.
Contrary to popular belief, the French nuclear industry is by no means “triumphant”, “the best in the world” or “at the cutting edge of technology”: in fact, EDF (bankrupt), Areva (renamed Orano after filing for bankruptcy) and CEA (subsidized by public money) are constantly making fools of themselves and leaving the French with astronomical bills.
The Fessenheim closure is not the cause of electricity shortages in France and imports from Germany
Mr. Bouglé claims that France was an exporter to Germany before the closure of Fessenheim and that it has suddenly become an importer because of the plant’s closure in 2020. He’s talking nonsense.
In reality, there are exchanges (in both directions) between the two countries throughout the year. When the balance sheet is drawn up on December 31, France is still an importer from Germany (*), and has been for over 25 years (**), long before Fessenheim was shut down.
This phenomenon is mainly due to the absurd choice of electric heating, developed on a massive scale in France to “justify” nuclear power: as soon as it gets cold, electricity consumption is such that it far exceeds the capacity of the French nuclear fleet, even when it’s working properly!
It’s also worth noting the ridiculous claim that life was wonderful in France with 58 reactors, and that it has suddenly gone into crisis with “only” 56 reactors, which in reality is an insane number. For the record, during the stress corrosion crisis, France was saved by importing massive amounts of electricity from neighboring countries, which have only a few reactors, if any at all.
(*) Of course, we can criticize the fact that a significant proportion of Germany’s electricity is generated by coal-fired power plants (even if the share of renewables is increasing exponentially), but the fact is that it’s this “dirty” electricity that heats France every winter, and French nuclear enthusiasts don’t go so far as to refuse this electricity and stay in the cold and dark!
(**) Except, very narrowly, in 2011: following the Fukushima disaster, Germany immediately shut down 8 reactors. But by 2012, France was once again a net importer from Germany.
The joke about waste-eating reactors
Let’s start by noting that nuclear reactors continually produce insane quantities of radioactive waste of various kinds, from nuclear fuel to the tools and clothing used in power plants, which are contaminated… and can’t be “eaten”!
But let’s concentrate on the most radioactive, the spent fuel that comes out of the reactor core after use.
Spent fuel comprises four types of element: plutonium, uranium, fission products and minor actinides. Note that the vast majority of radioactivity is contained in these last two categories.
To attempt reuse this waste fuel, separation work must already be carried out in a gigantic plant such as La Hague. These operations require huge amounts of electricity and using large quantities of terribly corrosive and dangerous chemicals: a far cry from the “clean” energy that could “save the planet”.
– Plutonium
Listening to Mr. Bouglé, the uninformed viewer (and the ignorant journalist) think that all they have to do is recover this fuel and put it in the so-called “waste-eating reactor”, which will make this waste disappear… while producing electricity! Jackpot, bravo and thanks for everything. But Santa Claus doesn’t exist, and it’s all poppycock. And here’s why.
It is used by the military for their atomic weapons. Some of this plutonium can be recovered to make fuel (known as “mox”) for use in today’s power plants, which exacerbates the consequences of an accident when it occurs. Various studies show that this option reduces only slightly the amount of uranium needed from mining. But in no case is this plutonium “eaten” or “incinerated”; it is almost entirely recovered after use.
– Uranium
The uranium resulting from these separation operations, known as “reprocessed uranium”, can theoretically be reused in place of mined uranium, but in reality, this option poses a number of technical problems. EDF has been trying to use it for years in its Cruas power plant (Ardèche), after re-enrichment… in Russia (thanks Putin!). But this remains very marginal, and in no case is this uranium “eaten” or “incinerated”; it is almost entirely recovered after use.
– Fission products
There’s nothing we can do with them, except vitrify them and store them for millennia!
– Minor actinides
These are the only elements of radioactive waste that could theoretically have their lifespan reduced in breeder reactors… while becoming even more radioactive! But even if such a “feat” were to happen (provided we finally manage to operate breeder reactors properly), minor actinides would not be “eaten”, “incinerated” or “disintegrated”. In fact, they are vitrified like fission products and have to be stored for millennia.
Conclusion
Of course, there is no technology that can “eat” nuclear waste. At most, it is theoretically possible (but not in practice) to degrade a tiny fraction of it, and even then, at the cost of new radioactive and chemical contamination and very high energy consumption.
Once and for all, let’s remember that there will never be a nuclear miracle, be it with magic reactors, or by replacing uranium with thorium (the thorium sector is also that of fast-breeder reactors!), or with fusion, or by calling old projects that have never worked “4th generation” or “SMR”.
Stéphane Lhomme is Director of the Nuclear Observatory.
Musk’s SpaceX is building spy satellite network for US intelligence agency, sources say
By Joey Roulette and Marisa Taylor, March 17, 2024
WASHINGTON, March 16 (Reuters) – SpaceX is building a network of hundreds of spy satellites under a classified contract with a U.S. intelligence agency, five sources familiar with the program said, demonstrating deepening ties between billionaire entrepreneur Elon Musk’s space company and national security agencies.
The network is being built by SpaceX’s Starshield business unit under a $1.8 billion contract signed in 2021 with the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO), an intelligence agency that manages spy satellites, the sources said.
The contract signals growing trust by the intelligence establishment of a company whose owner has clashed with the Biden administration and sparked controversy, opens new tab over the use of Starlink satellite connectivity in the Ukraine war, the sources said.
The Wall Street Journal reported, opens new tab in February the existence of a $1.8 billion classified Starshield contract with an unknown intelligence agency without detailing the purposes of the program.
Reuters reporting discloses for the first time that the SpaceX contract is for a powerful new spy system with hundreds of satellites bearing Earth-imaging capabilities that can operate as a swarm in low orbits, and that the spy agency that Musk’s company is working with is the NRO.
Reuters was unable to determine when the new network of satellites would come online and could not establish what other companies are part of the program with their own contracts.
SpaceX, the world’s largest satellite operator, did not respond to several requests for comment about the contract, its role in it and details on satellite launches. The Pentagon referred a request for comment to the NRO and SpaceX.
In a statement the NRO acknowledged its mission to develop a sophisticated satellite system and its partnerships with other government agencies, companies, research institutions and nations, but declined to comment on Reuters’ findings about the extent of SpaceX’s involvement in the effort…………………………………………..
The U.S. Is Betting Big on Small Nuclear Reactors (done up with green paint)

Oil Price, By Felicity Bradstock – Mar 14, 2024,
- After decades of decline, the U.S. is significantly increasing its investment in nuclear energy to address climate change and strengthen energy security.
- The recently passed Atomic Energy Advancement Act simplifies approval processes for novel reactor designs, aiming to expedite the development of new nuclear power plants.
………. The U.S. is set to accelerate the rollout of new nuclear power plants and reactors following the passing of new legislation this month. This follows a movement away from nuclear power for several decades due to the poor political and public perception of nuclear power due to several notable nuclear disasters………………..
This month, the House approved legislation aimed at developing U.S. nuclear power capacity in the coming years, with a vote of 365 to 36. The Atomic Energy Advancement Act was widely approved by both the Democrat and Republican parties ………
……………………………..The law will see that the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) streamlines its processes for the approval of new reactor designs, and will increase hiring at the commission, reduce fees for applicants, establish financial prizes for novel types of reactors, and encourage the development of nuclear power at the sites of retiring coal plants. The legislation is expected to support the greatest development of U.S. nuclear power of this generation. ……………………………..
The Biden administration has repeatedly demonstrated its support for nuclear power by passing laws and approving funding to keep existing nuclear projects afloat. Two policies, passed in 2021 and 2022, provided the funding needed to save 22 reactors, with further investment being rolled out this year. This financing is expected to keep the existing U.S. nuclear reactor fleet online until at least 2032, by which time the government hopes greater investment will be being made into new nuclear projects. The policies also provide funding for research and development into the next generation of modular, more flexible nuclear plants
The passing of the Atomic Energy Advancement Act is expected to speed up the deployment of new nuclear energy technology, supported by previous Biden administration policies that provide greater investment to the sector. While strict safety regulations must be upheld, the government is putting pressure on the NRC to modernize and approve innovative reactor designs to allow for new nuclear energy capacity to be rolled out …. https://oilprice.com/Alternative-Energy/Nuclear-Power/The-US-Is-Betting-Big-on-Small-Nuclear-Reactors.html
What Does Amazon Want With Nuclear?
Microsoft signed a deal with Constellation to supply power to data centers in Virginiaand hired an official from the Tennessee Valley Authority to be its director of nuclear and energy innovations, while Microsoft founder Bill Gates and Sam Altman, the head of Microsoft-backed OpenAI have both invested in nuclear startups, as has Google.
The tech giant’s $650 million deal with Talen Energy has a lot to unpack.
Heat Map MATTHEW ZEITLIN•, MARCH 13, 2024
When Talen Energy, which owns a 90% interest in the Susquehanna nuclear power plant in Northeastern Pennsylvania, announced it was selling a data center site adjacent to its power plant to Amazon Web Services, it raised some eyebrows in the energy world. The surprise was not because a large tech company made a big deal with a carbon-free power provider, or even that a tech company made a deal to buy power generated by a nuclear power plant. It was because Amazon was making this deal.
Amazon is a massive buyer of renewable power — it claims to be the world’s largest and says it’s responsible for 28 gigawatts of clean energy capacity — signing contracts with new wind and solar projects all over the world.
But a divide has opened up among tech giants when it comes to energy, with Amazon on one side and Alphabet and Microsoft on the other. The difference hinges on how much it matters where and when the new carbon-free power a company buys in order to match its electricity use.
What’s odd about the Talen deal is that it fits awkwardly into either approach, especially Amazon’s. Amazon does not count nuclear towards its renewable power goals, and in any case, it’s not a “new” source of carbon-free power. Instead, it allows Amazon to siphon somewhere between 480 and 960 megawatts of capacity from the 2,500 megawatt plant.
“Amazon needs power, they’re getting it at cheap rates. They don’t even want to talk about it like a climate thing,” Mark Nelson, the founder of Radiant Energy Group, told me.
In the past decade or so, technology companies have gone on a clean-power buying spree, funding new wind and solar projects all over the world. But there has been a divergence in what is thought to be the best way to go about it.
In 2019, Amazon announced a goal to add enough renewable power to the grid to match its own emissions by 2030 (since moved up to 2025) and to reach net zero by 2040.
Google has been 100% renewable in terms of buying clean power in the same amounts that it consumes since 2017. So in 2020, it set a new goal: to “run on 24/7 carbon-free energy on every grid where we operate by 2030.” This would mean not just matching total renewable purchases with total emissions, as Amazon is seeking to do, but also trying to get every hour ofdata center operation “matched” with an hour of renewable generation on the same grid.
Microsoft has a similar goal, and as a result, both companies have shown much more interest in nuclear power of late than is typical in the technology world……
Microsoft signed a deal with Constellation to supply power to data centers in Virginiaand hired an official from the Tennessee Valley Authority to be its director of nuclear and energy innovations, while Microsoft founder Bill Gates and Sam Altman, the head of Microsoft-backed OpenAI have both invested in nuclear startups, as has Google.
Amazon’s approach — which it shares with several other large companies, including Meta — is not to match 24 hours of its operations with clean power bought locally, but rather to develop and purchase new wind and solar at the same scale of the power it consumes, especially in areas with dirty grids, thus matching the emissions from its consumption with the emissions reductions of new renewables projects. While a 24/7 matching approach may be naturally complementary with nuclear power, Amazon’s strategy doesn’t require it.
“We believe a focus on emissions is the fastest, most cost-effective and scalable way to leverage corporate clean energy procurement to help decarbonize global power grids at the fastest pace,” an Amazon spokesperson told me. “This includes procuring renewable energy in locations and countries that still rely heavily on fossil fuels to power their grids, and where energy projects can have the biggest impact on carbon reduction.”
Contracting out new renewable energy projects can have more bang for your buck in dirty grids, according to proponents of the Amazon philosophy, known as carbon matching. The hypothesis is that a renewable project in a fossil fuel-heavy grid will displace more dirty power than one that’s located near a datacenter in an already relatively clean grid like California or Washington State……………… https://heatmap.news/technology/amazon-nuclear-talen-energy—
Nuclear industry wants Canada to lift ban on reprocessing plutonium, despite proliferation risks


The CANDU Owners Group is far from neutral or independent…………… First, Canadian Nuclear Laboratories is a private company owned by a consortium of multi-national companies: AtkinsRéalis (formerly SNC Lavalin), Fluor, and Jacobs. ……...has overseas members, including utilities from China, Pakistan, India, South Korea, Argentina, and Romania. The first three countries are nuclear weapons states that either possess reprocessing plants for military purposes (India and Pakistan) or reportedly divert plutonium extracted from commercial spent fuel for military purposes (China), while South Korea and Argentina have for decades flirted with the idea of reprocessing.
Bulletin, By Gordon Edwards, Susan O’Donnell | March 11, 2024
Plutonium is “the stuff out of which atomic bombs are made.” Plutonium can also be used as a nuclear fuel. Reprocessing is any technology that extracts plutonium from used nuclear fuel. In Canada, the nuclear industry seems determined to close the nuclear fuel cycle by pushing for a policy to permit reprocessing—thereby seeking to lift a 45-year-old ban.
In 1977, Canada tacitly banned commercial reprocessing of used nuclear fuel, following the lead of the Carter administration, which explicitly opposed reprocessing because of the possibility it could lead to increased proliferation of nuclear weapons around the world.[1] That unwritten policy in Canada has held sway ever since.[2] New documents obtained through Canada’s Access to Information Act reveal that, behind closed doors, the nuclear industry has been crafting a policy framework that, if adopted, would overturn the ban and legitimize the extraction of plutonium from Canada’s used commercial nuclear fuel.
For over two years, documents show that the Canadian government has held a series of private meetings with industry representatives on this subject, keeping such activities secret from the public and from parliament. This raises questions about the extent to which nuclear promoters may be unduly influencing public policymaking on such sensitive nuclear issues as reprocessing in Canada.[3] But, given the stakes for the whole society and even the entire planet, the public must have a say about nuclear policy decisions…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Before the ban. Dreams of a plutonium-fueled economy were spawned in 1943-44 by British, French, and Canadian scientists working at a secret wartime laboratory in Montreal, which was part of the Anglo-American Project to build the first atomic bombs. Canada’s first heavy-water reactors were designed by the Montreal team, in part, to produce plutonium for weapons. The team also had hopes that after the war, plutonium might become a dream fuel for the future. They envisioned a “breeder reactor” that could produce more plutonium than it uses, thereby extending nuclear fuel supplies.
For 20 years after the war, Canada sold uranium and plutonium for US bombs. Two reprocessing plants were operated at Chalk River Nuclear Laboratories in Ontario. In addition, all the pilot work on plutonium separation needed to design Britain’s Windscale reprocessing plant was carried out at Chalk River.
After the ban. Although the 1977 ban scuppered AECL’s hopes for commercial reprocessing, plutonium remained the holy grail. In the decades that followed, AECL researchers studying the geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste clandestinely carried out reprocessing experiments at the Whiteshell Nuclear Research Establishment in Manitoba. Instead of burying used nuclear fuel bundles, the scientists anticipated burying solidified post-reprocessing waste. Meanwhile, AECL scientists at Chalk River fabricated three tonnes of mixed-oxide fuel (MOX) in glove boxes, using plutonium obtained from CANDU fuel reprocessed overseas. In 1996, Prime Minister Jean Chrétien volunteered to import weapons-grade plutonium from dismantled US and Soviet warheads to fuel CANDU reactors. Facing fierce public opposition in Canada, the project never came to pass.
But the dream of a plutonium economy remained. In 2011, a sprawling mural on three walls of the Saskatoon Airport depicted the nuclear fuel chain, from mining uranium to the reprocessing of used fuel to recover “potential energy” before disposing of the leftovers. Although the word plutonium appeared nowhere, reprocessing was presented as the inevitable final step in this vision of a virtuous nuclear fuel cycle. The mural was commissioned by Cameco, the giant Canadian multi-national corporation that helped make the central Canadian province of Saskatchewan into the “Saudi Arabia of uranium.” At the time, Cameco co-owned the largest operating nuclear power station in the world, the eight-reactor Bruce complex beside Lake Huron bordering the United States.
Despite such hopes, it became fashionable to publicly downplay reprocessing as expensive and therefore economically unlikely.[5] But the technology stayed on the books as a possibility, especially in case future generations would want to extract plutonium from used nuclear fuel for re-use before disposing of the remaining radioactive waste.
Back to the future? New Brunswick has one 660-megawatt-electric CANDU reactor at Point Lepreau on the Bay of Fundy in eastern Canada. The plant has been operating for over 40 years. In March 2018, two start-up companies—UK-based Moltex Energy and US-based ARC Clean Technology—offered to build “advanced” (fast) reactors on the same site.
The Moltex design is a 300-megawatt-electric molten salt reactor called “Stable Salt Wasteburner.” It is to be fueled with plutonium and other transuranic elements extracted from CANDU used fuel already stored on that site. Accordingly, the Moltex proposal requires a reprocessing plant in tandem with the reactor. The ARC design is a 100-megawatt-electric liquid sodium-cooled reactor, inspired by the second Experimental Breeder Reactor (EBR-2) operated by the Argonne National Laboratory in Idaho between 1964 and 1994. Although the ARC-100 does not require reprocessing at the outset, its optimal performance requires that the used fuel be recycled, likely through reprocessing.
From the beginning, Moltex claimed its proposed molten salt reactor would “recycle” CANDU used fuel and “burn” it in its molten salt reactor. Moltex claims that this would virtually eliminate the need for a deep geologic repository by turning a million-year disposal problem into a roughly 300-year storage problem. This claim has been flatly rebuffed.[6] Only later did the public learn that the Moltex technology requires reprocessing CANDU used fuel to extract plutonium using an innovative process called “pyroprocessing.” (In pyroprocessing, used fuel is converted to a metal and immersed in molten salt, then the plutonium and other transuranic elements are recovered by passing a current through the salt and collecting the desired products on electrodes.)
ARC Clean Technology maintains that its reactor design is proven by the 30-year operating experience of the EBR-2 reactor, despite differences in size and fuel enrichment.[7] The company, however, says nothing about the intimate connection between breeder reactors and plutonium, nor does it mention the chequered history of liquid sodium-cooled reactors globally—including the Fermi Unit 1 reactor’s partial meltdown near Detroit, the commercial failure of France’s Superphénix, the conversion of a German breeder reactor into an amusement park, or the dismal performance of Japan’s Monju reactor.
For either of the proposed New Brunswick reactors to operate as intended, Canada would need to lift its 45-year-old ban on commercial reprocessing of used nuclear fuel.
Testing the limits. The first sign that Canada’s reprocessing ban might be lifted came in 2019, when the federal government’s Impact Assessment Act exempted specified projects from environmental assessment. The exemption included any reprocessing plant with a production capacity of up to 100 metric tons (of used nuclear fuel) annually—just above the reprocessing capacity required for the Moltex project.[8]
Public calls to explicitly ban reprocessing started shortly after March 2021, when the federal government gave 50.5 million Canadian dollars in funding for Moltex’s project. This project clearly requires reprocessing: Without the plutonium produced by CANDU reactors to fuel its proposed molten salt reactor, the Moltex project can go nowhere.
In addition, Moltex hopes to eventually export the technology or the fuel, or both. Many Canadians are alarmed at the prospect of normalizing the use of recycled plutonium as a nuclear fuel in Canada and abroad.
In 2021, in response to a recommendation by the International Atomic Energy Agency, the Canadian government conducted public consultations to develop a modernized policy on commercial radioactive waste management and decommissioning. Over 100 citizens groups participated, and many called for an explicit ban on reprocessing.
Public attention to the issue of reprocessing grew after nine US nonproliferation experts sent an open letter to Prime Minister Justin Trudeau in May 2021. The letter expressed concern that by funding a spent fuel reprocessing and plutonium extraction project, Canada would “undermine the global nuclear weapons nonproliferation regime that Canada has done so much to strengthen.” …………………..
A second letter sent to Trudeau in July 2021 refuted “misleading claims” that Moltex posted on-line in rebuttal to the first letter. Moltex’s rebuttal claims were quickly taken down. And a third letter authored by one of the US nonproliferation experts was sent in November 2021. None of the government responses to these three letters addressed the core issue, which is the request for an independent review of the proliferation implications of Canada’s funding of reprocessing.
The federal government released its draft policy for radioactive waste management and decommissioning in March 2022, hinting that reprocessing might be permitted in the future. Public interest groups made their opposition to that suggestion very clear. A national steering group coordinated by Nuclear Waste Watch, a Canada-based network of public interest organizations, released an alternative policy proposal that explicitly banned reprocessing. The Council of Canadians, a national advocacy group, sent out an action alert that generated 7,400 letters calling for the explicit prohibition of reprocessing.
The Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission, tasked with the job of licensing Moltex’s proposed reactor, declared that a policy framework for reprocessing is necessary and that such a policy must come from the federal government.[9] Moltex’s Chief Executive Officer, Rory O’Sullivan, observed that Canada was chosen by Moltex because the country had no explicit policy on reprocessing: “Moltex would likely not have come to Canada if a reprocessing policy had been mandated at the time.”
In November 2021, Canada’s Ministry of Natural Resources—the lead federal department on nuclear issues—issued an internal memo entitled “Policy Development on Reprocessing” that refers to a series of planned meetings on reprocessing with industry representatives starting December 1, 2021.[10] The CANDU Owners Group—a nonprofit corporation assembling utilities operating CANDU reactors, Canadian Nuclear Laboratories, and nuclear suppliers—was singled out by the ministry to prepare a policy paper on reprocessing.[11]
The CANDU Owners Group is far from neutral or independent.
First, Canadian Nuclear Laboratories is a private company owned by a consortium of multi-national companies: AtkinsRéalis (formerly SNC Lavalin), Fluor, and Jacobs. The company is currently constructing a government-funded facility with hot cells at Chalk River to conduct research, including on reprocessing and plutonium extraction. Canadian Nuclear Laboratories operates under a “government-owned contractor operated” agreement with Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, the same publicly owned corporation that pushed for commercial reprocessing in the late 1970s.
The CANDU Owners Group also has overseas members, including utilities from China, Pakistan, India, South Korea, Argentina, and Romania. The first three countries are nuclear weapons states that either possess reprocessing plants for military purposes (India and Pakistan) or reportedly divert plutonium extracted from commercial spent fuel for military purposes (China), while South Korea and Argentina have for decades flirted with the idea of reprocessing.
By all evidence, the government of Canada is currently enlisting private entities that favor reprocessing to assist in the development of an industry-friendly policy on reprocessing. And the government does this without involving the public, parliament, or outside experts—all of whom have expressed a keen interest—and repeatedly asked to participate—in plutonium policy discussions. In the process, misleading information about reprocessing is being forwarded to government officials with no other voices to correct the record.[12]
In the most recent move, a dozen US nonproliferation experts wrote again to Prime Minister Trudeau on September 22, 2023, after the release of documents obtained through an access to information request. In their letter, the experts reiterated their concerns that the Canadian government is funding a project that would lead to increase the availability—and therefore potential proliferation—of weapons-usable plutonium for civilian purposes in Canada and beyond.
Democratic deficit. Despite all these developments, there has been no public discussion or parliamentary deliberation about the implications of introducing civilian reprocessing into Canada’s nuclear fuel cycle. Absence of transparency and public debate means the democratic process is being ignored. Yet, the issue is of great public importance because of the taxpayer money invested, proliferation risks involved, and the long-term societal implications of the security measures needed to safeguard nuclear weapons usable materials.
This makes one wonder why it took a group of concerned citizens and an access to information request to find out that, behind closed doors, the nuclear industry has been drafting its own policy to permit commercial reprocessing, expecting its adoption by the government of Canada against all objective criteria of democracy.
n 1976, British nuclear physicist Brian Flowers authored a Royal Commission report to the UK parliament. He wrote: “We regard the future implications of a plutonium economy as so serious that we should not wish to become committed to this course unless it is clear that the issues have been fully appreciated and weighed; in view of their nature we believe this can be assured only in the light of wide public understanding.”
The same precept should apply to nuclear policy in today’s Canada.
Notes…………………………………………………………………. https://thebulletin.org/2024/03/nuclear-industry-wants-canada-to-lift-ban-on-reprocessing-plutonium-despite-proliferation-risks/
U.S. Congress about to fund revival of nuclear waste recycling to be led by private start-ups.
Jimmy Carter Killed This Technology 50 Years Ago. Congress Is About To
Fund Its Revival. The spending bill the House just passed contains $10
million for recycling nuclear waste. The nuclear waste sitting at power
plants across the United States contains enough energy to power the country
for more than 100 years.
But recycling spent uranium fuel was banned in
1977 because President Jimmy Carter feared that nuclear reprocessing could
lead to more production of atomic weapons. In the last 47 years, China,
France, Japan, Russia and the United Kingdom have all developed the tools
to recycle nuclear waste.
The U.S., by contrast, made a plan to bury that
spent fuel underground and even built a facility — but then abandoned the
strategy without any clear alternative. The short-term spending bill passed
this week in the U.S. House to avert a government shutdown contains the
first major funding for commercializing technology to recycle nuclear
waste. The legislation earmarks $10 million for a cost-sharing program to
help private nuclear startups pay for the expensive federal licensing
process ― and for the first time explicitly makes waste-recycling
companies eligible.
Huffington Post 8th March 2024
Russia and China announce plan to build shared nuclear reactor on the moon by 2035, ‘without humans’

Live Science, By Harry Baker, 8 Mar 24
The proposed nuclear reactor, which could be transported and assembled without human assistance, would provide energy to a lunar base that Russia and China have agreed to build together.
Russia’s space agency Roscosmos has announced plans to work with China to build an automated nuclear reactor on the moon by 2035. The proposed reactor will help power a proposed lunar base that the two countries will jointly operate.
Back in 2021, Roscosmos and the China National Space Administration (CNSA) revealed that they intended to build a shared base on the moon, named the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS), which they claimed at the time would be “open to all interested countries and international partners.”
However, NASA astronauts are unlikely to be allowed to visit this base due to historically frosty relations with CNSA and a more recent split with Roscosmos, which will leave the International Space Station by 2025 in response to sanctions from the U.S. over Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022.
On Tuesday (March 5), Roscosmos announced that it will eventually attempt to build a nuclear reactor alongside CNSA, which would theoretically be able to power the ILRS.
“Today we are seriously considering a project — somewhere at the turn of 2033-2035 — to deliver and install a power unit on the lunar surface together with our Chinese colleagues,” Roscosmos director general Yury Borisov told state-owned Russian news site TASS.
Borisov added that the challenging construction job would likely be carried out autonomously “without the presence of humans” and that the necessary technological solutions to pull it off are “almost ready.”
Roscosmos is also looking to use massive nuclear-powered rockets to transfer cargo to the moon to build this base, but the agency has not yet figured out how to build these spacecraft safely, Reuters reported……………………………………..
Roscosmos and CNSA, neither of which have put humans on the moon’s surface, have contrasting track records when it comes to recent lunar exploration.
Last year, Russia’s first moon mission in 47 years ended in disaster when the Luna-25 lander crashed into the lunar surface, leaving behind a 33-foot (10 meter) wide crater.
However, China has had a presence on the moon since 2013, when the Chang’e 3 mission put a lander and rover on the lunar surface. The subsequent Chang’e 4 and Chang’e 5 missions, which occurred in 2019 and 2020 respectively, also successfully landed spacecraft on the moon. The most recent mission also successfully returned lunar samples to Earth — a feat that CNSA will attempt to repeat later this year.
Last week, CNSA also announced that it will start launching giant reusable rockets over the next two years as part of the agency’s plan to put boots on the moon by 2030.
However, NASA is still on track to return humans to the lunar surface before then, despite the first crewed Artemis mission being delayed until 2026. https://www.livescience.com/space/space-exploration/russia-and-china-announce-plan-to-build-shared-nuclear-reactor-on-the-moon-by-2035-without-humans
Russia says it is considering putting a nuclear power plant on the moon with China
Reuters, March 6, 2024, https://www.reuters.com/technology/space/russia-china-are-considering-putting-nuclear-power-unit-moon-ria-2024-03-05/
MOSCOW, March 5 (Reuters) – Russia and China are considering putting a nuclear power plant on the moon from 2033-35, Yuri Borisov, the head of Russia’s space agency Roscosmos said on Tuesday, something he said could one day allow lunar settlements to be built.
Borisov, a former deputy defence minister, said that Russia and China had been jointly working on a lunar programme and that Moscow was able to contribute with its expertise on “nuclear space energy”.
“Today we are seriously considering a project – somewhere at the turn of 2033-2035 – to deliver and install a power unit on the lunar surface together with our Chinese colleagues,” Borisov said.
Solar panels would not be able to provide enough electricity to power future lunar settlements, he said, while nuclear power could.
“This is a very serious challenge…it should be done in automatic mode, without the presence of humans,” he said of the possible plan.
Borisov spoke also of Russian plans to build a nuclear-powered cargo spaceship. He said all the technical questions concerning the project had been solved apart from finding a solution on how to cool the nuclear reactor.
“We are indeed working on a space tugboat. This huge, cyclopean structure that would be able, thanks to a nuclear reactor and a high-power turbines…to transport large cargoes from one orbit to another, collect space debris and engage in many other applications,” Borisov said.
Russian officials have spoken before of ambitious plans to one day mine on the Moon, but the Russian space programme has suffered a series of setbacks in recent years.
Its first moon mission in 47 years failed last year after Russia’s Luna-25 spacecraft spun out of control and crashed.
Moscow has said it will launch further lunar missions and then explore the possibility of a joint Russian-China crewed mission and even a lunar base.
China outlines position on use of space resources

Space News Andrew Jones, March 6, 2024
HELSINKI — China holds a seemingly positive stance towards the use of space resources, according to a recent submission made by a Chinese delegation to the United Nations.
The delegation appears to state that China considers space resource utilization as permissible, but must be conducted in accordance with the Outer Space Treaty (OST) of 1967.
China’s submission treats the use of space resources as legal, but also calls for adherence to the existing frameworks of international space law, with the OST as the cornerstone.
The document was submitted to the Working Group on Legal Aspects of Space Resource Activities of the Legal Subcommittee of the Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS).
COPUOS is a body of the United Nations tasked with governing the exploration and use of space for the benefit of all humanity, overseeing matters related to space science and technology and their applications. The Working Group plays a critical role in addressing the legal challenges posed by the utilization of space resources, helping to shape the international legal framework that will govern these activities.
The submission could be seen as a beneficial development, helping to set the stage for a dialogue on the legal frameworks for governing the use of space resources.
“This engagement by China on the international discussion on space resources is a positive development,” Christopher Johnson, director of legal affairs and space law for the Secure World Foundation, told SpaceNews. “It tells us that China is taking international fora like COPUOS seriously, and seems to be engaging in good faith with the fora and with the process.
“Additionally, it’s welcome to have a clear statement of Chinese positions on these issues, and this informs other States in their approach and preparations to the international discussions going on at the UN.”
Johnson interprets the Chinese stance as seemingly largely aligned with the broader international consensus on the use of space resources. That is, the right to possess and use space resources is not only desirable by space agencies and national governments, but is also permissible under the current international law.
Discussion and consideration of the use and legality utilizing space resources has grown in recent years due to advancements in the space sector, the rise of commercial companies and renewed interest in the moon.
This has made international law and diplomacy related to the subject matters of key focus, with the distance between the respective stances of the U.S. and China likely to be pivotal. ……………….
There are a number of issues for the international community to settle going forward, some of which are noted in the Chinese submission. These include how space resources can be utilized in a sustainable fashion and in a way that fosters scientific investigations, while also ensuring peaceful relations in space between states and other actors in space.
Another key matter is the question of how states supervise their national activities, making sure private companies comply with the law. Additionally, all such activities will also need to preclude any national territorial annexation of the moon or other celestial bodies, as prohibited by Article II of the OST. ……………………………………………………………….. more https://spacenews.com/china-outlines-position-on-use-of-space-resources/
More fusion hot air, literally!

Megajoules and megaheadlines are all meganonsense
By Linda Pentz Gunter, https://beyondnuclearinternational.org/2024/03/04/more-fusion-hot-air-literally/ 4 Mar 24
Another week, more fusion news, cue another overblown headline, as the mainstream media once again paid homage to industry hype, digesting nuclear propaganda soundbites without even a hiccup.
On February 8, we learned that the Joint European Torus fusion project, also known as JET, had broken its own record in energy output during a last gasp attempt to make fusion work. The 40-year old project is now closed down for good.
The moment — and just a fleeting moment it truly was, lasting a mere 5.2 seconds — was duIy celebrated as another breakthrough for fusion.
“Nuclear fusion: new record brings dream of clean energy closer,” trumpeted the BBC who were especially smug since Torus is based in the UK.
“Nuclear Fusion World Record Smashed in Major Achievement”, said Science Alert.
“Scientists have made a record-setting fusion energy breakthrough,” blared the headline on Vice.
Below – A jolly video about JET in which the narrator’s voice perhaps generates more energy than the reactor itself.
What actually happened? JET generated 69 megajoules of energy in those 5.2 seconds, breaking its previous record of 59 megajoules over 5 seconds in 2021.
For those of us who don’t go about measuring things in megajoules, I deferred to our colleague, physicist, M.V. Ramana, for an explanation.
What are they really talking about here and is it actually a breakthrough?
“One can start with the annual average consumption of one US household,” Ramana said. “That’s about 10,500 kilowatt hours which is equivalent to 37,800 megajoules. Essentially using one hour = 3,600 seconds, and one joule = one watt-second.”
Head already spinning, I hoped he would do the rest of the math. He did.
“The 69 megajoules generated by JET”, Ramana explained, “is equivalent to roughly 0.06 percent of the electricity consumed by an average US household.”
So a minuscule contribution. But here’s the catch. “The JET machine produced 69 megajoules, but this is all heat,” explained Ramana. “Only about a third of that can be converted into electricity under ideal circumstances.”
Mostly heat, and hardly any electricity. So what the JET fusion so-called breakthrough actually delivered was all hot air. Literally!
Then came some more hot air. “First ‘private’ nuclear reactor to power 2 million British homes” ran another headline. The private sector nuclear company in question is Westinghouse. Yes, that Westinghouse! The one whose executives are in jail over a failed new nuclear power plant project in South Carolina. The Westinghouse that went bankrupt, forcing its mega-giant parent company, Toshiba, to shed not only Westinghouse but all Toshiba’s nuclear assets to avoid going down with the Westinghouse ship.
The same Westinghouse that is now $20 billion over budget at its other new nuclear project at Vogtle in Georgia.
But the British press were all “oh joy, oh rapture unforeseen” over this announcement, a project that has about as much credibility as the whimsical plot of HMS Pinafore.
And finally, we learned that Michigan governor, Gretchen Whitmer, is seeking another $150 million to restart the old and decrepit Palisades nuclear plant.
Palisades has been closed for almost two years and the company that would re-open and run it, Holtec, which specializes in decommissioning and radioactive waste management, has zero experience running a nuclear power plant.
This latest ask comes on top of $150 million already approved last year for a Palisades restart and could be augmented by a $1.5 billion loan from the federal government as well.
All of this nuclear nonsense comes on the heels of other hyperbole surrounding previous so-called advances in fusion (see our earlier coverage here and here), misrepresented almost universally as an imminent answer to our worsening climate crisis.
But, as the song goes in Pinafore, “Things are seldom what they seem.”
Linda Pentz Gunter is the international specialist at Beyond Nuclear and writes for and edits Beyond Nuclear International
Microsoft’s Kate Crawford: ‘AI is neither artificial nor intelligent’

who benefits and who is harmed by this AI system? And does it put power in the hands of the already powerful? What we see time and again, from facial recognition to tracking and surveillance in workplaces, is these systems are empowering already powerful institutions – corporations, militaries and police
The AI researcher on how natural resources and human labour drive machine learning and the regressive stereotypes that are baked into its algorithmsSun 6 Jun 2021 18.00 AESTShare
Kate Crawford studies the social and political implications of artificial intelligence. She is a research professor of communication and science and technology studies at the University of Southern California and a senior principal researcher at Microsoft Research. Her new book, Atlas of AI, looks at what it takes to make AI and what’s at stake as it reshapes our world.
……………………………………… What’s the aim of the book?
We are commonly presented with this vision of AI that is abstract and immaterial. I wanted to show how AI is made in a wider sense – its natural resource costs, its labour processes, and its classificatory logics. To observe that in action I went to locations including mines to see the extraction necessary from the Earth’s crust and an Amazon fulfilment centre to see the physical and psychological toll on workers of being under an algorithmic management system. My hope is that, by showing how AI systems work – by laying bare the structures of production and the material realities – we will have a more accurate account of the impacts, and it will invite more people into the conversation. These systems are being rolled out across a multitude of sectors without strong regulation, consent or democratic debate.
………………………..systems might seem automated but when we pull away the curtain we see large amounts of low paid labour, everything from crowd work categorising data to the never-ending toil of shuffling Amazon boxes. AI is neither artificial nor intelligent. It is made from natural resources and it is people who are performing the tasks to make the systems appear autonomous.
Problems of bias have been well documented in AI technology. Can more data solve that?
Bias is too narrow a term for the sorts of problems we’re talking about. Time and again, we see these systems producing errors – women offered less credit by credit-worthiness algorithms, black faces mislabelled – and the response has been: “We just need more data.” But I’ve tried to look at these deeper logics of classification and you start to see forms of discrimination, not just when systems are applied, but in how they are built and trained to see the world. Training datasets used for machine learning software that casually categorise people into just one of two genders; that label people according to their skin colour into one of five racial categories, and which attempt, based on how people look, to assign moral or ethical character. The idea that you can make these determinations based on appearance has a dark past and unfortunately the politics of classification has become baked into the substrates of AI.
……………………………Beginning in 2017, I did a project with artist Trevor Paglen to look at how people were being labelled. We found horrifying classificatory terms that were misogynist, racist, ableist, and judgmental in the extreme. Pictures of people were being matched to words like kleptomaniac, alcoholic, bad person, closet queen, call girl, slut, drug addict and far more I cannot say here. ImageNet has now removed many of the obviously problematic people categories – certainly an improvement – however, the problem persists because these training sets still circulate on torrent sites [where files are shared between peers].
And we could only study ImageNet because it is public. There are huge training datasets held by tech companies that are completely secret. They have pillaged images we have uploaded to photo-sharing services and social media platforms and turned them into private systems.
……………………………………………. What do you mean when you say we need to focus less on the ethics of AI and more on power?
Ethics are necessary, but not sufficient. More helpful are questions such as, who benefits and who is harmed by this AI system? And does it put power in the hands of the already powerful? What we see time and again, from facial recognition to tracking and surveillance in workplaces, is these systems are empowering already powerful institutions – corporations, militaries and police……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Atlas of AI by Kate Crawford is published by Yale University Press (£20). To support the Guardian order your copy at guardianbookshop.com. Delivery charges may apply https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2021/jun/06/microsofts-kate-crawford-ai-is-neither-artificial-nor-intelligent
AI’s craving for data is matched only by a runaway thirst for water and energy

John Naughton, https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2024/mar/02/ais-craving-for-data-is-matched-only-by-a-runaway-thirst-for-water-and-energy
The computing power for AI models requires immense – and increasing – amounts of natural resources. Legislation is required to prevent environmental crisis.
One of the most pernicious myths about digital technology is that it is somehow weightless or immaterial. Remember all that early talk about the “paperless” office and “frictionless” transactions? And of course, while our personal electronic devices do use some electricity, compared with the washing machine or the dishwasher, it’s trivial.
Belief in this comforting story, however, might not survive an encounter with Kate Crawford’s seminal book, Atlas of AI, or the striking Anatomy of an AI System graphic she composed with Vladan Joler. And it certainly wouldn’t survive a visit to a datacentre – one of those enormous metallic sheds housing tens or even hundreds of thousands of servers humming away, consuming massive amounts of electricity and needing lots of water for their cooling systems.

On the energy front, consider Ireland, a small country with an awful lot of datacentres. Its Central Statistics Office reports that in 2022 those sheds consumed more electricity (18%) than all the rural dwellings in the country, and as much as all Ireland’s urban dwellings. And as far as water consumption is concerned, a study by Imperial College London in 2021 estimated that one medium-sized datacentre used as much water as three average-sized hospitals. Which is a useful reminder that while these industrial sheds are the material embodiment of the metaphor of “cloud computing”, there is nothing misty or fleecy about them. And if you were ever tempted to see for yourself, forget it: it’d be easier to get into Fort Knox.
There are now between 9,000 and 11,000 of these datacentres in the world. Many of them are beginning to look a bit dated, because they’re old style server-farms with thousands or millions of cheap PCs storing all the data – photographs, documents, videos, audio recordings, etc – that a smartphone-enabled world generates in such casual abundance.
But that’s about to change, because the industrial feeding frenzy around AI (AKA machine learning) means that the materiality of the computing “cloud” is going to become harder to ignore. How come? Well, machine learning requires a different kind of computer processor – graphics processing units (GPUs) – which are considerably more complex (and expensive) than conventional processors. More importantly, they also run hotter, and need significantly more energy.
On the cooling front, Kate Crawford notes in an article published in Nature last week that a giant datacentre cluster serving OpenAI’s most advanced model, GPT-4, is based in the state of Iowa. “A lawsuit by local residents,” writes Crawford, “revealed that in July 2022, the month before OpenAI finished training the model, the cluster used about 6% of the district’s water. As Google and Microsoft prepared their Bard and Bing large language models, both had major spikes in water use – increases of 20% and 34%, respectively, in one year, according to the companies’ environmental reports.”
Within the tech industry, it has been widely known that AI faces an energy crisis, but it was only at the World Economic Forum in Davos in January that one of its leaders finally came clean about it. OpenAI’s boss Sam Altman warned that the next wave of generative AI systems will consume vastly more power than expected, and that energy systems will struggle to cope. “There’s no way to get there without a breakthrough,” he said.
What kind of “breakthrough”? Why, nuclear fusion, of course. In which, coincidentally, Mr Altman has a stake, having invested in Helion Energy way back in 2021. Smart lad, that Altman; never misses a trick.
As far as cooling is concerned, it looks as though runaway AI also faces a challenge. At any rate, a paper recently published on the arXiv preprint server by scientists at the University of California, Riverside, estimates that “operational water withdrawal” – water taken from surface or groundwater sources – of global AI “may reach [between] 4.2 [and] 6.6bn cubic meters in 2027, which is more than the total annual water withdrawal of … half of the United Kingdom”.
Given all that, you can see why the AI industry is, er, reluctant about coming clean on its probable energy and cooling requirements. After all, there’s a bubble on, and awkward facts can cause punctures. So it’s nice to be able to report that soon they may be obliged to open up. Over in the US, a group of senators and representatives have introduced a bill to require the federal government to assess AI’s current environmental footprint and develop a standardised system for reporting future impacts. And over in Europe, the EU’s AI Act is about to become law. Among other things, it requires “high-risk AI systems” (which include the powerful “foundation models” that power ChatGPT and similar AIs) to report their energy consumption, use of resources and other impacts throughout their lifespan.
It’d be nice if this induces some investors to think about doing proper due diligence before jumping on the AI bandwagon.
-
Archives
- January 2026 (246)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (376)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
- March 2025 (319)
- February 2025 (234)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS





