Families sickened by radiation exposure want Congress to revive this key compensation program.
7 Mar 2025
The Radiation Exposure Compensation Act or RECA, first enacted in 1990, created a compensation program to process claims from people exposed to radiation leftover from nuclear testing done by the U.S. government.
After the latest expansion of the bill expired in June 2024, communities across the country, including Missouri and the Navajo Nation say they are waiting for the legislation to not only be taken up again, but also to include communities like theirs that were never originally included. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0icfLF6AVEQ
Nuclear reactors killing Americans at accelerating rate

John LaForge Guest columnist, Feb 27, 2025 https://www.hometownsource.com/monticello_times/nuclear-reactors-killing-americans-at-accelerating-rate/article_7cb060d2-eef6-11ef-836b-8349ae8997a8.html
A new analysis of public health data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reveals alarming evidence that cancer deaths are rising in communities surrounding America’s oldest nuclear power plants.
Epidemiologist Joseph Mangano, executive director for the Radiation and Public Health Project in New York, has conducted a study showing a disturbing correlation between prolonged exposure to nuclear radiation and increased cancer mortality in affected counties.
According to Mangano’s research, which examines county-by-county cancer mortality data over three distinct time periods, radiation routinely released from nuclear reactors is directly impacting public health.
His findings indicate that cancer deaths in counties hosting 15 of the nation’s 16 oldest nuclear facilities have significantly increased over time, reinforcing longstanding concerns about the safety of prolonged nuclear plant operations.
“There is no safe dose of radiation,” Mangano states, citing the National Academy of Sciences’ BEIR VII report, which confirms that every exposure to ionizing radiation has the potential to trigger cancer.
As nuclear reactors age and continue to release radioactive gases such as helium, xenon and krypton into the atmosphere, residents in nearby communities are at increasing risk of developing cancer due to prolonged exposure.
The data further illustrates the impact of these radiation releases varies based on geographical factors, including wind patterns and local topography.
For example, in Wisconsin, excess cancer deaths were significantly lower near the Point Beach nuclear facility than in counties downwind of the Palisades and DC Cook plants on Lake Michigan’s eastern shore.
These findings suggest that radiation exposure is not uniform and that some communities bear a greater burden than others.
The implications of Mangano’s research are particularly concerning for residents of Wright and Sherburne counties in Minnesota, home to the Monticello Nuclear Generating Plant.
Since the plant began operating in 1971, the once-lower-than-average cancer mortality rate in these counties has risen sharply. Projections estimate that between 2031 and 2050, as many as 1,662 excess cancer deaths could occur if Monticello’s operating license is extended through 2051.
“These findings should serve as a wake-up call,” said Kelly Lundeen, a staff member at the Wisconsin-based environmental and nuclear watchdog Nukewatch. “We are urging local, state, and federal officials to take immediate action to phase out commercial nuclear power before more lives are lost.”
Despite growing concerns, the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) has already approved license extensions for several aging reactors, allowing some to operate for up to 80 years.
Given the demonstrated public health risks, advocates are calling for an immediate halt to these extensions and a transition toward safer, renewable energy sources.
The Coalition for a Nuclear-Free Mississippi River was planning to rally outside of the Minnesota Public Utilities Commission hearing earlier this month to maintain the current shutdown date of the Monticello reactor.
The Radiation and Public Health Project, the organization behind Mangano’s analysis, is pushing for greater transparency in radiation monitoring, stricter regulations on radioactive emissions, and a comprehensive plan to phase out aging nuclear plants.
John LaForge serves as the co-director of Nukewatch, a Wisconsin-based environmental and peace action watchdog group.
Doctors fear health fallout from nuclear energy plans

Canberra Times, By Marion Rae, February 12 2025
Doctors have warned of no “safe” level of radiation from a proposed network of nuclear reactors as battlelines are drawn for the federal election.
Similar to other nuclear-powered nations, Australians living within a certain radius of a reactor would need to be issued potassium iodide tablets for use in a radiation emergency, a nuclear briefing has learned.
“The only reason that everyone in that radius is given that is because they might need it,” Assistant Minister for Climate Change and Energy Josh Wilson told a nuclear briefing on Tuesday.
If anyone comes to buy your house, the proximity of a reactor will be noted on the land titles register, and insurers will not cover nuclear accidents, he said.
The warning came as doctors fronted parliament to warn of long-term health risks for workers and surrounding communities, particularly children.
Evidence included a meta-data analysis of occupational and environmental exposure that accumulated data on more than seven million people.
It found living within 30km of a reactor increased overall cancer risk by five per cent, with thyroid cancer increasing by 14 per cent and leukaemia by nine per cent.
A separate study of workers in the nuclear industry in France, the United Kingdom and the United States analysed results from more than 300,000 people who were monitored for over 30 years.
Finding not only increased cancer rates but surprisingly increased rates of heart attacks and strokes, it found impacts at low doses were larger than previously thought.
“There is no ‘safe’ lower dose of radiation. The science is clear. All exposure adds to long-term health risks,” vice-president of the Medical Association for Prevention of War Dr Margaret Beavis said……………………………
Under the coalition’s nuclear energy blueprint, seven reactors would be built across five states to replace ageing coal-fired power plants with more gas-fired plants to provide baseload power in the interim.
“Zero-emissions nuclear plants” are a key part of the Nationals’ election pitch to regions where coal plants are already closing, while Labor is pressing ahead with the transition to renewable energy backed up by big batteries.
Public Health Association of Australia spokesman Dr Peter Tait said the idea that the nuclear industry was free of greenhouse gas emissions was a “furphy”, given the construction and uranium supply chain involved.
Emissions would rise threefold under the nuclear plan due to increased coal and gas use, he warned, with the first plant not due to come online until the late 2030s.
From a public health perspective, Australians can’t afford that delay, Dr Tait said.
Executive director of Doctors for the Environment Dr Kate Wylie said prolonging the dependency on fossil fuels would mean more Australians would be affected by their known health risks, including increased rates of asthma.
Nuclear energy would also put communities at risk during the next drought, when reactors would be first in line for scarce water, Dr Wylie said.
“The ethical thing to do is to choose the least water-intensive energy sources, which are wind and solar,” she said. https://www.canberratimes.com.au/story/8890265/doctors-fear-health-fallout-from-nuclear-energy-plans/?fbclid=IwY2xjawIan3hleHRuA2FlbQIxMQABHaAJ7wF9BUi9CgA1_tQDXS5gC2WCrX8HSFZUrOQPGgXABnNkhEvlgHKolQ_aem_OShH2FPpE3tO3RIv_gAgBg
Two workers contaminated with radioactive material at Borssele nuclear plant
NL Times 8th Feb 2025, https://nltimes.nl/2025/02/08/two-workers-contaminated-radioactive-material-borssele-nuclear-plant
Two workers at the Borssele nuclear power plant were reportedly contaminated with radioactive material during maintenance work, plant operator EPZ confirmed. Both employees were wearing respiratory protection, preventing internal contamination.
The incident occurred on November 26, 2024, but was only disclosed last week. A small amount of radioactive material was released during the work, triggering an alarm in the facility. The area was immediately evacuated.
The two affected workers had radioactive particles on their skin. After decontamination showers, they were cleared to go home. A third worker, who was also in the room but was not wearing respiratory protection, left as soon as the alarm sounded and later tested negative for contamination.
All three workers underwent additional testing for internal exposure, but no contamination was found. The affected area was cleaned, and work resumed after safety checks.
40% of workers cite radiation concerns at Fukushima plant

By KEITARO FUKUCHI/ Asahi Shimbun, Staff Writer, February 2, 2025
Forty percent of the workforce at the crippled Fukushima No. 1 nuclear plant worry about radiation issues on the job, a nearly three-fold spike over the previous year, a survey found.
More than half of those respondents cited fears of their body coming into contact with a radioactive substance.
Tokyo Electric Power Co., the plant operator that conducted the annual survey, said recent incidents at the plant probably contributed to the heightened concerns.
For example, two workers were hospitalized in October 2023 after they were accidentally splashed with waste liquid containing highly radioactive substances while cleaning piping in a contaminated water treatment facility.
The survey was carried out between September and October to improve the working environment. TEPCO distributed a questionnaire to all workers at the plant and received responses from 5,498 individuals, or 94.5 percent……………………….
Asked to choose specific issues they were concerned about, 52.2 percent, the largest percentage, picked “physical contamination,” up about seven points from 2023.
In another incident, about 1.5 tons of contaminated water flowed out of a water purification facility at the plant through an air exhaust opening in February 2024…… more https://www.asahi.com/ajw/articles/15609878
Towns near Fukushima plant struggle to attract families with children
Japan Times 27th Jan 2025
The Great East Japan Earthquake on March 11, 2011, and the subsequent meltdowns at the Fukushima No. 1 nuclear power plant have left deep scars on Fukushima Prefecture, which has seen a significant decline in its estimated population.
Futaba County, home to the Fukushima plant that straddles the towns of Futaba and Okuma, has been hit particularly hard, with the prolonged evacuation of residents drastically reducing the number of children in the area. The region’s population decline due to the disaster is beyond the scope of natural or social population shifts.
Municipalities in the region are trying to come up with measures to bring back residents or attract new ones, but increasing the number of children remains a tall order.
Futaba County once enjoyed a high birth rate and strong ties among its residents thanks to stable job opportunities provided by the Fukushima No. 1 and No. 2 power plants and related industries.
Saki Yoshizaki, 36, a worker who lives in the city of Iwaki, gave birth to her eldest daughter, now 14, in her hometown of Okuma in 2010, a year before the nuclear disaster.
“With many relatives, friends and acquaintances around, the whole community helped raise children. I had almost no worries about becoming a parent,” Yoshizaki said, recalling her hometown fondly. “In a good way, it was a tight-knit community.”
However, such an environment changed suddenly following the nuclear incident as residents fled elsewhere. Today, young parents who are bearing and rearing children in the region are voicing their feelings of loneliness where community ties have been severed.
Minami Suzuki, 34, a co-representative of the volunteer group Cotohana in the Futaba town of Tomioka, worries about the future of the region. “If we don’t strengthen connections among parents, it might become increasingly difficult for the younger generations to choose to have children here,” she says……………………………………………………………………………………..
https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2025/01/27/japan/society/fukushima-children-decline/
Nukes kill kids.

Dr Tony Webb, 17 Jan 25.
One moment from my work in the USA in the early 1980s stands out in my memory. I’d driven from Chicago to Cleveland at the invitation of the Health and Safety Officer of the US Boilermakers Union to speak to the members meeting held on the night ahead of the recruitment of members for work on the annual ‘clean-up’ of the local Nuclear Power plant. The hired workers would be ‘radiation sponges’ – short-term casuals recruited for the ‘dirty jobs’ that would result in significant radiation exposures sometimes up to the permitted annual exposure limit and ‘let go’ if they reached that limit. The practice offered some protection to the company’s full -time employees whose skills would be needed on an ongoing basis and whose exposures needed to be kept below the limit. The meeting was well attended , rowdy, with a lot of questions and discussion which spilled over into the carpark after the meeting closed. I noticed one man hanging back from the circle and invited him to join and share his thoughts. As I recall them the essences was:
“I will be going in to apply for work tomorrow. I understand what you shared about the risks . . . no safe level of exposure and chance of getting cancer perhaps 20 years from now . . . It will put a roof over my family’s heads and food on the table . . . BUT my wife and i have had all the family we want. If we hadn’t, what you shared about the genetic risks, the damage to our children and future generations . . . no I wouldn’t be going . . . “
It is a sad fact that workers, both men and women will choose, often from necessity, to put their health at risk from the work environment. What is however consistent in my experience of working on radiation and other occupational health and safety issues is that they are far more concerned, cautious and likely to prioritise safety when it comes to risks to their children.
We now have solid evidence that workers in nuclear power plants routinely exposed to radiation face significantly increased cancer risks, risks of cardiovascular disease including heart attacks and strokes, dementia and potentially other health effects. There is also an increased risk of genetic damage that can be passed on to their children and future generations. But perhaps most significant of all there is now solid evidence of increased rates of leukaemia in children living close to nuclear power plants.
To put it simply and in language that will resonate with workers and their families in the communities around the seven nuclear power plant sites the federal Liberal-National Coalition proposes to build if elected to government; nuclear kills kids. It matters little whether or not these nuclear plants can be built on time, within budget, make a contribution to climate change, reduce electricity prices, or secure a long-term energy future; these nuclear power plants will kill kids who live close by. They cannot operate without routine releases of radioactive material into the environment and our young will be exposed and are particularly susceptible to any exposure that results.
Now add to that if you care that women are more susceptible than men, that workers in these plants face greater exposure and health risks than adults in the community, that nuclear plants have and will continue to have both major accidents and less major ‘incidents’ resulting in radiation releases, community exposures and consequent health damage. Add also that quite apart from the workers and others exposed when these plants need to be decommissioned, the radioactive wastes resulting from perhaps 30-50 years life will need to be safely stored and kept isolated from human contact for many thousands of years longer than our recorded human history. And, again if you care, also add in the concerns around proliferation of nuclear weapons which historically has occurred on the back of, enabled by and sometimes concealed by countries’ developing so called peaceful nuclear power.
All these arguments add weight to the absurdity of Australia starting and the world continuing down this nuclear power path. But if we want a single issue that strikes at the heart of human concerns it is this – and forgive me saying it again, it needs to be repeated many times until the electorate in Australia hears it loud and clear – Nuclear Kills Kids
How Fukushima’s radioactive fallout in Tokyo was concealed from the public
Because of the controversy surrounding Satoshi’s paper and the lack of research on the health impacts of these particles, it remains unclear to what extent Tokyo residents have been exposed to dangerous radiation levels as a result of the Fukushima accident.
Because CsMPs are so small, typically two microns or less in diameter, if humans breathe them, they could potentially reach the bottom of the lung, and be lodged into sacs known as alveoli, where the lung generally cannot expel them.
By unit of mass, CsMPs are much more radioactive than even spent reactor fuel
Japanese radiochemist Satoshi Utsunomiya found that air samples from March 15, 2011, in Tokyo contained a very high concentration of insoluble cesium microparticles. He immediately realized the implications of the findings for public safety, but his study was kept from publication for years.
Bulletin, By François Diaz-Maurin, January 13, 2025 [excellent illustrations]
On March 14 and 15, 2011—three days after the Great East Japan Earthquake and its resulting tsunami hit the Fukushima nuclear power plant—explosions at two of the plant’s reactor buildings released a huge amount of invisible radioactivity. These radioactive plumes were blown away by the wind, descending over the surrounding area and into the ocean. Eventually, the radiation emitted from the Fukushima plants spread over the entire Northern Hemisphere. It also spread to Japan’s capital, Tokyo.
Following the explosions, Japanese researchers rushed to collect and study radioactive materials from the soil and the air to find out what had happened inside the reactors, believed now to have melted down because their cooling systems failed. On March 13, the Tokyo Metropolitan Industrial Technology Research Institute, the agency responsible for measuring the air quality of particulate matter in the Tokyo area, started to collect air samples more frequently. This effort was part of the Tokyo metropolitan government’s emergency monitoring program for environmental radiation, which aimed to detect gamma-emitting nuclides in airborne dust. The filters revealed that at around 10 a.m. on March 15, 2011, a large plume of radioactivity reached Tokyo, some 240 kilometers (149 miles) south of Fukushima. All samples taken on March 14 and March 15 showed spikes in radioactivity.
The institute’s researchers published their first results in the journal of the Japan Radioisotope Association in June 2011 (Nagakawa et al. 2011); they estimated the total exposure dose to humans from radioactive substances, including iodine 131 and cesium 137 found in airborne dust, foodstuffs, and drinking water from the Setagaya ward in the old Tokyo City. Extrapolating from their measurements from March 13 to May 31, they calculated the corresponding annual cumulative dose of radiation in that part of Tokyo as being 425.1 microsieverts, which is less than half the annual dose limit to the public recommended by the International Commission on Radiological Protection. In a second conference publication in English (Nagakawa et al. 2012), the researchers extended their monitoring period to October and estimated that the total annual effective dose due to inhalation for adults in the Tokyo metropolitan area from the Fukushima radioactive plumes was far lower, at 25 microsieverts.
But two years after the accident, Japanese scientists discovered a new type of highly radioactive microparticle in the exclusion zone around the Fukushima plant. The microparticles, which had been ejected from the Fukushima reactors, contained extremely high concentrations of cesium 137—a radioactive element that can cause burns, acute radiation sickness, and even death. Satoshi Utsunomiya, an environmental radiochemist from Kyushu University in southwestern Japan, soon found that these particles were also present in air filter samples collected in Tokyo in the aftermath of the Fukushima accident.
The controversy surrounding his attempts to publish his findings nearly cost him his career and prevented his results from being widely known by the Japanese public ahead of the 2020 Summer Olympics in Tokyo.[1] Scientists still don’t know if these highly radioactive microparticles present significant danger to people, and Satoshi is one of the very few scientists who is focused on trying to find out. “We have the measurements now that tell that the particles did pass over population centers and were being deposited in places,” Gareth Law, a radiochemist from the University of Helsinki, told me. “We should answer the question.”
The discovery
In May 2012, Toshihiko Ohnuki, an accomplished environmental radiochemist then at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), visited Yoshiyasu Nagakawa at the Tokyo Metropolitan Industrial Technology Research Institute, also known as TIRI. Nagakawa was the first author of two TIRI studies on radiation exposure in Tokyo, and Ohnuki asked Nagakawa if he could obtain some air samples for further analysis. Ohnuki had already studied how radioactive cesium fallout from Fukushima reacted with components of contaminated soil. Now, he wanted to do the same with the airborne dust samples from Tokyo.
Nagakawa gave Ohnuki five small filters that had been collected from the Setagaya ward in old Tokyo City at different times on March 15, 2011—the day the radioactive plume reached Tokyo. Ohnuki received the samples without restriction on their use, and no written agreement was made.[2]
Back in his laboratory at JAEA, Ohnuki performed autoradiography of the five samples, revealing many radioactive spots on all of them. The bulk radioactivity on each sample was measured to be between 300 counts per minute for the filter that covered the midnight to 7 a.m. period and 10,500 counts per minute between 10 a.m. and 11 a.m. on March 15.[3] The radiation rate was so high that Ohnuki had to cut some of the filters into small pieces, less than one square centimeter, to keep from saturating the scanning electron microscope. Ohnuki stored the unexamined filters for future analysis.
Months later, in August 2013, four researchers from the Meteorological Research Institute in Japan reported for the first time about a new type of spherical radioactive cesium-bearing particle that had been ejected in the early days of the Fukushima accident (Adachi et al. 2013). The researchers had collected air samples on quartz fiber filters at their institute in Tsukuba, located 170 kilometers southwest of the Fukushima plant. Their findings, published in Scientific Reports, were about to revolutionize the way environmental radiochemists understood the radioactive fallout from Fukushima.
Back in the lab, the researchers placed the filters on an imaging plate and inserted them into a portable radiography scanner. The images revealed many black dots, which indicated the presence of radioactive materials on the filters, with a maximum radioactivity level measured on the sample at 9:10 a.m. on March 15, 2011, four days after the Fukushima accident began. The researchers placed this sample under a scanning electron microscope and then into an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer to directly observe the shape and composition of the radioactive materials on the filters. What they saw stunned them………………………………………………………………
Shocking results
The newly discovered entities were initially called spherical cesium-bearing particles, but Satoshi and his co-workers coined the term cesium-rich microparticles, or CsMPs, in 2017, which is now what researchers call them generally (Furuki et al. 2017). CsMPs had not been noted in earlier major reactor accidents.
Scientists knew the microparticles came from the Fukushima reactors because their isotopic ratio between cesium 134 and cesium 137 matched the average ratio for the three damaged reactors calculated by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory.[5] Because these particles emanated from the Fukushima reactors, Satoshi and the other scientists studying them thought that they may contain evidence about reactions that occurred during the accident. But the environmental radiochemist’s curiosity was also triggered by the unique features of these microparticles: Their size is very small, typically two to three microns, even smaller than one micron in some cases.[6] And the cesium concentration in each of the particles is very high relative to their size.
After Satoshi obtained four small pieces of the Tokyo air filters, he designed what he calls “a very simple procedure” to find out whether the filters contained cesium-rich microparticles. In April 2015, he took autoradiograph images of the four pieces, confirming what Ohnuki had already seen with a digital microscope at JAEA. Then Satoshi moved to characterize the structural and chemical properties of the particles using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Although the procedure’s design was simple, executing these steps would prove to be extremely difficult.
In July 2015, as Satoshi was busy working on the Tokyo air filters in his lab at Kyushu University, Ohnuki received a note from Nagakawa, the TIRI researcher who had provided the samples, asking him to return them so they could be reanalyzed. In his e-mail, Nagakawa did not specify the motive for his request, which appeared innocuous: “Please return at least some of the materials we gave you for reanalysis … if the location is unknown, it can’t be helped.”
Ohnuki immediately sent Nagakawa two filters from March 15, including the filter from 10 a.m. to 11 a.m. that had the highest level of radioactivity and contained the largest number of radioactive spots. Ohnuki added that he had discarded the other three filters after he analyzed them in 2013.
Nagakawa also asked Ohnuki whether he was planning to publish papers based on the samples. Ohnuki explained that he stopped analyzing them after his inconclusive attempts in 2013, but did not mention he had given Satoshi part of the filters for study.[9]
Satoshi was now ready to publish his results in a scientific journal. These were important findings that the scientific community needed to know. But Satoshi also understood that they could create a public relations crisis in Japan because his findings contradicted previous statements that played down the implications for public health of Fukushima fallout in Tokyo.
The Goldschmidt Conference—the foremost such international meeting on geochemistry—that year was held in the Japanese city of Yokohama. Satoshi was invited to give a plenary talk and present his research on environmental contamination from the Fukushima disaster (Utsunomiya 2016). During the talk, he presented his new findings on the Tokyo air filters. His talk received a lot of attention and was even reported by several Japanese and international newspapers. After his presentation, the scientific chair of the conference, Hisayoshi Yurimoto, said: “Very interesting results. And also very shocking results.”[1
In April and June 2016, Satoshi conducted dissolution experiments and quickly confirmed that the CsMPs were insoluble in water. The experiments also showed that most of the cesium activity on these filters came from CsMPs. In fact, up to 90 percent of the cesium radioactivity came from these microparticles, not from soluble forms of cesium—meaning that most of the cesium radioactivity detected during the March 15 plume in Tokyo was from CsMPs.
Between 2016 and 2019, a Kafkaesque sequence of events circled about Ohnuki, the former JAEA researcher who gave Satoshi the Tokyo air filter samples, and Satoshi. During that sequence of events, Satoshi’s research paper was accepted for publication by a prestigious scientific journal after peer review—but the journal delayed publication of the paper for years, eventually deciding not to publish it based on mysterious accusations of misconduct that, it turned out, were unwarranted. As a result, Satoshi’s findings were not made widely known, saving the Japanese authorities a possible public relations crisis as the summer Olympics in Tokyo neared. Because of the controversy surrounding Satoshi’s paper and the lack of research on the health impacts of these particles, it remains unclear to what extent Tokyo residents have been exposed to dangerous radiation levels as a result of the Fukushima accident.
I worked to reconstruct the sequence of events related to Satoshi’s research paper to find out whether the controversy over its publication was the result of some unethical practice on his part; competition between research laboratories; or attempted suppression of scientific results. The account that follows is based on the review of dozens of e-mails, letters, reports, and transcripts of phone conversations the Bulletin has obtained, as well as on multiple interviews with people directly involved in the events.
In August 2016, the leader of Nagakawa’s research group at TIRI, Noboru Sakurai, sent an e-mail to Ohnuki urging him to return filter samples he had earlier obtained from TIRI to the Tokyo Institute of Technology, where Ohnuki was now employed. Ohnuki responded that the filters had already been sent, but Sakurai maintained they had not received them. Ohnuki had asked a staff member of the research group he used to work in at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency to send the samples he had left there, but the samples were not sent. Because the samples were studied in a controlled area, theymay have been disposed of together with other Fukushima-related samples that had been stored at JAEA.
In October, as Ohnuki dealt with insistent requests that he return the filter samples, Satoshi submitted two research manuscripts to the journal Scientific Reports, one on the first successful isotopic analysis of individual cesium-rich microparticles based on soil samples collected from the exclusion zone at Fukushima, and one on the first characterization of the CsMPs from the Tokyo air filter samples that he had presented during his talk in Yokohama. Both articles were accepted in early January 2017 after peer review.[11]
The Tokyo paper, titled “Caesium fallout in Tokyo on 15th March, 2011 is dominated by highly radioactive, caesium-rich microparticles,” was co-authored by three graduate students from Satoshi’s lab—Jumpei Imoto, Genki Furuki, and Asumi Ochiai, who conducted the experiments—and three Japanese collaborators: Shinya Yamasaki from the University of Tsukuba who contributed to the measurement of samples; Kenji Nanba of Fukushima University, who contributed to the collection of samples; and Toshihiko Ohnuki, who had obtained the samples. The paper included two international collaborators who were world experts in the study of radioactive materials, Bernd Grambow of the French National Center for Scientific Research at the University of Nantes in France and Rodney C. Ewing of Stanford University, who contributed to the research ideas and participated in the analysis of the data. Satoshi was the lead author of the study.
……………………………………………..On the day of the visit, Moriguchi sent an e-mail to Ohnuki, pressing him to inform TIRI about the planned publication. “This type of information makes government agencies very sensitive,” Moriguchi wrote. “If the results obtained from these valuable sample collections conducted at a research institute under the administration were to incur the displeasure of government agencies and it becomes difficult to obtain cooperation from research institutions, we are concerned that this could hinder future research using these types of samples.”
…………………………………………………..Almost immediately, Sakurai moved to block the publication, according to e-mails obtained by the Bulletin.
………………………………………………………………………………………In July 2017, TIRI increased the pressure by sending a formal complaint to the Tokyo Institute of Technology, where Ohnuki was now employed. In a letter that the researchers were not able to see until a year after it was sent, TIRI accused Ohnuki of “suspected acts violating internal regulations, researcher’s ethics and code of conduct” in providing Satoshi with samples from TIRI without the institute’s consent.
As the issue became more political and involved more institutions, Satoshi continued his research on CsMPs and presented two other papers about Fukushima at the next Goldschmidt Conference in Paris in August 2017. Later that month, under pressure from the Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Industrial Technology, the Tokyo Institute of Technology opened a formal investigation of Ohnuki on suspicion of improper research activities with Satoshi. “It was like a court,” Satoshi said of being called before the compliance committee. Except that, unlike in a trial, he did not know the exact terms of what they were accused of. “The team at TIRI didn’t even allow Kyushu University to show me this letter,” Satoshi said. “So at that point, I didn’t understand what the problem was.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. Cleared but still harassed
During the investigation, Satoshi almost gave up on publishing the paper based on examination of the filters in Tokyo. He told the committee members that he would probably withdraw the paper, then “in press,” from Scientific Reports. Both the committee members and TIRI were pleased. “But then I talked to Rod [Ewing], and we did something clever,” Satoshi explained. They would not withdraw the paper; instead, they would keep it “in press” until the investigation was over.
…………………………………………………………………………….Tokyo Tech initiated a pressure campaign against Ohnuki and Satoshi to get the samples back…………………………………..
Satoshi did not want to give the samples away. “These are the only evidence to prove our article,” he said.
………………………………………………………“I sent all the samples to Stanford,” Satoshi said. Satoshi sent the air filter samples through regular postal services “in a UPS package.”[15] On September 13, Kyushu University’s executive vice president, Koji Inoue, called Satoshi to his office and yelled at him, urging him to give back the samples. Satoshi told Inoue that it was too late; he had already sent the samples to Stanford “for further investigation.”
Now the samples were secured, but Satoshi still needed his paper to be published.
……………………………………………………………………….. Thompson’s article in Scientific American was published on March 11, 2019, mentioning the fact that the paper had been rejected (Thompson 2019).
In June 2019, Satoshi and his co-authors posted their paper on arXiv (Utsunomiya et al. 2019), thereby making the findings public—two-and-a-half years after its acceptance by Scientific Reports. Ohnuki’s name does not appear in the list of co-authors on the arXiv paper, and Satoshi did not acknowledge TIRI for providing the samples.
……………………………………………………………………………………. After the paper was made public, the researchers received some attention, but not the visibility commensurate with the implications that the study had for public health in Japan.[16] The three institutions—TIRI, Tokyo Tech, and Kyushu University—were all “very happy,” Satoshi said. “People may think that we lost, but for me, we actually protected science.“
New risks
In the early days after the Fukushima accident, radiochemists thought that the situation was very different from Chernobyl. The three reactor-core damage events at Fukushima were considered to be of low energy, meaning that no actual explosion of the reactors had occurred, as was the case for Chernobyl. This led radiochemists to assume that radioactive particles probably had not come out of the reactors or, at least, not in large volume. A lot of the early post-accident research, therefore, focused on the traditional environmental radiochemist approach of collecting soils and sediments, doing bulk analysis, and learning from that.
It was only after scientists discovered the existence of cesium-rich microparticles that researchers, including Satoshi, realized that particles had actually been ejected from the reactors.
…………………………………………………………………………Because they were unknown until recently, CsMPs pose new risks that are still underappreciated by the research community and public authorities.
Once formed, radioactive cesium 137 has a half-life of about 30 years, after which half of the nuclides will have decayed into stable barium 137, whereas the other half will remain radioactive. CsMPs tend to accumulate, forming hotspots that contain many of the particles.[17] Hotspots of the microparticles have been found inside and outside abandoned buildings in the Fukushima exclusion zone and in other places (Fueda et al. 2023; Ikenoue et al. 2021; Utsunomiya 2024a). “They’re actually there in great numbers in many places, and then that’s when the health questions start to come in,” Law said. Despite their great numbers and potential risks, hotspots of CsMPs have not been systematically mapped around Fukushima. “When we visited the exclusion zone, we could still see some hot spot occurrences on the roadside without any protection,” Satoshi said. “We shouldn’t be able to access freely that kind of hot spots.”
Because CsMPs are so small, typically two microns or less in diameter, if humans breathe them, they could potentially reach the bottom of the lung, and be lodged into sacs known as alveoli, where the lung generally cannot expel them.[18] Scientists don’t know what would happen then. For instance, a typical immune system response would consist of some kind of clearance mechanism that seeks out foreign bodies and tries to either envelop or dissolve them. But it is still unknown how exactly CsMPs would dissolve in lung fluids.
Most knowledge about breathing and radioactive particulates is based on the assumption that particles dissolve, and researchers have calculated the rates for their dissolution in the human body. But because CsMPs don’t dissolve easily, once inhaled, they will likely stay longer in the human body. Researchers believe that, because CsMPs are so slow to dissolve, they may stay much longer—certainly for several months, maybe longer—in the body, compared to hours or days for suspended cesium.[19]
By unit of mass, CsMPs are much more radioactive than even spent reactor fuel. Some researchers from the Japan Atomic Energy Agency have shown that cultured cells exposed to the radiation from suspended CsMPs display a stronger local impact compared to what is known from previous radiological simulation studies using soluble radionuclides (Matsuya et al. 2022). Scientists are only now seeing some emerging evidence that the point-source nature of the radioactivity from CsMPs could lead to damage to cell systems. This is qualitatively different from the conventional estimate of internal radiation dose at the organ level based on uniform exposure to soluble cesium.
Despite the new risks that CsMPs might pose, the study of their impacts has received little interest.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….Satoshi continues to study CsMPs actively and regularly presents his results to the Goldschmidt Conference and publishes his results in scientific journals. He and his collaborators work relentlessly to understand better the fate of CsMPs in the environment and their impacts on human health. In 2024, Satoshi received the Geochemical Society’s Clair C. Patterson Award in recognition of his innovative contributions to the understanding of CsMPs.[21]……………… more https://thebulletin.org/premium/2025-01/how-fukushimas-radioactive-fallout-in-tokyo-was-concealed-from-the-public/?utm_source=SocialShare&utm_medium=Facebook&utm_campaign=Facebook&utm_term&fbclid=IwY2xjawHyUndleHRuA2FlbQIxMQABHb1H3gK2UVzfBC5I7-s75EVtx4t5Q9uUi2MspvTqpluEOqbarYJJnhIwUA_aem_ok6x3HQOxccGg2I-7KnZjA
Radioactive nightmare: A community’s fight for survival amid soaring cancer rates

by Jay Salley, News EditorJanuary 8, 2025, https://sciotovalleyguardian.com/2025/01/08/radioactive-nightmare-a-communitys-fight-for-survival-amid-soaring-cancer-rates/
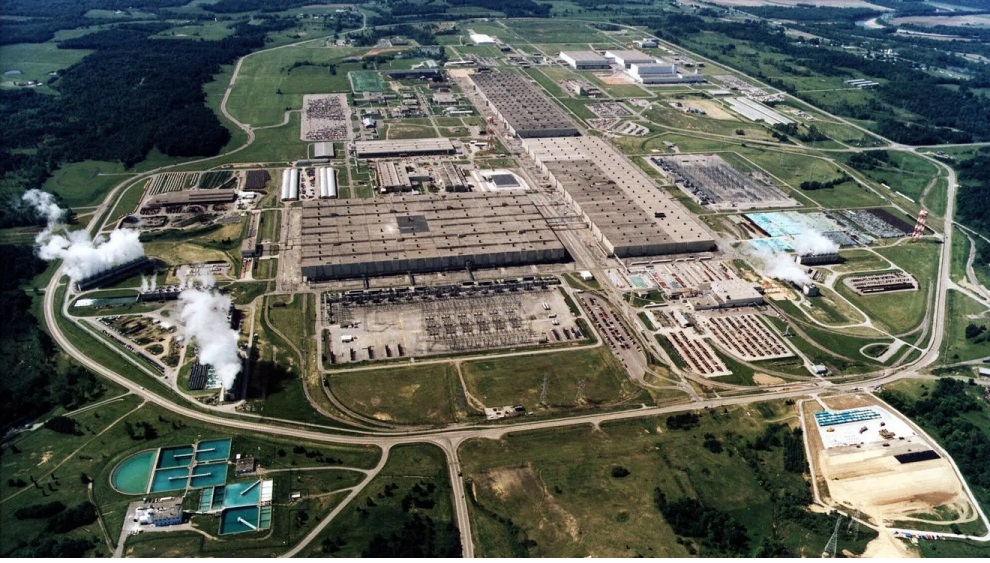
PIKETON, Ohio — Pike County, Ohio, is facing a severe health crisis that’s attracted national attention. The region has some of the highest cancer and premature death rates in the U.S. This alarming trend is linked to decades of uranium enrichment and ongoing demolition at the Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant.
A study by Joseph J. Mangano, an epidemiologist with the Radiation and Public Health Project, sheds light on the impact of radioactive contamination on Pike County. Released last summer, the study shows significant increases in cancer, infant mortality, and premature deaths in areas downwind of the plant.
From 2021 to 2023, Pike County’s premature death rate for those under 74 years old was 107% higher than the national average, up from 85% between 2017 and 2020. Over 750 premature deaths occurred in this period in a county with a population of just over 27,000.
Cancer rates in Pike and six neighboring counties—Adams, Gallia, Jackson, Lawrence, Scioto, and Vinton—were 17.5% above the national average from 2015 to 2019. Infant mortality rates in the region were 31.9% higher than the U.S. average from 1999 to 2020, and middle-aged adults saw mortality rates more than double the national average.
In 2019, concerns about radioactive contamination peaked when Zahn’s Corner Middle School in Piketon was permanently closed after radioactive isotopes, including enriched uranium and neptunium-237, were found inside. The school district later sold the building to a Christian ministry, which plans to reopen it as a STEM academy, raising safety concerns.
The Portsmouth plant, operational from 1954 to 2001, enriched uranium for nuclear weapons and reactors, releasing radioactive particles into the environment. Despite ceasing uranium enrichment in 2001, the plant remains active with demolition and decommissioning projects, raising concerns about further contamination.
The Guardian spoke with local activist Gina Doyle. Gina heads the group, Don’t Dump On Us. When asked about the study, Doyle said that in both of Dr. Mangano’s reports, the rate of cancer deaths and other related illnesses has a direct link to the Portsmouth plant. “The contamination is growing, too. It is in everything and everywhere in the surrounding communities. Past instances at the Portsmouth plant show not only human error but deaths of workers. DDOU has a compiled list of cancer victims from the community that grows every single day. I add to that list names of cancer victims; the stories are heartbreaking and infuriating.
The push for nuclear in our country is growing and that will most definitely cause more sickness and deaths. Transparency has been called for by activists and we still don’t know the whole truth because all of the information is kept hush-hush by the DOE. We do know that other agencies like the OEPA, DOH, and NRC who are supposed to be working to protect our communities have also turned their backs. Questions are never answered; we are kept in the dark by our government. Why? In my opinion, because of money and power. It is time to put people first and stop the lies and covering up the truth. The truth is they are killing innocent people and children. Remediation without any chance of bringing it back to background is not possible. We are forever contaminated. Forever the community will be affected.”
Families in Pike County and neighboring areas have experienced high rates of rare cancers and aggressive diseases, believed to be linked to exposure to radioactive materials from the plant. The closure of Zahn’s Corner Middle School and the deaths of students and staff have become a grim symbol of the crisis.
Emily Stone, another resident, told the Guardian “that when you have world-renowned, out-of-state epidemiologists and scientists who are all saying there is a major problem in Piketon, then that should be taken with the utmost priority and urgency. It is not normal for so many people in one area to be sick and die from some of the rarest cancers and illnesses to exist. For the cause of all of those sicknesses to have a direct link to radioactive materials is truly unreal. When will someone care that an entire community, and its surrounding counties, are all being harmed by this one place and do something to stop it? How many more kids and adults have to die before enough is enough?”
Despite the health risks, the Department of Energy (DOE) has proposed new projects at the Portsmouth site, causing further concern among residents. Advocates are calling for independent investigations and comprehensive public health monitoring for affected communities to prevent further harm.
The fight for accountability and action to address the region’s toxic legacy continues for Pike County residents.
Independent testing of radiation levels in air- Woolsey Fire and Santa Susana Field Lab Site.

 WOOLSEY FIRE: ARE YOU BREATHING TOXIC AND RADIOACTIVE AIR? http://lancasterweeklyreview.com/woolsey-fire-radiation-toxic-testing by fdr | Nov 14, 2018 Preliminary Independent Radiation Test Results from US Nuclear Corporation from The Woolsey Fire and Santa Susana Field Lab Site
WOOLSEY FIRE: ARE YOU BREATHING TOXIC AND RADIOACTIVE AIR? http://lancasterweeklyreview.com/woolsey-fire-radiation-toxic-testing by fdr | Nov 14, 2018 Preliminary Independent Radiation Test Results from US Nuclear Corporation from The Woolsey Fire and Santa Susana Field Lab Site
After various complaints and talking with numerous concerned parents The Lancaster Weekly Review has ordered a commission in a preliminary study in order to finally answer some of the community’s concerns regarding potential toxic materials released from the Woolsey Fire as well as radiation from the Santa Susana Field Laboratory. The Field Lab was the site of a nuclear meltdown in 1959 with many locals and doctors condemning subpar cleanup efforts that point to high cancer rates which are 60% higher for those people living within a 2 mile radius of the SSFL. A lingering effect of the various toxins within the Field Labs vicinity.
It appears that the recent Woolsey Fire which has devastated swathes of Ventura and northwestern Los Angeles Counties, originated at the Santa Susa Field Lab and Testing Site with varied reports to the damage to the facility as well as the contamination area of the nuclear meltdown. The Southern California Edison Chatsworth Substation which is on the SSFL site shut down 2 minutes prior to start of the Woolsey Fire.
An independent study of air testing was conducted by US Nuclear Corporation of Canoga Park on Tuesday, November 13, five days after the Woolsey fire began. The owner, Mr. Bob Goldstein, was more than happy to help with the study and dispatched David Alban and Detwan Robinson to the Santa Susana Field Laboratory on Tuesday, November 13th at 3PM. They took two types of measurements for radiation with the US Nuclear Fast-Cam Air Monitor and another with a filter air tape. Twenty minute samples were taken at high flow rate of 40cfm at the Lab Entrance, which is up wind from the Lab. Another 20 minute sample was taken on the down wind side, which is North of the Lab. Given the proximity of the company’s headquarters to the Woolsey Fire US Nuclear Corporation’s team also took indoor samples at their office in Canoga Park.
It appears that many of the preliminary tests are picking up increased levels of Radon. Mr. Goldstein of US Nuclear Corporation commented, “Ordinary background radiation from minerals in the soil (and also from the solar wind and from cosmic rays) gives a dose rate of 0.015mR/hr (milliRem per hour) in the San Fernando Valley. But at the Santa Susana Field Laboratory background levels were found to be elevated to 0.040mR/hr. which is 0.025mR/hr higher than expected.”
Mr. Goldstein also stated, “The radioactivity collected on the filters decayed down to undetectable levels within 3 hours, leading us to conclude that this radioactive material is from Radon gas which decays after a short half life.” Overall, the tests that were conducted found that the area’s Radon levels are about 3 times higher than the surrounding San Fernando Valley.
Additional independent testing of other contaminants and toxins will take place in the coming days and will be published as soon as testing has taken place.
Ohio Community Faces Cancer Crisis from Radioactive Contamination
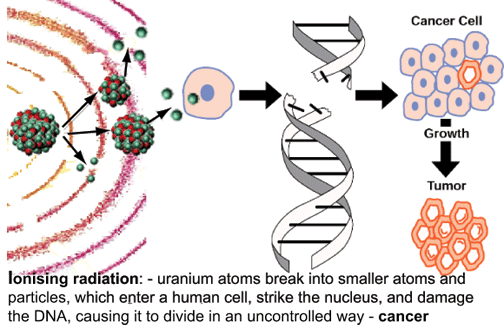
PIKETON, OH – A growing health crisis in Pike County, Ohio, has brought national attention to a region plagued by some of the highest cancer rates and premature death rates in the country. Decades of uranium enrichment and ongoing demolition at the Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant are now being linked to the troubling health trends impacting this community and six surrounding counties.
A recent study by Joseph J. Mangano, epidemiologist and executive director of the Radiation and Public Health Project, paints a stark picture of the consequences of radioactive contamination in Pike County. Released last summer, the study highlights significant increases in cancer, infant mortality, and premature death rates in communities located downwind of the former uranium enrichment plant.
Cancer Rates and Premature Deaths
The numbers are alarming. Between 2021 and 2023, Pike County’s premature death rate for individuals under 74 years old was 107% higher than the national average, a sharp rise from 85% above the national average between 2017 and 2020. Over 750 premature deaths occurred during this period in a county with a population of just over 27,000.
Cancer rates in Pike County and six neighboring counties—Adams, Gallia, Jackson, Lawrence, Scioto, and Vinton—were 17.5% above the national average between 2015 and 2019. Infant mortality rates in the region were also 31.9% higher than the U.S. average between 1999 and 2020, and middle-aged adults saw mortality rates more than double the national average.
A School at the Center of Controversy
In 2019, concerns about radioactive contamination reached a tipping point when Zahn’s Corner Middle School in Piketon was permanently closed after radioactive isotopes, including enriched uranium and neptunium-237, were discovered inside the building. The school, located just a few miles from the Portsmouth plant, became a symbol of the community’s struggle with the health impacts of the site. Over the years, several students and staff members at Zahn’s succumbed to rare cancers, further heightening concerns.
Recently, the school district sold the building to a Christian ministry, which plans to reopen it as a STEM academy. While the sale marks a new chapter for the facility, it has reignited fears about whether the site is truly safe, given the radioactive materials previously found within its walls.
Radioactive Contamination and Ongoing Demolition
The Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant, operational from 1954 to 2001, enriched uranium for nuclear weapons and reactors, releasing radioactive particles such as Americium-241, Plutonium-238, and Uranium-235 into the environment. These isotopes, which remain hazardous for thousands of years, have contaminated the air, water, and soil in the surrounding area.
Although uranium enrichment operations ceased in 2001, the plant remains active with demolition and decommissioning projects. Experts have raised concerns that open-air demolition of contaminated buildings is releasing additional radioactive particles into the environment. Critics argue that the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) air monitoring, which detects only “background” levels of radiation, fails to capture the full extent of the contamination.
Community Devastation
The impact on the community has been profound. Families across Pike County and neighboring areas have experienced unusually high rates of rare cancers and aggressive diseases, particularly among children and young adults. Many residents believe these illnesses are tied to decades of exposure to radioactive materials released by the plant.
The closure of Zahn’s Corner Middle School and the deaths of students and staff members have become a grim reminder of the broader crisis affecting the region. Parents and advocates continue to demand answers about the plant’s role in the contamination and the steps being taken to ensure the safety of current and future generations.
A Call for Accountability
Despite mounting evidence of health risks, the DOE has proposed new projects at the Portsmouth site, including uranium purification and experimental reactors. These plans have fueled further concerns among residents, who argue that additional activities could exacerbate the environmental and health challenges they already face.
Advocates and researchers are calling for independent investigations into the health impacts of the Portsmouth plant and comprehensive public health monitoring for affected communities. Many argue that stricter oversight is urgently needed to prevent further harm.
A Community Demanding Justice
The study by Mangano highlights the devastating and long-lasting effects of radioactive contamination in Pike County. The ongoing health crisis, coupled with incidents like the closure of Zahn’s Corner Middle School, underscores the urgent need for accountability and meaningful action to address the region’s toxic legacy. For residents of Pike County and surrounding areas, the fight for answers—and justice—continues.
Cellphone radiation warning as researchers reveal new risk factor
by Matthew Phelan Senior Science Reporter For Dailymail.Com, 4 Jan 25 https://www.msn.com/en-au/health/other/cellphone-radiation-warning-as-researchers-reveal-new-risk-factor/ar-AA1wVrvG [good diagrams and pictures]
Anyone uploading videos of their scenic hike in a rural area with 5G is exposed to nearly twice the radiation of someone in a city, according to a new study.
Researchers believe the extra radiation stems not from 5G cell towers, but from users’ own mobile devices which work overtime to get out a signal in rural areas.
A team at the Swiss Tropical And Public Health Institute (Swiss TPH), tracked 5G cell phone users’ exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMF) across two cities and three rural communities
RF-EMF are the means by which radio waves transfer energy, allowing wireless devices to communicate across frequencies that include microwave radiation — which under the wrong circumstances can deliver a dangerous amount of energy.
The team found that the average exposure in the rural areas was 29 milliwatts-per-square-meter (mW/sq-m) when uploading, nearly three-times the safety risk threshold recommended by the World Health Organization, 10 mW/sq-m.
That was also much higher than the amount recorded for phones uploading content in the two Swiss cities, for which the team found an average reading of 16 mW/sq-m.
The measurement represents how much radiofrequency energy is passing through a given surface area (like human skin) in the path of these wireless signals.
In summary, this study shows that environmental exposure is lower when base station density is low,’ said the study’s lead author, epidemiology researcher Adriana Fernandes Veludo.
‘However,’ she added, ‘in such a situation, the emission from mobile phones is by orders of magnitude higher.’
‘This has the paradoxical consequence that a typical mobile phone user is more exposed to RF-EMF in areas with low base station density,’ according to Fernandes Veludo, a PhD student collaborating with the 5G investigation Project GOLIAT.
But Fernandes Veludo also noted that the new findings ‘might underestimate the real exposure’ coming from these 5G cell phones, when operated in rural areas.
While European nations deem such levels as 29 mW/sq-m high, they are well below America’s own more lax threshold limits.
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has set the maximum permitted exposure level to 10,000 mW/sq-m.
The rollout of 5G has sparked conspiracy theories that the new form of wireless technology somehow causes Covid-19 or might be even a secret and high-tech new form of mind control.
While the new research out of Switzerland does not weigh-in on the health risks, it does provide new detailed information on what people are being exposed to out in real world scenarios.
The possible underestimate stems from how Fernandes Veludo and her colleagues collected their 5G cell phone radiation data in the first place.
The team measured exposures in each of their five test municipalities by traveling to specific locations wearing a backpack with a portable device that measured RF-EMF exposure plus a smartphone equipped with sensors and radiation-tracking software.
‘We have to keep in mind that, in our study, the phone was about 30 cm [11.8 inches] away from the measuring device,’ Fernandes Veludo noted.
‘A mobile phone user will hold the phone closer to the body and thus the exposure to RF-EMF could be up to 10 times higher,’ she said.
The Project GOLIAT team tracked the RF-EMF output from cell phone tower base stations and mobile phone devices in two cities, Zurich and Basel, against three rural towns, Hergiswil, Willisau and Dagmersellen.
In all five areas, they conducted comparison experiments in ‘microenvironments’ where different factors and human behaviors come into play, including: residential neighborhoods, industrial areas, schools, public parks or riding public transit.
But the researchers also ran all of these same experiments while the devices were interacting with the local 5G towers in two other common scenarios.
In the first scenario, the backpacking researchers collected data while the cell phone was in ‘flight mode’ or ‘airplane mode’ — meaning that their sensors were mostly only exposed to ambient signal coming from the 5G cell towers.
In the other scenario, ‘maximum data download was triggered,’ as opposed to maximum upload, by setting the phone to download large files off the web.
The results from both of these other tests, as published online in the journal Environmental Research in December, were slightly less surprising with the urban areas showing higher exposure to RF-EMF radiation.
The average for their rural test villages came to 0.17 mW/sq-m, while the average for Basel was 0.33 mW/sq-m and for Zurich 0.48 mW/sq-m.
‘The highest levels were found in urban business areas and public transport,’ according to co-author Dr Martin Röösli, a professor of environmental epidemiology at Swiss TPH who specializes in atmospheric physics.
Dr Röösli emphasized that all of these values were ‘still more than a hundred times below the international guideline values.’
In the maximum download scenario, the radiation increased almost uniformly to about 6–7 mW/sq-m, which the Project GOLIAT team noted likely comes from a technique deployed by 5G towers called ‘beamforming.’
As its name implies, ‘beamforming’ redirects and focuses signals from the tower directly at the phone that it is delivering download information to, which leads to more RF-EMF exposure in the process.
The effect was slightly higher in the two cities.
Fernandes Veludo noted this was only the first study of its kind. Future efforts to collect 5G levels in the environment for cell phone users would continue, with repeat studies to be conducted in nine more European nations over the next three years.
Protect your girls: We show that biological sex IS a factor in radiation outcomes, WIDELY

Mary Olson, GENDER AND RADIATION IMPACT PROJECT, 1 Jan 25
NEWS: We show in a new paper that the finding that girls and women suffer greater harm from radiation exposure compared to boys and men (who are also harmed) can be seen WIDELY in recent radiation research literature.
Dr Amanda Nichols, University of California at Santa Barbara, lead author, joins Mary Olson, founder of Gender and Radiation Impact Project in the new paper, entitled “Gender and Ionizing Radiation: Towards a New Research Agenda Addressing Disproportionate Harm.”
The paper is available to view or download at no charge, from the publisher: United Nations Institute for Disarmament Research .
The news here is the simple difference between standing on a relatively slender branch, and standing on a robust limb—apply this image to research and it is the difference between evidence found in a limited case, versus the same evidence being FOUND widely—beyond what could have been limited application.
In terms of radiation—a finding was made that radiation harms girls and women more than boys and men in one set of data as early as 2006. That data was in the National Academy of Science (NAS) watershed report called the Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation VII (BEIR VII).
Now, thanks to the invitation by the UN Institute for Disarmament Research (UNIDIR), I and my co-author Dr Amanda Nichols have sampled the research literature since 2006 (post-BEIR VII) and find that in studies that report data on males and females separately (now common) the sex-based difference can be seen, and in all cases where it is seen, females are harmed more than males. ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. more https://www.genderandradiation.org/blog/2024/12/31/protect-your-girls-we-show-that-biological-sex-is-a-factor-in-radiation-outcome-widely
Improved way to gauge radiation doses developed for Fukushima
Asahi Shimbun, By KEITARO FUKUCHI/ Staff Writer, December 31, 2024
[Ed. they studied only 30 people]
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency said it has developed a more accurate method to estimate radiation exposure doses among people who spend time around the stricken Fukushima No. 1 nuclear plant.
The JAEA has adapted the method, based on daily life patterns, into program format and is offering it for free on a municipal government website and elsewhere.
When the central government designated evacuation zones following the 2011 triple meltdown at the plant operated by Tokyo Electric Power Co., it estimated radiation doses among residents using a simple evaluation method that assumed they spent eight hours outdoors and 16 hours indoors a day.
That method allowed for quick estimation, but it tended to overestimate the doses.
Other existing evaluation methods also have shortcomings, including a failure to reflect the actual environment.
The JAEA began developing the new method in 2017.
JAEA researchers drew on data compiled by the Nuclear Regulation Authority to calculate average air dose rates for 100-meter-by-100-meter areas.
They also took into account where and for how long the residents and workers frequented near the plant, and how they moved between different locations, such as on foot or by car, the officials said.
They asked around 30 people working in former and current evacuation zones to carry personal dosimeters and then compared the measurements and estimates for their exposure doses in 106 patterns……………………………………………………………….. https://www.asahi.com/ajw/articles/15553626?fbclid=IwY2xjawHh0Y9leHRuA2FlbQIxMQABHRIRfUukVbNPX60rGOQi_qUp5oMiYFThXBvPZN4h0XJiPQ_xn8trGYEIkA_aem_GwPtrY24MPxB4L0v2u8SuA
-
Archives
- January 2026 (227)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (377)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
- March 2025 (319)
- February 2025 (234)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS




