Nuclear power will never be “beneficial”.

by beyondnuclearinternational, https://beyondnuclearinternational.org/2025/12/07/nuclear-power-will-never-be-beneficial/
Abandoning radiation protection will further endanger vulnerable populations, writes Cindy Folkers
As its name suggests, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) was created to regulate the nuclear power industry in order to protect people and the environment from the inherent dangers of that technology. As much as the NRC is currently failing to fully meet this mission, recent political maneuvers to curtail its influence threaten public health and safety even further.
A May 23 executive order from President Trump will now transform the stated mission of NRC from safety regulator to industry enabler, and in fact, NRC mission wording has been changed to say that nuclear power “benefits” society, despite the evidence to the contrary given the often serious health impacts of all nuclear power-related operations. This mission shift has sparked alarm among experts and safety advocates who argue that abandoning core principles of radiation protection will further endanger communities, sacrifice vulnerable populations, and increase the nuclear industry’s grip on energy policy.
The slate of executive orders issued by President Trump on May 23 are designed to “fast-track everything nuclear.” Beyond Nuclear has already highlighted the many concerns posed by these orders. For example, EO 14300 – titled Ordering the Reform of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission – will weaken radiation exposure standards, posing grave risks to public health from nuclear technology.
Among the decades of hard-won protections this executive order undermines is the scientifically supported foundation that there is no safe level of radiation exposure. The changes threaten not just U.S. regulatory integrity but global public health and environmental safety.
Section 5(b) of EO 14300 is particularly alarming. It calls on the NRC to adopt “science-based radiation limits” and demands the NRC reconsider its longstanding reliance on the Linear No Threshold (LNT) model. But in effect, this request contradicts itself.
The LNT model targeted for “reconsideration” is the scientific basis for radiation protection standards worldwide and rests on two principles:
1. Linear risk — the risk of disease rises proportionally with the radiation dose.
2. No threshold — there is no dose so low that it poses zero risk.
The NRC distorts the first principle by claiming that lower doses are less “effective” at damaging health than higher doses, despite studies supporting a linear model.
The NRC has ignored the second principle by allowing exposures in the first place – since all nuclear power operations release radioactivity – while also minimizing and even dismissing the damage this has done to health, all in service of ensuring the nuclear power industry’s continued existence.
Such allowance also keeps nuclear power in the forefront of energy choices, despite being one of the most expensive forms of energy when including upfront capital costs.
Trump’s EO demands that the NRC find a radiation exposure threshold deemed “safe,” essentially ignoring science to further suit industry needs, rather than adhering to the scientific consensus that no such threshold exists.
But this request has put the NRC in an untenable position for two reasons. First, the NRC itself reaffirmed use of the LNT model in 2022. Second, contemporary health research has confirmed that LNT already underestimates cancer risk at lower doses in about half of cases.
These findings are particularly striking because they were based on studies of nuclear workers, a part of the adult population and predominantly male that research has shown are at less risk from radiation exposure. Therefore, these studies do not adequately reflect the heightened vulnerabilities of women, children, and pregnancy to cancer or other radiation-associated diseases.
Exposures that may appear statistically small for adult male workers can translate into devastating risks for others. By discarding LNT, regulators would not only further ignore these findings but also codify a system that accepts — even demands — more sacrificial victims of radiation exposure.
By undermining LNT, the executive order provides industry with a regulatory green light: higher allowable exposures, fewer safety restrictions, and a streamlined licensing process for new reactors, including small modular nuclear reactors. The scientific implication is clear, and by extension so are the policy implications: every exposure, however small, carries some risk of harm. And even though the NRC tacitly recognizes this by using LNT, it still allows radiation exposures because if it didn’t, the nuclear power and weapons industry couldn’t exist.
Even more chilling is the NRC’s stated interpretation of the EO: “This EO provides the NRC with a great opportunity to rethink its radiation protection regulatory framework to…safely enable the nation’s use of nuclear power.” But the NRC’s history with regulation shows a willingness to stretch and redefine what is “safe”, and to muddle that definition with concepts such as “permissible” and “reasonable” that form the basis of the concept of ALARA or “as low as reasonably achievable.”
Industry has a much larger say than members of the public in what constitutes reasonable, achievable, or safe. In fact, historically, such distortion of the LNT model was necessary for the nuclear power industry to continue.
We already know that any radiation exposure poses a risk, and that women, children, (girls more so) and pregnancies are more at risk than the reference man used as the basis for U.S. radiation standards. To pretend that some radiation exposure is safe is already promoting a lie. In truth, there should be no allowable exposure.
The consequences of loosening radiation protections are far-reaching. Ionizing radiation is a proven cause of cancer, genetic mutations, infertility, birth defects, and developmental harm. The impacts are not confined to immediate exposures but ripple through generations with cancers occurring in the exposed and future offspring.
Furthermore, the effects of radiation are not abstract: they manifest in communities near uranium mines, uranium enrichment plants, nuclear reactors, and radioactive waste dumps. For these populations, exposure is not a distant risk but a daily reality.
A very small radiation dose to a pregnant woman doubles her risk of having a leukemic child and living near nuclear power facilities doubles the risk of leukemia in children. Abandoning the LNT model is tantamount to legitimizing their suffering as the price of nuclear expansion.
A mistake with wind or solar may cause a temporary power loss, unlike a mistake with nuclear which has led to meltdowns with cascading catastrophic and never-ending impacts that can render entire regions uninhabitable for centuries. Scientific evidence associates exposure to radiation from catastrophic releases with increases in birth defects, spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, mental and developmental disorders, heart defects, respiratory illness, and cancers – particularly in children. This fundamental incompatibility with human fallibility means nuclear power is not aligned with who we are as human beings. A catastrophic release of radioisotopes from nuclear power leaves behind hazards that persist for millennia.
The current trajectory of US nuclear policy represents a profound betrayal of public trust. By reorienting the NRC toward the false assumption that nuclear power is “beneficial” and that nuclear power can be enabled by further eroding the Linear No Threshold model, the Trump administration’s executive order prioritizes industry expansion, and economic and security interests over human health.
Cindy Folkers is the Radiation and Health Hazard Specialist at Beyond Nuclear.
All French nuclear power plants are releasing tritium, according to Criirad.
December 5, 2025 , https://reporterre.net/Toutes-les-centrales-nucleaires-francaises-ont-rejete-du-tritium-selon-la-Criirad
All French nuclear power plants are releasing tritium. This is the finding of the Independent Research and Information Commission on Radioactivity (CRIIRAD), which issued a warning on December 3rd about uncontrolled releases.
Between 2015 and 2024, 16 power plants recorded levels exceeding 10 Bq/l in groundwater, some exceeding 1,000 Bq/l such as Bugey, Gravelines and Tricastin, the association details.
The three other power plants (Golfech, Nogent-sur-Seine, Paluel) experienced similar episodes before or after this period, notably Nogent-sur-Seine on January 17, 2025.
Criirad emphasizes that no power plant has been able to guarantee the permanent protection of groundwater and that any massive discharge would quickly affect the aquatic environment.
According to the Sortir du nucléaire network , the toxicity of tritium has been underestimated, particularly when it is absorbed by the body, where it then enters the DNA of cells.
‘A New Form of Genocide’: Gazans Feel Little Relief from Israeli Strangulation Since the Ceasefire.

December 6, 2025 By Tareq S. Hajjaj Republished from Mondoweiss, https://scheerpost.com/2025/12/06/a-new-form-of-genocide-gazans-feel-little-relief-from-israeli-strangulation-since-the-ceasefire/
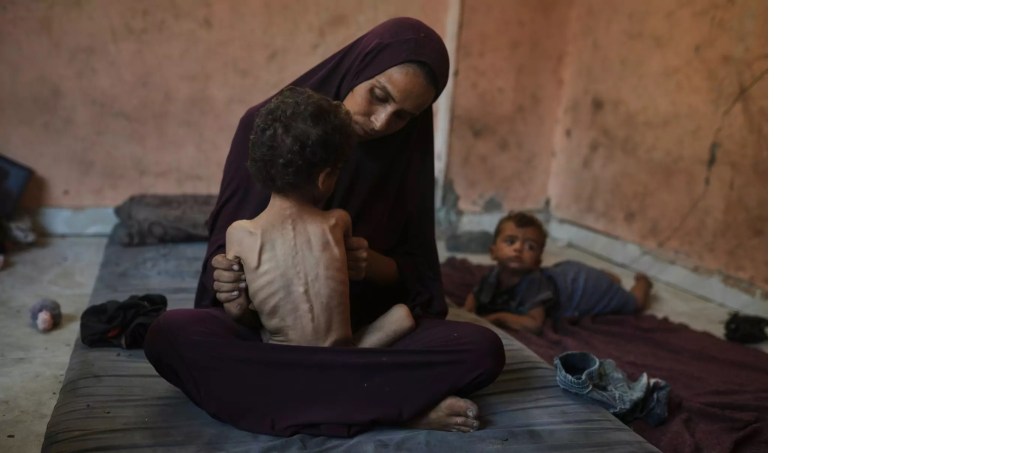
It’s been nearly two months since the ceasefire was reached in Gaza. Hopes were high among the 2 million Palestinians in the besieged Strip that not only would the Israeli bombings stop, but that everything they had been deprived of for the past two years – food, clean water, adequate medicine and healthcare – would flood into Gaza to ease their struggles. The hopes of regaining a fragment of the life they knew before the war, have dissipated, as the reality of a “new genocide” sets in.
Though some aid has come into Gaza, and people have tried to restore some semblance of normalcy, the reality in Gaza is far from peacetime. Israeli bombs are still falling, people cannot return to their home, and sufficient food aid and medicines are still in short supply.
The strain being felt by Gaza’s institutions, particularly its hospitals, and by ordinary Gazans, remains alarmingly close to wartime conditions. The Government Media Office in Gaza says that the humanitarian situation has not changed during or after the ceasefire, contrary to Israeli claims, and that the siege on Gaza has continued, with border crossings remaining effectively closed. What little goods do enter Gaza, the government says, does not meet “even the minimal needs of the population.”
In the first month of the ceasefire, according to the UN, Israel rejected over 100 requests for the entry of humanitarian aid into Gaza. Today, the World Food Programme says that dietary diversity remains low, and roughly 25 percent of households in Gaza are still reporting eating only one meal daily.
Ismail al-Thawabteh, Director of the Government Media Office in Gaza, says Israel is trying to present a misleading image suggesting it allows the flow of goods. In reality, the amount entering Gaza does not exceed one-third of what was agreed upon in the humanitarian protocol of the ceasefire. “Instead of 600 trucks per day—the minimum needed to meet essential requirements—Israel permits only about 200 trucks, most of which carry limited-value commercial or aid items.”
The UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UN OCHA) has reported that agencies are still required to coordinate all entry of humanitarian aid convoys with Israeli authorities. For reference, between the 12th and 18th of November, OCHA said humanitarian organizations coordinated 51 missions with the Israeli authorities. Of those 51 missions, just over half (27) were actually facilitated into Gaza; five were cancelled, 15 were impeded and four were denied.
Palestinians in Gaza tell Mondoweiss that they are feeling “suffocated,” as authorities remain unable to resolve crises such as malnutrition, shortages of food and medicine, or provide even minimal protection against harsh weather conditions.
“This is a new form of genocide,” says Khalil al-Deqran, spokesperson for the Ministry of Health in Gaza. “The policy of refusing to allow in what is necessary for people’s survival mirrors what happened earlier, when food was withheld, and malnutrition was deliberately created.”
The Ministry of Health only receives about 25% of its basic needs, causing the condition of hospitals in Gaza, according to the spokesperson, to be “deplorable and difficult”, especially in winter, when large numbers of patients, particularly children, seek care. He notes that some pediatric wards are operating at five times their bed capacity, as children live in torn tents or on the streets, leading to widespread disease. “With Israel preventing the entry of shelter materials and reconstruction supplies, the health environment becomes even more dangerous, increasing mortality and the spread of illnesses.”
The Ministry of Health said that essential medications for chronic diseases such as hypertension, heart conditions, and diabetes, which affect 350,000 patients in Gaza, are still barred by Israel from entering the Strip. Infant formula also continues to be restricted, allowed only through a few traders and in minimal quantities. Israel also prevents the entry of critical hospital supplies, including electrical generators, lab equipment, imaging devices, incubators, intensive care units, and operating room equipment – all the essential supplies needed by Gaza’s already devastated hospitals to continue functioning. “The situation remains terrible and exceedingly difficult,” the spokesperson says. Israel has not committed to the humanitarian protocol, and what has been allowed in does not amount to a drop in the ocean of the health sector’s needs.”
“There are multiple cases of malnutrition across Gaza due to the lack of infant formula and the blocking of protein-rich foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy. What enters today consists mainly of non-essential food items, which perpetuates malnutrition” the health ministry said.
“The majority of the trucks Israel allows in carry low-nutritional-value items such as processed foods, chocolate, soft drinks, and snacks, as an attempt to evade humanitarian obligations while keeping the population in a state of absolute food deprivation,” al-Thawabteh said.
According to al-Thawabteh, the Gaza Strip requires a consistent flow of essential goods: grains, flour, proteins, livestock, red and white meat, table eggs, nutritional supplements, shelter materials, construction supplies, agricultural inputs, and raw materials for local industries. He stresses that Israel treats these goods as “prohibited or heavily restricted items.”
By his measure, there have been no real improvements on the ground since the ceasefire. Instead, he says Gaza is witnessing a “deliberate engineering of a starvation policy,” in which Israel showcases images of aid trucks to appear compliant, while “in reality blocking essential supplies and rationing aid in ways that worsen the humanitarian crisis.” This behavior, he explains, “confirms that Israel uses the agreement as a political cover to prolong crises, not as a humanitarian or legal commitment toward civilians. The siege continues, restrictions continue, and the humanitarian infrastructure remains under immense pressure.”
‘The war is not over’
Ordinary families in Gaza are feeling the squeeze every day. Niveen al-Sharfa, a mother of five living in a tent in Gaza City, says nothing has changed since the ceasefire. Even when some goods are available in the markets, her family still cannot afford to buy them. “We expected that once the war ended and the ceasefire began, we would see reconstruction, open border crossings, improvements in hospitals, and the entry of winter essentials such as clothing, shelter, and other necessities. But none of this happened. We are still living in torn tents, and still far from our homes.”
Al-Sharfa recalls that during the war she lived in constant fear under bombardment, but says that even now she remains afraid of hearing at any moment that someone has been killed. “Nothing has changed… everything is the same,” she says.
Even those who experienced slight improvements in daily life after the ceasefire find their hopes diminished when looking at the broader picture.
Amer al-Sultan was displaced from his home in the Jabalia Camp in northern Gaza. He says that life has changed “a little” after the ceasefire in terms of the availability of some food— though prices remain high — unlike during the height of the war, when famine pushed people to eat the leaves off of trees. “I expected to return to my home, but unfortunately, I did not. My home lies inside the yellow zone, and this makes me feel every day that the war has not ended.”
“The world thinks the war is over, but as long as there is an army inside the yellow zone, the war is not over. Just last night, we woke up to the sound of bombardment, explosions, and gunfire in those areas. How can we believe the war has ended when we sleep and wake to the sound of bombs?”
Nidaa al-Dahdouh, a mother of two, sees no sign that the war has ended as long as her children are not living normal lives. She wants to see them going to school, instead of waking up in the morning to collect firewood or to stand in long lines for food aid. “When the war ends, I will see my children getting ready in the morning to go to school wearing warm clothes,” she says. “But so far, they are still suffering in tents and the cold that comes with it.”
“We hoped for safety after the war, that we would return to our homes, and feel that the endless killing had stopped. But none of that happened. We hoped that basic goods would return to their normal prices, but that did not happen either. Yes, some items are available—like fish, for example—but the price is extremely high, and I cannot afford it. So for me, it is as if it does not exist at all.”
Tareq S. Hajjaj is the Gaza Correspondent for Mondoweiss and a member of the Palestinian Writers Union. Follow him on Twitter/X at @Tareqshajjaj.
The mysterious black fungus from Chernobyl that may eat radiation
Mould found at the site of the Chernobyl nuclear disaster appears to be
feeding off the radiation. Could we use it to shield space travellers from
cosmic rays? In May 1997, Nelli Zhdanova entered one of the most
radioactive places on Earth – the abandoned ruins of Chernobyl’s exploded
nuclear power plant – and saw that she wasn’t alone.
Across the ceiling,
walls and inside metal conduits that protect electrical cables, black mould
had taken up residence in a place that was once thought to be detrimental
to life. In the fields and forest outside, wolves and wild boar had
rebounded in the absence of humans. But even today there are hotspots where staggering levels of radiation can be found due to material thrown out from the reactor when it exploded.
BB 28th Nov 2025, https://www.bbc.co.uk/future/article/20251125-the-mysterious-black-fungus-from-chernobyl-that-appears-to-eat-radiation
CT scans: benefits vs cancer risks
Program: CT scans: benefits vs cancer risks
CT scans can be vital in diagnosing disease, but they do come with small
increased risks because of the radiation exposure. A recent US study found
that if current practices persist, CT-associated cancer could account for
up to five per cent of all new diagnoses. So what can be done to drive down
the risk? One radiologist thinks mandating informed consent before a scan
is done would be a good start.
ABC 28th Nov 2025, https://www.abc.net.au/listen/programs/healthreport/ct-scans-cancer-radiation-risk/106076780
Prawns, sneakers and spices: What we know about Indonesia’s radioactive exports

Thu 27 Nov, https://www.abc.net.au/news/2025-11-27/indonesia-radiation-contamination-explained/106057730
Indonesian authorities are conducting a criminal investigation into the cause of radioactive contamination in a number of its exports.
It comes amid growing concern from the country’s trading partners, after traces of radiation were found in items such as prawns, spices and even sneakers.
So how does a radioactive element end up in such a variety of items?
Here’s what we know.
What has been affected?
Concerns about contamination first surfaced after Dutch authorities detected radiation in shipping containers from Indonesia earlier this year.
A report stated that several boxes of sneakers were found to be contaminated.
That was followed by a safety alert from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in August, urging consumers not to eat certain imported frozen prawns from a company known as PT Bahari Makmur Sejati.
The FDA later found the same radioactive compound in a sample of cloves from PT Natural Java Spice.
In all three cases, the products were recalled.
The FDA also banned products from the two Indonesian companies until they were able to demonstrate they had resolved issues that allowed the contamination to occur.
What has been detected?
Both Dutch and American authorities say they found a radioactive element known as caesium-137.
The US Federal Drug Administration says long-term, repeated low-dose exposure to caesium-137 increases health risks.
But the agency adds that the levels detected in the Indonesian products posed no acute risk to health.
The radioactive isotope, which is created via nuclear reactions, is used in a variety of industrial, medical and research applications.
What is the source of radioactive contamination?
Investigations have so far centred on a metal-processing factory at the Cikande Industrial Estate, in Banten province on the island of Java.
The smelting company, called PT Peter Metal Technology, is believed to be China-owned, according to investigators.
Around 20 factories linked to the Cikande industrial estate are affected, including facilities that process shrimp and make footwear, authorities say.
Nine employees working on the industrial estate were detected to have been exposed to caesium-137. They have been treated at a government hospital in Jakarta and all contaminated facilities in the industrial area have been decontaminated.
In August, Indonesian authorities said the government would impose a restriction on scrap metal imports, which were reportedly a source of the contamination.
What is being done about it?
Indonesia’s nuclear agency last month said the sprawling industrial estate would be decontaminated.
On Wednesday, Indonesian authorities scaled up their probe into the suspected source of the contamination.
“The police have launched the criminal investigation,” said Bara Hasibuan, a spokesperson for the investigating task force.
Indonesian authorities have had difficulty conducting investigations as the management of PT Peter Metal Technology — which produces steel rods from scrap metal — has returned to China, Setia Diarta, director general of the Metal, Machinery, Transportation Equipment, and Electronics at Indonesia’s Ministry of Industry, told a hearing with politicians earlier this month.
In addition, Indonesian authorities say they are preventing goods contaminated with caesium-137 from entering Indonesia.
At one port, authorities said they detected and stopped eight containers of zinc powder from Angola that were contaminated with caesium-137.
After being re-exported, containers of the mineral were last month reported as being stranded off the Philippine coast amid a stoush between Jakarta and Manila over what to do with them.
Minnesota’s aging nukes pose national threat
In a review of published studies of 136 nuclear reactor sites in the European Journal of Cancer Care in 2007, elevated leukemia disease rates in children were documented in the US, UK, France, Germany, Spain, Japan, and Canada. This is not a new story.
by beyondnuclearinternational, https://beyondnuclearinternational.org/2025/11/23/minnesotas-aging-nukes-pose-national-threat/
More than electricity, the reactors supply a steady dose of radioactive tritium in drinking water, writes Susu Jeffrey
“Sometimes before I give a speech, I ask the audience to stand up if they or someone in their family has had cancer,” says John LaForge of Nukewatch. “Eighty percent of the audience gets up.”
The Monticello nuclear power reactor is on the Mississippi River about 35-miles northwest of Minneapolis. Xcel’s twin Prairie Island reactors, plus about 50 giant dry casks storing waste reactor fuel, are all in the floodplain of the Mississippi. This waste is sited 44 to 51 miles southeast of Minneapolis and St. Paul.
There are no plans to move the waste off-island because there is no alternative destination. In fact, 34 more concrete encased steel casks are planned. There is no national hot radioactive waste repository. Think of these waste container sites as permanent radioactive waste dumps.
The greater Twin Cities’ 3.7 million people are in the nuclear “shadow” (within 50 miles) of all three nukes. The Mississippi River serves 20 million people with drinking water, way beyond the Minnesota state population of 5.7 million. Minnesota’s aging nukes are a national threat. For approximately the next six generations, radioactive tritium will be a part of the drinking water wherever those molecules wander.
The Monticello nuke was licensed in 1970 for 40 years, and went online in 1971, a year it had two radioactive cesium spills. In 2010, the license was renewed for another 20 years until 2030. Xcel Energy has even been granted an extension for another 20 years until 2050. It is a corporate financial security move not yet approved by the Minnesota Public Utilities Commission which holds the final consent. Paperwork is one thing, pipes are another.
In November 2022, a 50-year-old underground pipe leaked 829,000 gallons of tritium-contaminated wastewater that reached the Mississippi River, according to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Xcel failed to make public the radioactive spill for four months. After a May 15, 2024 public hearing in Monticello where citizens testified “We don’t trust you. You lie,” an NRC executive “clarified” Xcel’s “miscommunication.”
Senior Environmental Project Manager, Stephen J. Koenick admitted some tritium had been measured in the Mississippi. Tritium bonds with water and cannot be separated out. Water obeys gravity running downhill, in the case of Monticello, from the reactor to the Mississippi. The runaway tritium will persist in the environment for ten half-lives or about 123 years.
No telling where Xcel’s radioactive molecules will land. Men have a one in two chance of being diagnosed with cancer during their lifetimes; for women the chance is one in three (National Cancer Institute, 2/9/2022). There is tremendous popular, fear-driven support for the oncology industry.
The good news is that while cancer numbers are up so is the cancer survival rate. However, at nuke weapons, nuke reactors, and the virtually forever waste sites, “accidents” happen along with on-going radioactive decay. Radioactivity cannot be contained. When I was a newspaper reporter in Brevard County, Florida, where Cape Canaveral is located, I learned that nuclear waste cannot be rocketed off into space because it’s too hot, too heavy, and the rockets too faulty.
Nuclear Safety Regulations Changing
Among President Trump’s cost-cutting moves is a weakening of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s exposure standards. Staff would be cut and regulations “revised” virtually cutting off the commission’s independent status. The Monticello nuke was licensed for 40 years and was rubber stamped to work for 80. Octogenarian nukes are considered “safe enough” now by the nuclear/government consortium.
Piecemeal fix-it parts for geriatric machinery or people are a lucrative business. Locating a leaking tritium pipe underground, between buildings, removing and replacing it is a non-negotiable emergency at nuclear reactors with miles and miles of piping. Upkeep expenses figure in utility rate hikes.
Joseph Mangano and Ernest Sternglass did a study of eight downwind US communities in the two years after a nuclear reactor closure. A remarkable 17.4 percent drop in infant mortality was found. “We finally have peer-reviewed accurate data attaching nuclear power reactors to death and injury in the host communities,” New York State Assemblyman Richard Brodsky said of the 2002 report in the Archives of Environmental Health.
Monopoly capitalism or public service?
Clearly the Monticello reactor was designed to make money. In November 2024, Minnesota Attorney General Keith Ellison wrote that Xcel has “aggressively” pursued multi-year rate hikes while earning large profits. In 2024 Xcel reported $1.94-billion net earnings, a profit margin up 14% from 2023.
According to Xcel propaganda, the nuke is “the biggest employer and largest local taxpayer” in Monticello, MN, and generates an estimated $550 million in economic activity each year in the region. And like profits, cancer rates are up notably among people under 50 and rising faster among women than men the American Cancer Society reports.
Repeatedly, the Xcel corporation wins its rate hike and re-licensing “asks.” These asks get rewritten and resubmitted until a “compromise” is reached. In 2025, residential customers will pay $5.39 more per month, down from the original ask of $9.89, according to Minnesota Public Radio, which also noted that greater increases are on the horizon for EVs and data center capital improvements.
Cancer
St. Jude’s Children’s Hospital advertises heavily with videos of big-eyed, bald children cancer patients. In a review of published studies of 136 nuclear reactor sites in the European Journal of Cancer Care in 2007, elevated leukemia disease rates in children were documented in the US, UK, France, Germany, Spain, Japan, and Canada. This is not a new story.
The danger of mental retardation of fetuses exposed in the womb was reported in The New York Times (page A1 on 12/20/1989). Tritium crosses the placenta. In addition to the health costs of breathing and ingesting exhausts from nuclear power reactors, there is the problem of what to do with and how to contain its long-lived waste. The nuclear profit god is a once and future terrorist.
The Coalition for a Nuclear-Free Mississippi River is working for the immediate decommissioning of the Monticello nuclear reactor by educating the public on dangers of the nuclear power reactors and safe alternatives. To learn more, visit our website. See our Monticello report “Serial Killers on the Loose: Cancer Death Rates Rising in Reactor Host Communities”.
Department of Energy Seeks to Eliminate Radiation Protections Requiring Controls “As Low As Reasonably Achievable”
Santa Fe, NM – An internal Department of Energy (DOE) memorandum eliminates worker and public radiation protection rules known “As Low As Reasonably Achievable” (ALARA). This fundamental departure from decades of accepted health physics practices is being promoted by senior DOE political appointees with little background in health or radiation control. It is marked as “URGENCY: High” under the auspices of the DOE Deputy Secretary, the Under Secretary for Science, and the Administrator of the National Nuclear Security Administration. The memorandum awaits the final signature of DOE Secretary Chris Wright.
The memo’s stated goal is to:
“…remove the ALARA principle from all DOE directives and regulations, including DOE Order 458.1, Radiation Protection of the Public and the Environment, NE [Office of Nuclear Energy] Order 458.1, Radiation Protection of the Public, and, upon completion of the rulemaking process, 10 CFR [Code of Federal Regulations] 835, Occupational Radiation Protection.” [1]
It follows the playbook of the Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025, which called for:
“Set[ting] clear radiation exposure and protection standards by eliminating ALARA (“as low as reasonably achievable”) as a regulatory principle and setting clear standards according to radiological risk and dose rather than arbitrary objectives.”[2]
Contrary to Project 2025’s assertion that ALARA is just “arbitrary objectives,” the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration declares it to be:
“…the cornerstone principle of radiation safety, emphasizing that radiation exposure should be minimized to the lowest possible levels while still allowing essential tasks to be performed. This principle applies everywhere radiation is present, including medical, industrial, nuclear, and research settings… ALARA is not just a recommendation—it is a legal and ethical requirement in radiation-related industries.”[3]
The elimination of ALARA protections is likely to increase radiation exposures to workers and weaken cleanup standards at contaminated sites where DOE has binding legal requirements with the impacted states (e.g., Los Alamos Lab, NM; Hanford Nuclear Reservation, WA and West Valley Demonstration Project, NY), as well as DOE Legacy Management sites where residual contamination remains after completion of claimed “cleanup” (e.g., Rocky Flats, CO and Weldon Spring, MO).
DOE’s memo purports to remove red tape constraining construction of new nuclear power plants, which inevitably experience huge cost overruns at ratepayers’ expense because of the inherent economic problems with nuclear power. However, because DOE’s primary mission is expanding nuclear weapons production, the elimination of ALARA protections will hit workers and nearby communities by allowing higher worker and public doses.
Two pertinent examples are the expanding production of plutonium “pit” bomb cores at the Los Alamos Lab and future pit production at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina. At the same time, the independent Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board’s role of nuclear safety oversight is being crippled by the Trump Administration’s refusal to nominate candidates to the Board. Moreover, DOE’s termination of ALARA rules can even downgrade international radiation protection standards because the Department provides staff and training for the United Nations’ International Atomic Energy Agency.
DOE’s high-level memorandum relies heavily upon a recent study by its Idaho National Laboratory.[4] According to the memo, the INL Report concluded:
“The balance of available scientific evidence indicates that annual dose rates of 5,000 mrem or less have not been shown to result in detectable increases in adverse health outcomes across diverse human populations and exposure scenarios. Furthermore, substantial evidence suggests that even 10,000 mrem/year may maintain a reasonable safety margin based on available epidemiological and radiobiological data.”
This is highly debatable (see comments by an independent epidemiologist below). By way of comparison, a standard chest X-ray is around 10 millirem (mrem) and an average annual radiation dose from all sources (including natural) to any one individual in the United States is around 600 mrem.[5] The INL report begins to rationalize public radioactive doses that are up to 16 times higher.
The Idaho National Laboratory is where DOE extracted weapons grade uranium from spent reactor fuel for warhead production, resulting in significant ground water contamination and “temporary” storage of liquid high-level waste now estimated to cost billions of dollars to stabilize. Nevertheless, according to INL Director John Wagner, the Idaho National Laboratory Report specifically recommends:
- Eliminating all ALARA requirements and limits below the 5,000 mrem occupational dose limit in order to reduce “unnecessary economic burdens.”
- Multiplying five-fold the allowed public radioactive dose limit from 100 mrem per year to 500 mrem per year.
- Supporting ongoing research on low-dose radiation effects to “further refine scientific understanding and regulatory approaches.”
Ongoing research on low-dose radiation effects” is aimed at the Linear No-Threshold principle, which maintains that no dose of radiation is safe. Related, ALARA is considered to be the global bedrock of radiation protection for nuclear workers and the public and is widely accepted as best practices by health physics professionals. Historically, more than 10,000 DOE workers have filed compensation claims for their occupational illnesses, which argues for strengthening, not weakening, occupational protection standards.
In parallel with DOE under Trump Executive Orders, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (which oversees the nuclear energy industry) is questioning the Linear No-Threshold (LNT) principle. In recent written comment to the NRC, epidemiologist Joseph Mangano summarized decades of studies supporting LNT. His cited evidence includes:
- Studies of low-dose pelvic X-rays to pregnant women in the mid-1950s that concluded that a single X-ray would nearly double the risk of the child dying of cancer or leukemia by age ten.
- A 1990 study by the Committee on the Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) that concluded that cancers and genetic damage increase with low-level radiation as a linear, non-threshold function of the dose. It included over 900 references that support LNT.
- A second BEIR study in 2005 that reiterated the risks of low-dose radiation exposures.
- A 2020 systematic review of 26 studies involving 91,000 individuals with solid cancers and 13,000 with leukemia that documented excess risks caused by low dose radiation.
- A 2023 study of 309,932 workers at nuclear plants in France, the United Kingdom, and the United States that found 28,089 had died of solid cancers with occupational doses well below Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bomb survivors. This suggests that the Linear No-Threshold model may actually underestimate the harmful effects of prolonged low radiation doses.[6]
Jay Coghlan, Director of Nuclear Watch New Mexico, concluded: “The Trump Administration is pumping taxpayers’ money into the much hyped “nuclear renaissance,” now in its third or fourth failed attempt, while cutting Medicaid for the poor and cutting taxes for the rich. But this time the corporate nuclear titans are being given a leg up by cutting nuclear safety protections for workers and the public, inevitably causing more illnesses. The good news is that fundamental market economics will eventually collapse the nuclear industry. However, one has to ask, at what safety costs to other sectors, such as the expanding production of nuclear weapons for the new arms race?”
Trump’s new radiation exposure limits could be ‘catastrophic’ for women and girls.
it has since been widely documented that women and young girls are significantly more vulnerable to radiation harm than men—in some cases by as much as a ten-fold difference………… Those most impacted by weaker exposure standards will be young girls under five years old
By Lesley M. M. Blume, Chloe Shrager | November 14, 2025, https://thebulletin.org/2025/11/trumps-new-radiation-exposure-limits-could-be-catastrophic-for-women-and-girls/
In a May executive order, aimed at ushering in what he described as an “American nuclear renaissance,” President Donald Trump declared moot the science underpinning decades-old radiation exposure standards set by the federal government. Executive Order 14300 directed the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) to conduct a “wholesale revision” of half-a-century of guidance and regulations. In doing so, it considers throwing out the foundational model used by the government to determine exposure limits, and investigates the possibility of loosening the standard on what is considered a “safe” level of radiation exposure for the general public. In a statement to the Bulletin, NRC spokesperson Scott Burnell confirmed that the NRC is reconsidering the standards long relied upon to guide exposure limits.
Now, some radiology and policy experts are sounding alarm bells, calling the directive a dangerous departure from a respected framework that has been followed and consistently reinforced by scientific review for generations. They warn that under some circumstances, the effects of the possible new limits could range from “undeniably homicidal” to “catastrophic” for those living close to nuclear operations and beyond.
“It’s an attack on the science and the policy behind radiation protection of people and the environment that has been in place for decades,” says radiologist Kimberly Applegate, a former chair of the radiological protection in medicine committee of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) and a current council and scientific committee member of the National Council on Radiation Protection (NCRP)—two regulatory bodies that make radiation safety recommendations to the NRC. According to Applegate, current government sources have told her and other experts that the most conservative proposed change would raise the current limit on the amount of radiation that a member of the general public can be exposed to by five times. That would be a standard “far out of the international norms,” she says, and could significantly raise cancer rates among those living nearby. The NRC spokesperson did not respond to a question from the Bulletin about specific new exposure limits being considered.
Kathryn Higley, president of the NCRP, warns that a five-fold increase in radiation dose exposure would look like “potentially causing cancers in populations that you might not expect to see within a couple of decades.”
“There are many things that Executive Order does, but one thing that’s really important is that it reduces the amount of public input that will be allowed,” says Diane D’Arrigo, the Radioactive Waste Project Director at the Nuclear Information and Resource Service, a nonprofit group critical of the nuclear energy industry. In a statement to the Bulletin, the NRC said that once its standards reassessment process is completed, the NRC will publish its proposed rules in the Federal Register for public comment.* The NRC spokesperson did not respond to questions about when the proposed new standards would be made public and whether or how the general public would be further alerted to the changes.
Once the proposed policy change hits the Federal Register, the final decision will likely follow in a few days without advertising a period for public input, Applegate adds.
“I’m not sure I know why the loosening is needed,” says Peter Crane, who served as the NRC’s Counsel for Special Projects for nearly 25 years, starting in 1975. “I think it’s ideologically driven.” He points out that the probable loosening of the standards is set to coincide with increased pressure to greenlight new nuclear plants and could weaken emergency preparedness in case of leaks or other accidents: “I think it’s playing with fire.” (The NRC’s Office of Public Affairs did not respond to questions about the rationale for loosening the standards and the timing of the reconsideration.)
Possible shorter timelines for building nuclear power plants, coinciding with weakened radiation exposure standards, could spell disaster, warn other experts. It would be “undeniably homicidal” of the NRC to loosen current US exposure standards even slightly, adds Mary Olson, a biologist who has researched the effects of radiation for over 40 years and published a peer-reviewed study titled “Disproportionate impact of radiation and radiation regulation” in 2019. Olson cites NRC equations that found that the current exposure standards result in 3.5 fatal cancers per 1,000 people exposed for their lifetimes by living near a nuclear facility; a five-fold rate increase in allowable radiation exposure could therefore result in a little over 17.5 cancers per 1,000 people. Expressed another way, that means “one in 57 people getting fatal cancer from year in, year out exposure to an NRC facility,” she says.
The NRC’s Office of Public Affairs did not respond to questions about whether the NRC could guarantee the current level of safety for the general public or nuclear workers if adopting looser radiation exposure standards, and about whether new protections would be put into place.
Are women and children more vulnerable? According to Olson, increased radiation exposure could be even more “catastrophic” for women and children. Exposure standards have long been determined by studies on how radiation affects the “reference man,” defined by the ICRP as a white male “between 20-30 years of age, weighing around 70 kilograms [155 pounds].”
But Applegate, Olson, and other experts say that it has since been widely documented that women and young girls are significantly more vulnerable to radiation harm than men—in some cases by as much as a ten-fold difference, according to Olson’s 2019 study. Olson and Applegate cite another 2006 review assessing and summarizing 60 years of health data on the survivors of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bombings; the study showed that women are one-and-a-half to two times as likely to develop cancer from the same one-time radiation dose as men.
Young girls are seven times more at risk, they say. Those most impacted by weaker exposure standards will be young girls under five years old, Olson says. Her 2024 study of the A-bomb bomb survivor data for the United Nations Institute for Disarmament Research, titled “Gender and Ionizing Radiation,” found that they face twice the risk as boys of the same age, and have four to five times the risk of developing cancer later in life than a woman exposed in adulthood.
“Protections of the public from environmental poisons and dangerous materials have to be focused on those who will be most harmed, not average harmed,” Olson says. “That’s where the protection should be.”
Infants are especially vulnerable to radiation harm, says Rebecca Smith-Bindman, a radiologist and epidemiologist who is the lead author of a just-released major study in the New England Journal of Medicine documenting the relationship between medical imaging (such as X-rays and CT scans) and cancer risk for children and adolescents; more than 3.7 million children born between 1996 and 2016 participated and have been tracked. Smith-Bindman contests the idea that women are overall more vulnerable to cancer than men, saying that “in general, maybe women are a little bit more sensitive, …[but] women and men have different susceptibilities to different cancer types,” with women being more vulnerable to lung and breast cancers, among other types. But it is “absolutely true that children are more susceptible,” she adds. With children under the age of one, “the risks are markedly elevated.” While these findings are sobering, she points out that with medical imaging, “there’s a trade-off…it helps you make diagnoses; it might save your life. It’s very different from nuclear power or other sources of radiation where there’s no benefit to the patient or the population. It’s just a harm.”
“We’ve known for decades that pregnancy is [also] more impacted” by radiation exposure, says Cindy Folkers, radiation and health hazard specialist at Beyond Nuclear, a nonprofit anti-nuclear power and weapons organization. “Radiation does its damage to cells, and so when you have a pregnancy, you have very few cells that will be developing into various parts of the human body: the skeleton, the organs, the brain,” and exposing those cells to radiation during pregnancy can impact the embryo’s health, she says. Smith-Bindman and her team are also studying the impact of radiation exposure on pregnancy, and while their results are not yet in, “we do know that exposures during pregnancy are harmful,” she says, “and that they result in elevated cancer risks in the offspring of those patients.”
For children, lifetime cancer risk will be increased not only because of the “sensitivity and vulnerability of developing tissues, but also partly [because] they would be living longer under a different radiation protection framework,” adds David Richardson, a UC Irvine professor who studies occupational safety hazards.
Several experts noted the irony that these changes are being mandated by the same administration that is also overseeing a policy of “Make America Healthy Again” (MAHA), an effort being spearheaded by Secretary of Health and Human Services Robert F. Kennedy Jr. “In terms of general [public] knowledge, I think there has not been very large coverage or acceptance of the idea that radiation affects different people differently on the basis of both age and biological sex,” says Olson. “But we now have enough reviews, enough literature to say that the biological sex difference is there. I don’t think MAHA mothers know this because it’s been underreported, [and] they would be concerned if they knew it.”
The NRC’s Office of Public Affairs did not respond to questions about concerns being raised by radiologists and epidemiologists about possible health consequences—especially for children—as a result of increased radiation exposure.
Continue readingHealth Care Workers Spoke Out for Their Peers in Gaza. Then Came Backlash.
Medical institutions are silencing their staff and impeding efforts to build solidarity with medical workers in Gaza.
By Marianne Dhenin , Truthout, November 17, 2025
handra Hassan, an associate professor of surgery at the University of Illinois Chicago (UIC) College of Medicine, spent three weeks in Gaza in January 2024, treating patients who had survived tank shelling, drone strikes, and sniper fire amid Israel’s ongoing genocide. When Nasser Hospital in Khan Younis came under siege, Hassan and the MedGlobal doctors he was serving with were forced to flee. “We were evacuated when they bombed just across the street from the hospital [and] tanks were rolling in,” Hassan told Truth
When Hassan returned home to Chicago, he was eager to share his experiences and advocate for an end to Israel’s assault on Gaza, which has killed an estimated 68,000 Palestinians since October 2023. Among the dead are over 1,500 health care workers, including doctors and nurses Hassan worked alongside.
But instead of being welcomed like he had been after previous missions to conflict zones in Ukraine and Syria, Hassan soon found himself on the receiving end of a doxxing and harassment campaign. StopAntisemitism, a pro-Israel group that doxxes people it accuses of antisemitism, shared screenshots of some of Hassan’s LinkedIn posts to its X account. Hassan said his employer received around 1,500 emailed complaints the day StopAntisemitism posted his information.
“I was speaking up for the human rights of Palestinians [because] it’s like, you’re witnessing another genocide, you need to talk about it,” Hassan told Truthout. But StopAntisemitism “put my picture, and they wrote that I’m [an] antisemite.”
Hassan is one of more than 15 health care workers in eight states who told Truthout they faced silencing, harassment, or workplace retaliation for Palestine-related speech, including giving a talk on health issues in Palestine, endorsing statements condemning the killing of health care workers in Gaza, or wearing a keffiyeh or other symbols of Palestine solidarity at work. Many said they felt that their hospitals, clinics, or professional societies had become increasingly hostile working environments since October 2023.
The experiences that health care workers shared suggest that organized campaigns of complaints and harassment from pro-Israel groups against health care workers have intensified, and that anti-Palestinian racism is entrenched across health care institutions nationwide. In a 2024 survey, the Institute for the Understanding of Anti-Palestinian Racism (IUAPR) also found widespread anti-Palestinian racism in health care: More than half of the 387 health care provider respondents “reported experiencing silencing, exclusion, harassment, physical threat or harm, or defamation while advocating for Gaza and/or Palestinian human rights.” Half said they were “afraid to speak out.”
Many of those who spoke to Truthout shared that fear and expressed concerns for their patients and profession: “The reality on the ground is that racism is running unchecked throughout our medical institutions, and as a result, health care workers don’t have the training they need, accountability is not happening at the level of the medical institutions, and our communities are not being served,” Asfia Qaadir, a psychiatrist specialized in trauma-informed care for BIPOC youth, told Truthout. “Racism is about erasure, and ultimately, our patients are paying the price.”
A Pattern of Censorship……………………………..
Non Government Organisations Warn that Recent Executive Orders Would Harm Public Health, Disproportionately Impacting Women and Children

“Young men like the Reference Man are harmed by radiation, but they’re more resistant to harm than are women and children. Radiation causes cancer in women at twice the rate of adult men, while the same exposure in early childhood, will, across their lifetimes, produce seven times more cancer in young females, and four times more in young males.”
Asheville, North Carolina – November 14, https://www.radiationproject.org/blog/ngos-warn-that-recent-executive-orders-would-harm-public-health-disproportionately-impacting-women-and-children?ss_source=sscampaigns&ss_campaign_id=6917d62bc4477007efdd4b63&ss_email_id=6917db9d43e3de1cada92627&ss_campaign_name=Welcome+to+GRIP%E2%80%99s+NEW+Blog&ss_campaign_sent_date=2025-11-15T01%3A47%3A30Z

Over forty citizen’s sector organizations including the national nonprofit Physicians for Social Responsibility have sent a joint letter to federal officials warning of public health consequences of a series of executive orders by President Trump which direct the NRC to dramatically weaken Standards for Protection Against Radiation in the US federal code. The letter points out sharply disproportionate impacts on women and children from weakening existing radiation exposure standards and calls for strengthening them.
The letter is posted here. It was spearheaded by the nonprofit Generational Radiation Impact Project (GRIP) and sent to US Nuclear Regulatory Commissioners, Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., Surgeon General Denise Hinton, and other key elected and appointed officials.
Recent Trump executive orders direct the NRC to “reconsider” the linear no-threshold (LNT) model. The joint letter argues that this “would undermine public trust by falsely claiming that the NRC’s radiation risk models lack scientific basis, despite decades of peer-reviewed evidence and international consensus.” The widely accepted LNT model has no limit “below regulatory concern,” i.e. no level below which radiation exposure can be treated as negligible or zero-risk. Where applied, LNT takes account of proportional cancer and health risks of all tiny exposures no matter how small.
Trump executive orders direct the NRC to undertake new rulemaking and “wholesale revision” of existing radiation regulations, which would likely lead to the NRC abandoning LNT and raising allowable exposure limits.
But past NRC opposition to such changes stands to be reversed by the Trump executive orders. If federal radiation regulations were weakened to permit exposures of 10 Rems a year, scientists estimate that over a 70-year lifetime, four out of five people would develop cancer they would not otherwise get.
Today’s joint letter stresses that health damage would not be evenly distributed across the population, but would disproportionately affect women and children, who are biologically more susceptible to ionizing radiation than men. And an article published today in the Bulletin of Atomic Scientists cites several lines of evidence “that women and young girls are significantly more vulnerable to radiation harm than men—in some cases by as much as a ten-fold difference” and that “infants are especially vulnerable to radiation harm.”
A July 2025 Idaho National Laboratory report commissioned by the Department of Energy recommended loosening the public radiation standard fivefold to 500 millirems. In 2021 the NRC roundly rejected a petition to raise allowable radiation exposures for all Americans, including children and pregnant women, to 10 Rems a year, 100 times the current limit.
“[NRC] bases its risk assessments on Reference Man, a model that represents a young adult male and fails to reflect the greater impacts to infants, children, and women—pregnant or not,” the joint letter states. “Newer research has shown that external radiation harms children more than adults and female bodies more than male bodies. Research on internal exposures…has not yet been sufficiently analyzed to discover if there are broad age-based or male/female differences in impact…. Existing standards should therefore be strengthened to account for these life-stage and gender disparities…not weakened. Radiation causes infertility, loss of pregnancy, birth complications and defects, as well as solid tumor cancer, leukemia, non-cancer outcomes including cardiovascular disease, increased incidence of autoimmune disease and ongoing new findings.”
In cases where cancer, heart disease, and vascular degradation including stroke are caused by radiation, they are documented at higher rates in women than in men, according to 2024 UNIDIR report Gender and Ionizing Radiation.
The joint letter urges the NRC to “to stand up to the Executive Order’s marching orders to ‘promote’ nuclear power—a mission outside its legal regulatory mandate,” and adopt “stronger, science-based radiation protections….Contemporary research shows that radiation’s impact is far greater on females, children, and fetuses—the most at-risk postnatal group being girls from birth to age five. A truly protective framework would replace Reference Man with a lifecycle model.”
“All US radiation regulations and most radiation risk assessments are based on outcomes for the Reference Man,” said Mary Olson, CEO of GRIP, the organization which spearheaded the joint letter, and co-author of Gender and Ionizing Radiation. “Young men like the Reference Man are harmed by radiation, but they’re more resistant to harm than are women and children. Radiation causes cancer in women at twice the rate of adult men, while the same exposure in early childhood, will, across their lifetimes, produce seven times more cancer in young females, and four times more in young males.”
“We know that exposure to radiation causes disproportionate harm from both cancer and non-cancer related disease outcomes over the course of the lifetime to women and especially to little girls, but radiation is dangerous for everyone,” said Amanda M. Nichols, Ph.D., lead author of Gender and Ionizing Radiation. “[President Trump’s] executive order will allow the industry to relax the current standards for radiological protection, which are already far from adequate. This will have detrimental health consequences for humans and for our shared environments and puts us all at higher risk for negative health consequences. “
“Living near nuclear power facilities doubles the risk of leukemia in children; and radiation is also associated with numerous reproductive harms including infertility, stillbirths and birth defects.,” said Cindy Folkers, Radiation and Health Hazard Specialist with the NGO Beyond Nuclear, a signatory to the joint letter. “Exposing people to more radiation, as this order would do if implemented, would be tantamount to legitimizing their suffering as the price of nuclear expansion.”
NFLAs welcome Remembrance Day award of medal to nuke test ‘Sniffers’, but fight not over as groundcrews exposed to radiation remain forgotten.
11th November 2025, https://www.nuclearpolicy.info/news/nflas-welcome-remembrance-day-award-of-medal-to-nuke-test-sniffers-but-fight-not-over-as-groundcrews-exposed-to-radiation-remain-forgotten/
The NFLAs have welcomed the Remembrance Day announcement that the Government has agreed to award the Nuclear Test Medal to gallant RAF aircrew of 27 and 543 Squadrons and sailors aboard the Royal Fleet
Auxiliary vessel Sir Percivale who passed through French and Chinese atmospheric nuclear tests in the Far East to carry out air sampling.
British personnel were ordered to fly or sail through the radioactive clouds of over 40 atomic and nuclear atmospheric tests carried out by China and France.
11th November 2025
NFLAs welcome Remembrance Day award of medal to nuke test ‘Sniffers’, but fight not over as groundcrews exposed to radiation remain forgotten
The NFLAs have welcomed the Remembrance Day announcement that the Government has agreed to award the Nuclear Test Medal to gallant RAF aircrew of 27 and 543 Squadrons and sailors aboard the Royal Fleet Auxiliary vessel Sir Percivale who passed through French and Chinese atmospheric nuclear tests in the Far East to carry out air sampling.
British personnel were ordered to fly or sail through the radioactive clouds of over 40 atomic and nuclear atmospheric tests carried out by China and France.
The NFLAs have been strong advocates for recognition, justice and compensation for Britain’s nuclear test veterans and their families, and the latest announcement comes just a month after NFLA Chair, Councillor Lawrence O’Neill, wrote to the new Veterans Minister, Louise Sandher-Jones, calling for the eligibility criteria for the medal to be extended to include these forgotten ‘sniffers’.
Unfortunately, the revised award criteria still wrongly exclude the RAF ground crew involved in decontaminating the aircraft on their return to the UK. The aircraft involved in sniffing operations were contaminated with radioactivity, and they were decontaminated by washing by groundcrew. Many of these groundcrew were unaware of the levels of radioactivity on the aircraft.
Consequently, many of these ground crew also developed cancers and other health conditions related to exposure to ionising radiation, some repeatedly. Some personnel died and others were able to access a War Pension as a result.
The latest decision by Ministers therefore only represents a part-victory. Councillor O’Neill believes that excluding the ground crew seems ‘not only unjust, but also bizarre and perverse’ given these veterans faced the same dangers as their colleagues who engaged in ‘sniffing’ duties on British tests and who will now qualify for the medal.
The fight therefore continues.
The remnants of Chernobyl are still present in the Black Sea

Forty years have passed since Chernobyl, but Chernobyl-related radioactive contamination in the Black Sea has not ended. TENMAK’s research has revealed that the concentration of caesium-137 in the Black Sea is seven times higher than in the Mediterranean Sea.
BirGün Daily, Giriş: 07.11.2025 , https://www.birgun.net/haber/the-remnants-of-chernobyl-are-still-present-in-the-black-sea-667018
Nearly 40 years have passed since the Chernobyl disaster, considered one of the world’s three largest nuclear accidents, but the radioactive contamination caused by the accident continues to affect the Black Sea. At the IVth National Symposium on Monitoring and Assessment in the Seas, Dr Aysun Kılınçarslan, presenting on behalf of the Turkish Energy, Nuclear and Mining Research Institute (TENMAK), announced the results of monitoring studies on radioactive contamination in Turkey’s coastal waters and sediments.
Analyses conducted in coastal sediments between 2015 and 2023 detected high levels of caesium-137 and strontium-90. While an average of 21 becquerels of caesium-137 isotope per kilogram was observed in the Black Sea, this rate was recorded as only 3.2 becquerels in the Mediterranean Sea. Values that are relatively high in the Sea of Marmara decrease as one moves towards the Aegean and Mediterranean Seas. The highest value found in the analyses exceeds 82 becquerels. This figure is 10 times higher than the highest value observed in the Mediterranean Sea. When viewed on a regional basis, the highest caesium-137 value in sediments, 50 becquerels, was found in Hopa. Hopa is followed by Trabzon and Sinop.
HIGH FIGURES IN TRABZON AND HOPA
In measurements taken in coastal surface waters between 2014 and 2023, the caesium-137 concentration averaged 9 millibecquerels per litre in the Black Sea, while this figure dropped to 1.6 millibecquerels in the Mediterranean Sea. Rates in the Bosphorus, Marmara and Çanakkale ranged between 8.4 and 6.9 millibecquerels, while the amount of caesium-137 in the water decreased in the Aegean Sea, falling to 1.8 millibecquerels. The highest figures were found in Trabzon and Hopa, which have been affected by Chernobyl for years and where cancer rates have increased. Tekirdağ, Ordu, Karasu and İğneada stand out as other regions with high measurements. Although the study’s findings indicate that these levels do not pose a risk to human health or environmental pollution, the significant difference between the Black Sea and the Mediterranean clearly demonstrates the consequences of Chernobyl-related contamination.
CHERNOBYL FLOWS
Another noteworthy finding of the study was the detection of plutonium-239, which does not occur naturally and is produced by nuclear reactions, alongside caesium-137. While average values do not differ between seas, the locations most affected by this contamination include Erdek, the Bosphorus Strait, Hopa, and Sinop. Experts point out that the sources of contamination linked to these isotopes are nuclear power plant accidents, nuclear weapons tests, and operational nuclear reactors. Chernobyl is also cited as a source of contamination in the Black Sea. Radioactive pollution from the out-of-control melted reactor and the surrounding area reaches the Black Sea via groundwater and the Dnieper River.
MARINE ASSESSMENT IS NECESSARY
Prof. Dr. İnci Gökmen, who revealed high levels of radiation in tea after Chernobyl, points out that the radiation level detected at 21 becquerels per kilogram is quite high. Gökmen states that data collected from the seas and coasts also highlights the need to measure radiation levels in the soil, adding, “It is surprising to see plutonium in the seas, even at low levels. Strontium is not surprising. However, since strontium does not emit gamma radiation and must be measured by chemical separation, measurements were rarely taken despite the presence of strontium in the environment and food after Chernobyl. However, the strontium values immediately after the accident can be estimated from the current results. By looking at the caesium levels in coastal surface water in some areas, it would be good to calculate the doses that swimmers or those working at sea, such as fishermen, would receive. It would be appropriate to take measurements in fish, mussels and other seafood. Thirty-nine years have passed since Chernobyl. Caesium has only undergone one half-life. This means that radioactive elements will remain in the seas for a long time to come,” he said. WHAT IS CAESIUM (CS-137)?
The most common radioactive form of caesium is Cs-137. Caesium-137 is produced by nuclear reactions. External exposure to Cs-137 can cause burns, acute radiation sickness and even death. Exposure to large amounts of Cs-137 can result from the misuse of a powerful industrial Cs-137 source, a nuclear explosion, or a major nuclear accident. Under normal conditions, large amounts of Cs-137 are not found in the environment. Exposure to Cs-137 can increase the risk of cancer due to the presence of high-energy gamma radiation. Ingestion or inhalation of Cs-137 increases the risk of cancer by causing the radioactive material to spread to soft tissues, particularly muscle tissue. Vascular plants do not accumulate high levels of caesium through root uptake because caesium is strongly adsorbed to the soil. However, the accumulation of radioactive residues on flora with large surface areas, such as lichens or mosses, is significant. Animals that feed on these plants can consume large amounts of radiocaesium (and other radionuclides present in radioactive fallout). Human consumption of the meat of such animals leads to the uptake of these radionuclides into the body.
Note: This article is translated from the original article titled Çernobil’in izleri hâlâ Karadeniz’de, published in BirGün newspaper on November 7, 2025.
The men who stared at mushroom clouds .
In a beige function room at the Pontins holiday park, Weston-super-Mare, a
man in a Hawaiian shirt addresses the veterans of Britain’s little-known
nuclear testing programme. There are about 130 people in the room. More
than half are in their late eighties and participated in the programme.
Also here are their children and, in a few cases, their children’s
children. They’re wearing Hawaiian shirts too, a tapestry of tropical print
and palm trees embellished with plastic flower garlands, tinsel, wigs and
novelty hats. It’s the third day of the All Tests Reunion, a week-long
gathering for this rarefied demographic, and the group chats excitedly as
they await the evening’s entertainment. Tables are laden with bottles of
house wine and pints of bitter, walking sticks propped behind chairs. In
the corner of the room, four women who are due to perform shuffle about as they attach te riri ni mwaie around their waists — heavy straw-like
dancing skirts that are native to Kiribati, a Pacific island nation that
was among several locations the British chose for nuclear weapons tests
during the 1950s and ’60s.
Until tonight, the group has been discussing
rather serious matters. Such as whether the Ministry of Defence (MoD) was
aware of the risks when it stationed thousands of young servicemen in
places such as Kiritimati (or Christmas Island) and started detonating
atomic and hydrogen bombs in the vicinity; and why it continues to deny or
delay access to the medical records of those deployed there. One
particularly urgent question is whether exposure to blast after blast,
without protective shielding, may be the reason so many of the veterans and their descendants have suffered health problems. Many of these questions remain unanswered. Some may be unanswerable.
FT 1st Nov 2025, https://www.ft.com/content/1fca6893-7dfe-43e3-b7ec-c00e3d4ad0b6
New Radiation Protection Standards in 2026?

Tony Webb – November 2025.
In May 2025 US President Donald Trump ordered the US Nuclear Regulatory
Commission (NRC) to review US radiation protection standards for workers and the public. The order claims that these and other NRC regulatory processes hinder development of US nuclear power generation and need to be revised – in line with another set of his ‘alternative facts’ that overturn almost all the established principles that provide the basis of national and international protection standards.
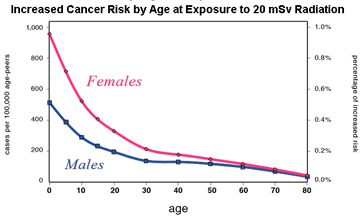
This latest diktat will result in a significant weakening of current protection at a time when we have mounting scientific evidence that the existing standards need to be significantly improved/tightened. Permissible radiation exposures to workers will likely increase five-fold. Exposures to the public could be 100 times greater than currently permitted. Changes in the USA will lead to pressure for similar changes to standards in other countries, including Australia. Whether we end up with better or worse protection will require a sustained awareness and advocacy campaign. This will need to involve exposed workers, trade unions, environment and public health
interests arguing: first that our government and radiation protection agencies should reject the US approach, and second that new and improved national standards in line with the latest evidence should be adopted.

Health effects of radiation exposure
It has long been recognised that all radiation exposures present a risk to human health. Put simply there is no safe level of radiation – whether naturally occurring or artificially generated. Some we cannot avoid. Some like diagnostic medical x-rays we accept as having other countervailing benefits. High doses, like those received
by Japanese residents of Hiroshima and Nagasaki from nuclear bombs in 1945, or some of the first responders to the Ukrainian Chernobyl nuclear reactor meltdown in 1986, cause ‘radiation sickness’ where whole organs are damaged often with fatal
effects.
The results from high-dose exposures are what are known as ‘determinate’ effects.
Above a threshold dose these effects occur with severity determined by the dose. Radiation standards are set to keep exposures below the threshold, so these do not occur.
Lower doses cause a different kind of damage. Particularly concerning are increased rates of a wide range of cancers and genetic damage being passed on to future generations. These are referred to as ‘stochastic’ effects. The damage is not ‘determinate’ with a threshold below which they do not occur. Stochastic damage is a ‘hit and miss’ affair. You either get this type of health damage or you don’t. And if you do the scale of the damage isn’t related to the radiation dose you received.
The initial damage occurs at the cellular level where a radiation strike can have one of three outcomes. (i) It may simply pass through causing no damage. Alternatively, (ii) the radiation may kill the cell which isn’t a problem, unless too many cells are killed at once affecting functioning of whole organs. Our bodies are eliminating and replacing dead and dying cells all the time. Problems arise however when (iii) the cell is merely damaged and goes on to replicate in this damaged form.
Our bodies do have well developed repair mechanisms that often result in adequate repair of the damage. There is even some evidence suggesting that some such radiation damage and repair may assist the body’s capacity for repair in the future.
But where radiation leaves the damaged cell to survive and replicate uncontrollably in this damaged form the result is what we call a cancer – sometimes detectable only decades after the initial radiation damage. The process can be complicated further as growth of some cancers involves a two-stage process – initiation, where damage (from radiation or other environmental pollutants) leaves the cell susceptible,
followed by promotion (again from radiation or other sources) which drives the cell-cancer process forward.
Stochastic radiation damage is real. it doesn’t involve a threshold dose. Any exposure can be the one that causes the initial and/or subsequent damage leading to the health effects. We are in the world of ‘probability’ – far from certainty at the individual level but with fairly predictable outcomes at the population level which allow us to assess the risk (i.e., probability of an adverse outcome) individuals face from receiving small, sometimes repeated, doses of radiation.
Radiation protection principles.
In light of these established mechanisms for harm from radiation, standard setting bodies have long adopted three principles – that any exposure needs to be: (i) justified as necessary against some social benefits; (ii) kept as low as reasonably achievable (the ALARA principle); and (iii) kept below specified limits set in regulations.
The last of these has been the subject of much controversy over the years.
Standards have been set for workers’ occupational exposures and for public exposures. These, first, ensure exposures are below the threshold levels where deterministic effects might occur. Below these high levels, they have been set such that the risk of stochastic effects – particularly cancers and genetic damage are at levels deemed ‘acceptable’. There have been arguments over both what is ‘acceptable’ and how the probable level of risk from any given low dose is estimated.
Estimates of risk
A number of early studies of patients exposed as part of medical procedures indicated a problem with radiation exposure and some early estimates of the stochastic risk. Since then, the bulk of the data for the estimates of risk has come from studies of survivors of the Japanese nuclear bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945. These Life Span Studies (LSS) have consistently shown
increases in cancer rates among survivors higher than those in the non-exposed population. There are a number of problems with this data – not least that survivors were not wearing film badges when the bombs went off, so all doses have had to be estimated later. They were also the ‘hardy’ survivors of wide-ranging traumatic
events, perhaps less vulnerable to damage from radiation Most of these survivors received relatively high doses as a single exposure or within a relatively short time period. More accurate measures of small exposures repeated over longer time periods to a general population, might be expected to yield different results.
However, these were the best data to be had. The risks at lower doses are estimated using the assumption that, if there is no safe level of exposure, no threshold below which stochastic effects do not occur, we can estimate lower dose risks on a straight line from these higher LSS doses. This Linear No Threshold (LNT) assumption, though adopted by all stands setting bodies, has at times been contested. Some have suggested a sub-linear relationship with a threshold for any effects. Others have made the case for a super-linear or marginally higher effect at lower doses where these are spread over longer time periods or result from radiative material that gets inside the body.
For now all the significant agencies agree that radiation protection for workers and the public should be based on LNT and the three radiation protection principles: justification, ALARA, and Specific Exposure Limits. These agencies include: the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) the United Nations
Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) the US National Academy of Sciences Committee on the Biological Effects of Ionising Radiation (known as the BEIR Committee) and national agencies like the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA). The cancer risk from low
dose radiation is estimated to be in the range of 4-6% per Sievert (1000 mSv) of exposure. The risk of genetic damage (first two generations only) is estimated to be around 1.5% per Sievert.
These estimates have resulted in national protection bodies setting standards that limit annual exposures. For workers the annual limit is 20 mSv as a target – but with 50 mSv allowed in any year provided the average over five years does not exceed 20 mSv. The annual limit for public exposures is 1 mSv. All of these are for
exposures in addition to what might be received from natural background radiation or exposures due to medical procedures such as diagnostic x-rays and nuclear medicine.
Change is coming – one way or another.
It is these protection principles and the exposure standards for workers and the public that the Presidential directive to the US NRC seeks to overturn. It calls on the NRC to reconsider reliance on LNT (and ALARA) as the basis for standard setting at low doses, where there is a need to protect against probable stochastic effects and
directs that instead the NRC set standards based on deterministic effects.
This will likely result in a significant weakening of the current standards at a time when the evidence strongly suggests that they are in need of further tightening. The current standards have been in place since 1991. Revisions at that time were the result of a sustained campaign throughout the 1980s led by trade unions in the UK, Europe, USA and Canada for reduction of the then 50 mSv occupational and 5 mSv public limits -justified in large part by emerging evidence from the Japanese lifespan studies. As previously noted, estimates of risk from these was based on one-off
short-term exposure to relatively high doses (at and above 100 mSv). Since then, studies in Europe and North America of workers exposed over years of work in nuclear industries to doses below the current occupational limits, indicate the risks are around 2 to 3 times greater than those used for setting the current standards.
They also show a doubling of expected rates of cardio-vascular diseases: strokes, arthro-sclerosis, and heart damage. In addition, studies of populations living close to nuclear facilities in Europe and the USA show childhood cancer rates significantly higher than expected. This evidence is cause for concern, suggesting that the
current standards provide inadequate protection and need to be tightened.
A new campaign for improved protection?
Past experience suggests that persuading national and international bodies to improve radiation protection standards is far from easy but not impossible. In the short term, a campaign would be seeking clear and unequivocal statements from national protection agencies that reject the US president’s directive that the NRC abandon the fundamental principles which have formed the basis for regulating worker and public exposures. If implemented Trump’s proposals would likely result in occupational exposure limits five times higher than presently allowed, and public exposure limits could be 100 times greater.
The campaign should seek assurances that there will be no change to the established principles underpinning radiation protection: that there is no safe level of radiation, that all exposures should be kept as low as can be reasonably achievable; and that occupational and public limits need to be based on the best scientific evidence of risk to human populations.
Raising the concern about, and seeking rejection of, the likely US NRC changes will require building an informed coalition of trade union, environment and public health interests. Occupational and public radiation exposures are more widespread that commonly appreciated. Workers are routinely exposed in mining, industry and medicine as well as those associated with the nuclear power industry. The. campaign could involve local initiatives that focus concerns of workers in , and people living close to sites of: proposed nuclear power plants; existing uranium, mineral sands, and hard rock mines; proposed ‘rare earth’ mines; medical and other
radioactive waste storage sites; and other activities that routinely release radiative materials.
Opposing Trump’s latest proposals to weaken standards is fairly straightforward. If implemented by the NRC they would dismantle the whole edifice on which radiation protection has been built over the past 80 years – a framework that many concerned about radiation protection within the affected industries have invested time and energy to establish and maintain.
Pressing the claim for improvements is harder but not impossible given the evidence for greater harm that is emerging. The case can already be made for at least halving the permissible occupational and public exposure limits. If we are successful in pressing for improved protection standards, the nuclear industry is unlikely to thank President Trump for opening this can of worms with his NRC directive. Once opened it will be hard to close without increasing worker and public awareness of how any, and all radiation exposures increase health risks to workers the public and to future generations.
Tony Webb has worked as a researcher, consultant and advisor on radiation and health issues to politicians, trade unions, environment and public health groups in the UK, Europe, USA , Canada and Australasia since the late1970s. He can be contacted for information on how to assist the latest evolving international campaign via tonyrwebb@gmail.com.
-
Archives
- February 2026 (192)
- January 2026 (308)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (376)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
- March 2025 (319)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS
