Year 4: The Timeline That Tells the Tale

Without historical context, which is buried by corporate media, it’s impossible to understand the war in Ukraine. Historians will tell the story, but journalists are cut short for trying to tell it now.
By Joe Lauria, Consortium News, February 24, 2026
The way to prevent the Ukraine war from being understood is to suppress its history.
A cartoon version has the conflict beginning on Feb. 24, 2022 when Vladimir Putin woke up that morning and decided to invade Ukraine.
There was no other cause, according to this version, other than unprovoked, Russian aggression against an innocent country.
Please use this short, historical guide to share with people who still flip through the funny pages trying to figure out what’s going on in Ukraine.
The mainstream account is like opening a novel in the middle of the book to read a random chapter as though it’s the beginning of the story.
Thirty years from now historians will write about the context of the Ukraine war: the coup, the attack on Donbass, NATO expansion, and the rejection of the Minsk Accords and Russian treaty proposals without being called Putin puppets.
It will be the same way historians today write of the Versailles Treaty as a cause of Nazism and WWII, without being called Nazi-sympathizers.
Providing context is taboo while the war continues in Ukraine, as it would have been during WWII. Context is paramount in journalism.
But journalists have to get with the program of war propaganda while a war goes on. Journalists are clearly not afforded the same liberties as historians. Long after the war, historians are free to sift through the facts.
THE UKRAINE TIMELINE
World War II— Ukrainian national fascists, led by Stepan Bandera, at first allied with the German Nazis, massacre more than a hundred thousands Jews and Poles.
1950s to 1990 – C.I.A. brought Ukrainian fascists to the U.S. and worked with them to undermine the Soviet Union in Ukraine, running sabotage and propaganda operations. Ukrainian fascist leader Mykola Lebed was taken to New York where he worked with the C.I.A. through at least the 1960s and was still useful to the C.I.A. until 1991, the year of Ukraine’s independence. The evidence is in a U.S. government report starting from page 82. Ukraine has thus been a staging ground for the U.S. to weaken and threaten Moscow for nearly 80 years.
November 1990: A year after the fall of the Berlin Wall, the Charter of Paris for a New Europe (also known as the Paris Charter) is adopted by the U.S., Europe and the Soviet Union. The charter is based on the Helsinki Accords and is updated in the 1999 Charter for European Security. These documents are the foundation of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe. The OSCE charter says no country or bloc can preserve its own security at another country’s expense.
Dec. 25, 1991: Soviet Union collapses. Wall Street and Washington carpetbaggers move in during ensuing decade to asset-strip the country of formerly state-owned properties, enrich themselves, help give rise to oligarchs, and impoverish the Russian, Ukrainian and other former Soviet peoples.
1990s: U.S. reneges on promise to last Soviet leader Gorbachev not to expand NATO to Eastern Europe in exchange for a unified Germany. George Kennan, the leading U.S. government expert on the U.S.S.R., opposes expansion. Sen. Joe Biden, who supports NATO enlargement, predicts Russia will react hostilely to it.
1997 :: The only thing that could provoke a “vigorous and hostile” Russian response would be needless NATO Expansion Far East right till the border of Russia – Sen. Joe Biden pic.twitter.com/hRW47hLL5y
— Rishi Bagree (@rishibagree) June 17, 2022
1997: Zbigniew Brzezinski, former U.S. national security adviser, in his 1997 book, The Grand Chessboard: American Primacy and Its Geostrategic Imperatives, writes:
“Ukraine, a new and important space on the Eurasian chessboard, is a geopolitical pivot because its very existence as an independent country helps to transform Russia. Without Ukraine, Russia ceases to be a Eurasian empire. Russia without Ukraine can still strive for imperial status, but it would then become a predominantly Asian imperial state.”
New Year’s Eve 1999: After eight years of U.S. and Wall Street dominance, Vladimir Putin becomes president of Russia. Bill Clinton rebuffs him in 2000 when he asks to join NATO.
Putin begins closing the door on Western interlopers, restoring Russian sovereignty, ultimately angering Washington and Wall Street. This process does not occur in Ukraine, which remains subject to Western exploitation and impoverishment of Ukrainian people.
Feb. 10, 2007: Putin gives his Munich Security Conference speech in which he condemns U.S. aggressive unilateralism, including its illegal 2003 invasion of Iraq and its NATO expansion eastward.
He said: “We have the right to ask: against whom is this [NATO] expansion intended? And what happened to the assurances our western partners made after the dissolution of the Warsaw Pact? Where are those declarations today? No one even remembers them.”
Putin speaks three years after the Baltic States, former Soviet republics bordering on Russia, joined the Western Alliance. The West humiliates Putin and Russia by ignoring its legitimate concerns. A year after his speech, NATO says Ukraine and Georgia will become members. Four other former Warsaw Pact states join in 2009.
2004-5: Orange Revolution. Election results are overturned giving the presidency in a run-off to U.S.-aligned Viktor Yuschenko over Viktor Yanukovich. Yuschenko makes fascist leader Bandera a “hero of Ukraine.”
April 3, 2008: At a NATO conference in Bucharest, a summit declaration “welcomes Ukraine’s and Georgia’s Euro-Atlantic aspirations for membership in NATO. We agreed today that these countries will become members of NATO”. Russia harshly objects. William Burns, then U.S. ambassador to Russia, and presently C.I.A. director, warns in a cable to Washington, revealed by WikiLeaks, that,
“Foreign Minister Lavrov and other senior officials have reiterated strong opposition, stressing that Russia would view further eastward expansion as a potential military threat. NATO enlargement, particularly to Ukraine, remains ‘an emotional and neuralgic’ issue for Russia, but strategic policy considerations also underlie strong opposition to NATO membership for Ukraine and Georgia. In Ukraine, these include fears that the issue could potentially split the country in two, leading to violence or even, some claim, civil war, which would force Russia to decide whether to intervene. … Lavrov stressed that Russia had to view continued eastward expansion of NATO, particularly to Ukraine and Georgia, as a potential military threat.”
A crisis in Georgia erupts four months later leading to a brief war with Russia, which the European Union blames on provocation from Georgia.
November 2009: Russia seeks new security arrangement in Europe. Moscow releases a draft of a proposal for a new European security architecture that the Kremlin says should replace outdated institutions such as NATO and the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE).
The text, posted on the Kremlin’s website on Nov. 29, comes more than a year after President Dmitry Medvedev first formally raised the issue. Speaking in Berlin in June 2008, Medvedev said the new pact was necessary to finally update Cold War-era arrangements.
“I’m convinced that Europe’s problems won’t be solved until its unity is established, an organic wholeness of all its integral parts, including Russia,” Medvedev said.
2010: Viktor Yanukovich is elected president of Ukraine in a free and fair election, according to the OSCE.
2013: Yanukovich chooses an economic package from Russia rather than an association agreement with the EU. This threatens Western exploiters in Ukraine and Ukrainian comprador political leaders and oligarchs.
February 2014: Yanukovich is overthrown in a violent, U.S.-backed coup (presaged by the Nuland-Pyatt intercept), with Ukrainian fascist groups, like Right Sector, playing a lead role. Ukrainian fascists parade through cities in torch-lit parades with portraits of Bandera.
March 16, 2014: In a rejection of the coup and the unconstitutional installation of an anti-Russian government in Kiev, Crimeans vote by 97 percent to join Russia in a referendum with 89 percent turn out. The Wagner private military organization is created to support Crimea. Virtually no shots are fired and no one was killed in what Western media wrongly portrays as a “Russian invasion of Crimea.”
April 12, 2014: Coup government in Kiev launches war against anti-coup, pro-democracy separatists in Donbass. Openly neo-Nazi Azov Battalion plays a key role in the fighting for Kiev. Wagner forces arrive to support Donbass militias. U.S. again exaggerates this as a Russian “invasion” of Ukraine. “You just don’t in the 21st century behave in 19th century fashion by invading another country on completely trumped up pre-text,” says U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry, who voted as a senator in favor of the U.S. invasion of Iraq in 2003 on a completely trumped up pre-text.
May 2, 2014: Dozens of ethnic Russian protestors are burnt alive in a building in Odessa by neo-Nazi thugs. Eight days later, Luhansk and Donetsk declare independence and vote to leave Ukraine.
Sept. 5, 2014: First Minsk agreement is signed in Minsk, Belarus by Russia, Ukraine, the OSCE, and the leaders of the breakaway Donbass republics, with mediation by Germany and France in a Normandy Format. It fails to resolve the conflict.
Feb. 12, 2015: Minsk II is signed in Belarus, which would end the fighting and grant the republics autonomy while they remain part of Ukraine. The accord was unanimously endorsed by the U.N. Security Council on Feb. 15. In December 2022 former German Chancellor Angela Merkel admits West never had intention of pushing for Minsk implementation and essentially used it as a ruse to give time for NATO to arm and train the Ukraine armed forces.
2016: The hoax known as Russiagate grips the Democratic Party and its allied media in the United States, in which it is falsely alleged that Russia interfered in the 2016 U.S. presidential election to get Donald Trump elected. The phony scandal serves to further demonize Russia in the U.S. and raise tensions between the nuclear-armed powers, conditioning the public for war against Russia.
May 12, 2016: U.S. activates missile system in Romania, angering Russia. U.S. claims it is purely defensive, but Moscow says the system could also be used offensively and would cut the time to deliver a strike on the Russian capital to within 10 to 12 minutes.
June 6, 2016: Symbolically on the anniversary of the Normandy invasion, NATO launches aggressive exercises against Russia. It begins war games with 31,000 troops near Russia’s borders, the largest exercise in Eastern Europe since the Cold War ended. For the first time in 75 years, German troops retrace the steps of the Nazi invasion of the Soviet Union across Poland.
German Foreign Minister Frank Walter-Steinmeier objects. “What we shouldn’t do now is inflame the situation further through saber-rattling and warmongering,” Steinmeier stunningly tells Bild am Sontag newspaper. “Whoever believes that a symbolic tank parade on the alliance’s eastern border will bring security is mistaken.”
Instead Steinmeier calls for dialogue with Moscow. “We are well-advised to not create pretexts to renew an old confrontation,” he warns, adding it would be “fatal to search only for military solutions and a policy of deterrence.”
December 2021: Russia offers draft treaty proposals to the United States and NATO proposing a new security architecture in Europe, reviving the failed Russian attempt to do so in 2009. The treaties propose the removal of the Romanian missile system and the withdrawal of NATO troop deployments from Eastern Europe. Russia says there will be a “technical-military” response if there are not serious negotiations on the treaties. The U.S. and NATO reject them essentially out of hand.
February 2022: Russia begins its military intervention into Donbass in the still ongoing Ukrainian civil war after first recognizing the independence of Luhansk and Donetsk.
Before the intervention, OSCE maps show a significant uptick of shelling from Ukraine into the separatist republics, where more than 10,000 people have been killed since 2014.
March-April 2022: Russia and Ukraine agree on a framework agreement that would end the war, including Ukraine pledging not to join NATO. The U.S. and U.K. object. Prime Minister Boris Johnson flies to Kiev to tell Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky to stop negotiating with Russia. The war continues with Russia seizing much of the Donbass.
March 26, 2022: Biden admits in a speech in Warsaw that the U.S. is seeking through its proxy war against Russia to overthrow the Putin government. Earlier in March he overruled his secretary of state on establishing a no-fly zone against Russian aircraft in Ukraine. Biden opposed the no-fly zone, he said at the time, because “that’s called World War III, okay? Let’s get it straight here, guys. We will not fight the third world war in Ukraine.”
September 2022: Donbass republics vote to join Russian Federation, as well as two other regions: Kherson and Zaporizhzhia.
May 2023: Ukraine begins counter-offensive to try to take back territory controlled by Russia. As seen in leaked documents earlier in the year, U.S. intelligence concludes the offensive will fail before it begins.
June 2023: A 36-hour rebellion by the Wagner group fails, when its leader Yevegny Prigoshzin takes a deal to go into exile in Belarus. The Wagner private army, which was funded and armed by the Russian Ministry of Defense, is absorbed into the Russian army. The Ukrainian offensive ends in failure at the end of November.
September 2024: Biden deferred to the realists in the Pentagon to oppose long-range British Storm Shadow missiles from being fired by Ukraine deep into Russia out of fear it would also lead to a direct NATO-Russia military confrontation with all that that entails.
Putin warned at the time that because British soldiers on the ground in Ukraine would actually launch the British missiles into Russia with U.S. geostrategic support, it “will mean that NATO countries — the United States and European countries — are at war with Russia. And if this is the case, then, bearing in mind the change in the essence of the conflict, we will make appropriate decisions in response to the threats that will be posed to us.”
November 2024: After he was driven from the race and his party lost the White House, a lame duck Biden suddenly switched gears, allowing not only British, but also U.S. long-range ATACMS missiles to be fired into Russia. It’s not clear that the White House ever informed the Pentagon in advance in a move that risked the very World War III that Biden had previously sought to avoid.
February 2025: The first direct contact between senior leadership of the United States and Russia in more than three years takes place, with a phone call between the countries’ presidents, and a meeting of foreign ministers in Saudi Arabia. They agree to begin negotiations to end the war.
August 15, 2025: Donald Trump and Vladimir Putin meet in Anchorage, Alaska for the first face-to-face meeting between U.S. and Russian leaders in more than four years. The Russians left believing Trump had thoroughly understood their position against a ceasefire and instead their desire to reach a comprehensive solution to the war that addressed the “root causes” and Russian security concerns, which have been outlined in this timeline. A series of follow-up diplomatic meetings have failed to advance that goal and the conflict continues to be decided on the battlefield with Russian gains as well as an increase in missiles being fired into each nations territory.
This timeline clearly shows an aggressive Western intent towards Russia, and how the tragedy could have been avoided if NATO would not allow Ukraine to join; if the Minsk accords had been implemented; and if the U.S. and NATO negotiated a new security arrangement in Europe, taking Russian security concerns into account.
Joe Lauria is editor-in-chief of Consortium News and a former U.N. correspondent for The Wall Street Journal, Boston Globe, and numerous other newspapers, including The Montreal Gazette and The Star of Johannesburg. He was an investigative reporter for the Sunday Times of London, a financial reporter for Bloomberg News and began his professional work as a 19-year old stringer for The New York Times. He is the author of two books, A Political Odyssey, with Sen. Mike Gravel, foreword by Daniel Ellsberg; and How I Lost By Hillary Clinton, foreword by Julian Assange. He can be reached at joelauria@consortiumnews.com and followed on Twitter @unjoe
National analysis of cancer mortality and proximity to nuclear power plants in the United States
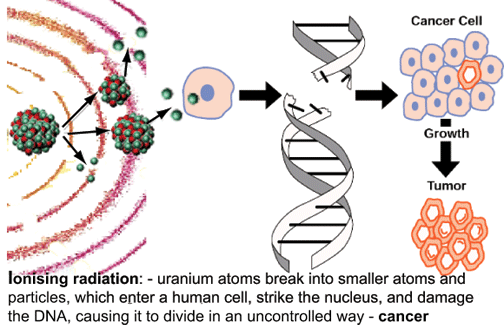
Nature Communications volume 17, Article number: 1560 (2026) , 23 February 2026 [Excellent graphics and tables]
Abstract
Understanding the potential health implications of living near nuclear power plants is important given the renewed interest in nuclear energy as a low-carbon power source. Here we show that U.S. counties located closer to operational nuclear power plants have higher cancer mortality rates than those farther away.
Using nationwide mortality data from 2000-2018, we assess long-term spatial patterns of cancer mortality in relation to proximity to nuclear facilities while accounting for socioeconomic, demographic, behavioral, environmental, and healthcare factors. Cancer mortality is higher across multiple age groups in both males and females, with the strongest associations among older adults, males aged 65–74 and females aged 55–64. While our findings cannot establish causality, they highlight the need for further research into potential exposure pathways, latency effects, and cancer-specific risks, emphasizing the importance of addressing these potentially substantial but overlooked risks to public health.
…………………………………………………………….Nuclear power plants emit radioactive pollutants that can disperse into the surrounding environment, leading to potential human exposure through inhalation, ingestion, and direct contact. These pollutants can be transported through air, water, and soil, contributing to long-term environmental contamination1. Populations residing near nuclear power plants may experience low-level chronic exposure to ionizing radiation via environmental release pathways. While our study does not include dosimetry, ionizing radiation is a well-established carcinogen2,3,4,5,6,7 and thus motivates investigation into proximity-based exposure patterns.
………………………Despite the importance and prevalence of nuclear power plants in the U.S., epidemiologic research regarding their health impacts remains rare. Most U.S. studies have focused on individual plants or limited regions, with only a few national assessments to date – many of which relied on fixed distance cutoffs to classify exposed populations8,9,11,12,19,21,22,23,24,25. These studies often focus on a single facility and its surrounding communities, which restricts their statistical power to detect effects and ability to capture broader exposure patterns. Furthermore, differences in study design, exposure assessment methods, and geographic scope make it difficult to draw generalizable conclusions.
In this work, we assess the association between county-level proximity to nuclear power plants and cancer mortality across the United States from 2000 to 2018. We find that counties located closer to operational nuclear power plants have higher cancer mortality rates, with stronger associations observed among older adults. These associations remain consistent across multiple sensitivity analyses and proximity definitions. The results highlight spatial patterns of cancer risk in relation to nuclear power generation and emphasize the importance of evaluating potential long-term health implications of nuclear energy infrastructure in population-scale studies…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-026-69285-4
Harrowing six final words of nuclear worker as his skin fell off during 83 days of agony
WARNING: DISTRESSING CONTENT Nuclear plant worker Hisashi Ouchi suffered the highest radiation dose in history after 1999 Japan accident, enduring 83 agonising days before death.
Edward Easton and Jane Lavender Associate Editor, 18 Feb 2026, https://www.dailystar.co.uk/news/world-news/harrowing-six-final-words-nuclear-36730407
What You Need to Know
Hisashi Ouchi, a 35‑year‑old nuclear plant worker, survived a 1999 criticality accident that delivered the highest recorded radiation dose to a human, enduring 83 days of severe medical complications before dying of multiple organ failure. A government probe later blamed inadequate supervision, safety culture, and training, leading to negligence charges against six plant officials.
Key points:
On September 30, 1999, a criticality accident at a Japanese nuclear fuel processing plant exposed worker Hisashi Ouchi to an estimated 17,000 millisieverts of radiation.
The dose Ouchi received was about 850 times the annual occupational limit for nuclear workers and roughly 140 times higher than the exposure of residents near Chernobyl.
Ouchi was hospitalized at the University of Tokyo Hospital, where he underwent experimental treatments for 83 days, during which his skin sloughed off, his eyelids fell off, and his digestive system collapsed.
Medical staff administered up to ten blood transfusions daily, and painkillers were reported to be ineffective; Ouchi reportedly said, “I can’t take it anymore. I am not a guinea pig.”
He died on December 21, 1999, and the official cause of death was recorded as multiple organ failure
****************************************************************************************************.
A nuclear facility worker suffered what many consider to be the most agonising death ever recorded after a routine procedure went catastrophically wrong.
Hisashi Ouchi, 35, was exposed to an incomprehensible level of radiation when colleagues accidentally added excessive uranium to a processing vessel, sparking an uncontrolled nuclear chain reaction on September 30, 1999.
The unfortunate Ouchi was positioned nearest to the vessel, consequently subjecting him to 17,000 millisieverts of radiation – equivalent to 200,000 X-rays.
The exposure he received was 850 times the safe yearly limit for nuclear facility workers, 140 times greater than what Chernobyl residents experienced after the 1986 catastrophe, and the most severe dose ever documented in human history.
Within seconds and minutes of his exposure, Ouchi became violently sick. Whilst most individuals subjected to such levels would die within days, Ouchi survived, reports the Mirror.
He was taken to hospital alert but in critical condition, as his white blood cell count had been virtually eliminated, leaving him completely without an immune system.
Medical staff moved him to the University of Tokyo Hospital, where they tried various experimental procedures in a frantic bid to preserve his life.
What ensued was 83 days of torment for the nuclear facility worker.
Radiation had completely obliterated Ouchi’s capacity to heal and regenerate cells, causing his skin to gradually slough away, his blood vessels to fail, and his eyelids to fall off.
Fluids seeped relentlessly from his ravaged flesh and accumulated in his lungs, compelling medics to maintain him on life support.
Making his ordeal even more harrowing, his digestive system collapsed entirely, inflicting excruciating agony and causing litres of fluid to drain from his body daily. Despite numerous skin grafts and stem cell treatments, his body remained unable to recover.
Breathing became impossible without mechanical assistance, and nourishment could only be administered via feeding tube.
The agony became so unbearable that, two months into his treatment, Ouchi’s heart ceased beating, yet medical staff chose to revive him.
His wife reportedly held onto hope that he would survive until at least January 1, 2000, so they could welcome the new millennium together.
During lucid moments, he remained fully aware of his deteriorating condition.
According to accounts, Ouchi eventually reached breaking point and spoke six chilling words to hospital staff: “I can’t take it anymore. I am not a guinea pig.”
Medical professionals were compelled to administer up to ten blood transfusions daily merely to sustain his life. Painkillers appeared utterly ineffective, and at one stage, he reportedly pleaded for the treatment to cease.
Ouchi passed away on December 21, 1999, from multiple organ failure, nearly three months following the incident. Multiple organ failure was recorded as the official cause of death.
Four months afterwards, in April 2000, his colleague Shinohara also died from multiple organ failure at the age of 40.
Supervisor Yokokawa, who had been seated at his workstation when the criticality incident unfolded, managed to survive.
A probe by the Japanese government determined that the accident was due to a lack of regulatory supervision, a deficient safety culture, and insufficient training for employees.
Six officials from the company running the plant were subsequently charged with professional negligence and breaches of nuclear safety laws. In 2003, they received suspended prison sentences for their deadly neglect.
DNA Mutations Discovered in The Children of Chernobyl Workers
Science Health15 February 2026, By David Nield, https://www.sciencealert.com/dna-mutations-discovered-in-the-children-of-chernobyl-workers
The DNA damage from ionizing radiation (IR) erupting from the Chernobyl nuclear disaster of 1986 is showing up in the children of those originally exposed, researchers have found – the first time such a transgenerational link has been clearly established.
Previous studies have been inconclusive about whether this genetic damage could be passed from parent to child, but here the researchers – led by a team from the University of Bonn in Germany – looked for something slightly different.
Rather than picking out new DNA mutations in the next generation, they looked for what are known as clustered de novo mutations (cDNMs): two or more mutations in close proximity, found in the children but not the parents. These would be mutations resulting from breaks in the parental DNA caused by radiation exposure.
“We found a significant increase in the cDNM count in offspring of irradiated parents, and a potential association between the dose estimations and the number of cDNMs in the respective offspring,” write the researchers in their published paper.
“Despite uncertainty concerning the precise nature and quantity of the IR involved, the present study is the first to provide evidence for the existence of a transgenerational effect of prolonged paternal exposure to low-dose IR on the human genome.”
The findings are based on whole genome sequencing scans of 130 offspring of Chernobyl cleanup workers, 110 offspring of German military radar operators who were likely exposed to stray radiation, and 1,275 offspring of parents unexposed to radiation, used as controls.
On average, the researchers found 2.65 cDNMs per child in the Chernobyl group, 1.48 per child in the German radar group, and 0.88 per child in the control group. The researchers say those numbers are likely to be overestimates due to noise in the data, but even after making statistical adjustments, the difference was still significant.
What’s more, a higher radiation dose for the parent tended to mean a higher number of clusters in the child. This fits with the idea that radiation creates molecules known as reactive oxygen species, which are able to break DNA strands – breaks which can leave behind the clusters described in this study, if repaired imperfectly.
The good news is that the risk to health should be relatively small: children of exposed parents weren’t found to have any higher risk of disease. This is partly because a lot of the cDNMs likely fall in ‘non-coding’ DNA, rather than in genes that directly encode proteins.
“Given the low overall increase in cDNMs following paternal exposure to ionizing radiation and the low proportion of the genome that is protein coding, the likelihood that a disease occurring in the offspring of exposed parents is triggered by a cDNM is minimal,” the researchers write.
To put this in perspective, we know that older dads are more likely to pass on more DNA mutations to their children. The subsequent risk of disease associated with parental age at the time of conception is higher than the potential risks from radiation exposure examined here, the researchers report.
There are some limitations to note. As the initial radiation exposure happened decades ago, the researchers had to estimate people’s exposure using historical records and decades-old devices.
Participation in the study was also voluntary, which may have introduced some bias, as those who suspected they’d been exposed to radiation may have been more likely to enrol.
Even with those limitations, we now know that with prolonged exposure, ionizing radiation can leave subtle traces in the DNA of the generations to come – emphasizing the need for safety precautions and careful monitoring for those at risk.
“The potential of transmission of radiation-induced genetic alterations to the next generation is of particular concern for parents who may have been exposed to higher doses of IR and potentially for longer periods of time than considered safe,” write the researchers.
The research has been published in Scientific Reports.
Residential proximity to nuclear power plants and cancer incidence in Massachusetts, USA (2000–2018)
18 December 2025, Springer Nature, Volume 24, article number 92, (2025)
“………………………………………. Results
Proximity to plants significantly increased cancer incidence, with risk declining by distance. At 2 km, females showed RRs of 1.52 (95% CI: 1.20–1.94) for ages 55–64, 2.00 (1.59–2.52) for 65–74, and 2.53 (1.98–3.22) for 75 + . Males showed RRs of 1.97 (1.57–2.48), 1.75 (1.42–2.16), and 1.63 (1.29–2.06), respectively. Cancer site-specific analyses showed significant associations for lung, prostate, breast, colorectal, bladder, melanoma, leukemia, thyroid, uterine, kidney, laryngeal, pancreatic, oral, esophageal, and Hodgkin lymphoma, with variation by sex and age. We estimated 10,815 female and 9,803 male cancer cases attributable to proximity, corresponding to attributable fractions of 4.1% (95% CI: 2.4–5.7%) and 3.5% (95% CI: 1.8–5.2%).
Conclusions
Residential proximity to nuclear plants in Massachusetts is associated with elevated cancer risks, particularly among older adults, underscoring the need for continued epidemiologic monitoring amid renewed interest in nuclear energy. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12940-025-01248-6
President Trump’s radical attack on radiation safety.

By Daniel Hirsch, Haakon Williams, Cameron Kuta | October 15, 2025, https://thebulletin.org/2025/10/president-trumps-radical-attack-on-radiation-safety/?variant=B&utm_source=ActiveCampaign&utm_medium=email&utm_content=Trump%20s%20attack%20on%20radiation%20safety&utm_campaign=20251009%20Thursday%20Newsletter%20%28Copy%29

In May, President Donald Trump issued a series of executive orders that, in part, require the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) to consider dramatically weakening its radiation protection standard. If federal radiation limits are gutted in the manner urged by the president, the new standard could allow four out of five people exposed over a 70-year lifetime to develop a cancer they would not otherwise get.
Contesting the scientific consensus. Section 5(b) of the executive order—formally titled “Ordering the Reform of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission”—directs the NRC to issue a proposed “wholesale revision of its regulations and guidance documents,” including reconsideration of the agency’s “reliance on the linear no-threshold (LNT) model for radiation exposure.” The LNT model maintains that risk from radiation exposure is proportional to the dose: Even a tiny amount of radiation causes some small but real increased risk of cancer, and that risk goes up linearly as the dose increases.
While most Americans have doubtless never heard of the LNT model, it has been the bedrock of radiation exposure risk analysis for decades and forms the basis of public health protection from radiation. The LNT model is scientifically robust, supported by the longstanding and repeatedly affirmed determinations on low-dose radiation by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, virtually all international scientific bodies, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the NRC itself.
Despite the LNT model’s long track record and the well-established body of scientific evidence upon which it is built, President Trump has unilaterally issued a presidential finding that this scientific consensus is wrong. His order could lead to LNT’s complete abandonment in a matter of months, posing a serious increase in the amount of radiation that industries and government agencies would be allowed to inflict upon the public.
If the NRC goes along with Trump’s assertion, the weakening of radiation protection standards would likely be extreme. Advocates of abandoning LNT have often asserted that low-dose radiation is harmless or even beneficial, and therefore, that the public health radiation limits should be hugely increased. In 2015, three petitions for rulemaking to the NRC proposed doing away with the LNT model and increasing allowable radiation exposures for everyone—including children and pregnant women—to 10 rem. (The Roentgen equivalent man (rem) is a unit of effective absorbed radiation in human tissue, equivalent to one roentgen of X-rays. One rem is equal to 0.01 Sievert in the international system of units.)
One petition to the NRC went so far as to ask, “Why deprive the public of the benefits of low-dose radiation?” The NRC strongly rejected the petitions in 2021, citing the conclusions of numerous scientific bodies that “[c]onvincing evidence has not yet demonstrated the existence of a threshold.
Low-level, or “low-dose,” radiation is generally defined as a dose range of 10 rem and below. However, “low dose” is something of a misnomer, as 10 rem is still relatively high. Even when doses are low, they nonetheless cause substantial harm when spread across a large population over time, especially for sensitive groups like children.
Raising radiation exposure limits. If President Trump’s executive order results in a new public radiation exposure limit of around 10 rem—the level LNT opponents often advocate—the increased health risks would be extraordinary. Longstanding radiation protection limits for members of the public are in the range of 10 to 100 millirem (0.01 to 0.1 rem) per year. A 10-rem limit would increase allowed exposures to radiation by factors of 100 to 1000—and so would increase the risk of cancer.
A single chest X-ray is about 2 millirem (0.002 rem) of radiation exposure. An annual limit of 10 rem would correspond to a person receiving a dose equivalent to 5,000 chest X-rays each year, from conception to death. Current official radiation risk estimates—adopted by EPA from the National Academies’ BEIR VII study on the health risks from exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation—indicate that receiving 10 rem per year over a 70-year lifetime would result in about four out of every five people exposed getting a cancer they would not get otherwise.
Despite what opponents of the LNT model claim, there is no threshold at 10 rem below which there is no measurable health harm. A substantial body of scientific work has demonstrated significant negative health impacts well below 10 rem. Beginning in the 1950s, pioneering Oxford researcher Alice Stewart demonstrated that a single fetal X-ray with a dose of 200 millirem (0.2 rem) was associated with a measurable increase in the risk of that child dying of cancer. The radiation establishment fought Stewart’s findings vigorously, but her research has long since been vindicated.
More recently, a major study covering an international cohort of over 300,000 nuclear facility workers has found that annual doses well below 1 rem create measurable increases in the risk of developing a variety of cancers, and that, as NRC put it, “even tiny doses slightly boost the risk of leukemia.” A second massive study of nearly one million European children found that those who received a CT scan, at an average dose of 800 millirem (0.8 rem), suffered a measurable increase in their risk of getting cancer.
Standards already weak. Radiation protection standards should be tightened, not weakened. The US government has a long history of underestimating radiation risks. The more scientists have learned about low-dose radiation, the more their estimates of the risk per unit dose have tended to increase. Yet the NRC has not updated in step with the science.
The NRC protection limit for workers of 5 rem per year was set in the early 1960s and has not changed since, despite decades of increasing official estimates of radiation risk. The current best estimate, from the National Academies’ BEIR VII, indicates that one out of every five workers receiving the NRC’s allowable dose each year from ages 18 to 65 would develop a cancer.
NRC’s radiation exposure limits for the public have not been updated in 35 years. Despite a requirement to employ EPA’s more conservative radiation risk standards, the NRC has long ignored it and instead continues to use 100 millirem per year—100 times lower than what Trump’s executive order could lead to. Current risk figures from the National Academies and the EPA indicate that 70 years of exposure at that level would result in nearly one in 100 people getting cancer from that exposure. That is 100 to 10,000 times higher than the EPA’s acceptable risk range. As the former director of EPA’s Office of Radiation and Indoor Air said years ago, “To put it bluntly, radiation should not be treated as a privileged pollutant. You and I should not be exposed to higher risks from radiation sites than we should be from sites which had contained any other environmental pollutant.”
The NRC held a webinar in July to gather public feedback on implementing President Trump’s executive order on abolishing the LNT model. Many presenters—including representatives from the National Council on Radiation Protection and the Union of Concerned Scientists—gave a vigorous defense of the LNT model, as did many of the comments from the public. Yet the NRC, despite itself having strongly reaffirmed this standard only 4 years ago, seemed to minimize low-dose radiation risks and suggested that all radiation cancer risk models be treated equally (including the long-discredited view that low-dose radiation has health benefits). More concerning, the NRC has put its thumb on the scale, giving special treatment to LNT opposition by posting among the general meeting materials a link to one presenter’s paper, which suggests that an annual dose of 10 rem is acceptably safe.
At a time when radiation protection should be strengthened, President Trump has directed action to weaken it markedly. If the NRC implements the executive order, the potential outcome would be a new, deeply flawed radiation standard as much as a thousand times weaker than the current standard, resulting in a massive increase in radiation-related health hazards across the American population.
Zionism: The Etymological and Ideological Unpacking of a “Political Pathogen”

22 January 2026 Dr Andrew Klein, P https://theaimn.net/zionism-the-etymological-and-ideological-unpacking-of-a-political-pathogen/
The term “Zionism,” the modern political ideology advocating for a Jewish homeland in Palestine, is often analysed through the lenses of history, politics, and conflict. However, to understand its full potency and impact – to see it as a “political pathogen” – we must first dissect the linguistic and cultural DNA from which it was synthesised. This paper posits that Zionism is a European ideological construct, born of a specific historical moment, which instrumentalised ancient religious and cultural symbols to forge a modern nationalist movement. Its power and subsequent global impact stem from this fusion of the ancient and the modern, a fusion that has proven both resilient and, in the view of its critics, deeply destructive.
I. The Etymological Core: From Sacred Hill to Nationalist Ideology
The linguistic root of “Zionism” is the Hebrew word “Zion” (Ṣîyyôn), originally referring to a specific hill in Jerusalem. Over millennia, particularly following the Babylonian Exile, “Zion” transformed from a geographic location into a potent synecdoche and poetic symbol for the entire Land of Israel and the Jewish people’s spiritual yearning for return. This meaning was deeply embedded in Jewish messianic belief, envisioning a future redemption.
The transformation into a modern political “-ism” occurred in late 19th-century Europe. The term “Zionism” (Zionismus) is first credibly attributed to the Austrian Jewish intellectual Nathan Birnbaum in an 1890 article. It was coined in reference to the activities of the Hovevei Zion (“Lovers of Zion”), proto-Zionist groups that promoted Jewish agricultural settlement in Ottoman Palestine. The movement was catapulted onto the world stage by Theodor Herzl, whose 1896 pamphlet Der Judenstaat (The Jewish State) and the subsequent founding of the Zionist Organization in 1897 popularised the term and defined its political objectives. The choice of “Zion” was deliberate: it grafted the new secular nationalist project onto the deep-rooted, sacred longings of Jewish tradition, providing an immediate and powerful historical legitimacy.
II. The European Crucible: Birth of an Ideology
Zionism did not emerge in a vacuum. It was a direct product of, and reaction to, the specific conditions of European society in the 19th century.
The “Jewish Question” in Europe: Zionism arose as one answer to the pervasive “Jewish Question” – the problem of how Jews, perceived as an unassimilable minority, could exist within European nation-states defined by ethnic homogeneity. Faced with persistent antisemitism, from violent pogroms in Eastern Europe to institutional discrimination in the West, thinkers like Herzl concluded that assimilation was impossible and that Jews constituted a distinct nation requiring sovereignty in their own land.
The Influence of European Nationalism: Zionism was fundamentally shaped by the Romantic nationalist movements sweeping Europe, which argued that every “people” or “nation” (Volk) required a state for its full expression. Zionists applied this model to Jews, asserting their right to national self-determination. The movement also internalised contemporary colonial and racial thinking, with early leaders at times explicitly framing a Jewish state in Palestine as a European outpost or “colonial” endeavour that would bring progress to the region.
Internal Jewish Debates: It is critical to note that Zionism was a contested ideology from its inception. Significant Jewish movements, most notably the socialist Bund in Eastern Europe, vehemently opposed it. These anti-Zionists argued that fleeing antisemitism validated the persecutors’ logic, that the diaspora was a legitimate and rich Jewish homeland, and that the future lay in fighting for socialist revolution and equality within Europe.
III. The Ideological Structure: Core Tenets and Internal Divergence
While unified by the core goal of a Jewish homeland, Zionism was never monolithic. Its internal structure comprised several competing strands:
Political Zionism (Herzl): Focused on achieving a Jewish state through high-level diplomacy and international legal charters.
Practical Zionism: Emphasized the “conquest of land” through immediate agricultural settlement in Palestine.
Labor Zionism: Merged socialist principles with nation-building, promoting collective enterprises like the kibbutz and forming the ideological backbone of Israel’s early leadership.
Revisionist Zionism (Jabotinsky): Advocated for a more militant, maximalist approach to establishing a Jewish state on both banks of the Jordan River, emphasizing military strength and capitalist development.
Cultural Zionism (Ahad Ha’am): Prioritised the creation of a new Jewish spiritual and cultural center in Palestine over immediate political sovereignty.
Religious Zionism: Fused Jewish religious messianism with nationalist politics, viewing the Zionist project as the beginning of divine redemption.
Despite these differences, a critical consensus emerged across most Zionist thought: the necessity of establishing a Jewish demographic majority in Palestine. This demographic imperative, confronting the reality of a majority Arab population, led to the conceptualisation of “transfer” – a euphemism for the removal or ethnic cleansing of Palestinians – as a logical, if debated, solution within mainstream Zionist discourse from the movement’s early decades.
IV. The “Pathogen” Metaphor: Mechanisms of Global Impact
Viewing Zionism through the lens of a “political pathogen” requires examining its replication and impact beyond Palestine/Israel. Its global influence operates through several key mechanisms:
The Logic of Domination: Scholar Vincent Lloyd reframes Zionism’s outcome as a transition from a movement seeking liberation from European domination to one that institutes a new structure of domination over Palestinians. This system is maintained through military occupation, legal discrimination, and the systemic denial of Palestinian dignity and political rights.
Christian Zionist Symbiosis: A critical vector for the ideology’s spread is Christian Zionism, particularly within Protestant evangelicalism. This theology supports Jewish return to Israel not out of solidarity with Jews, but as a prerequisite for the Second Coming of Christ, after which non-converted Jews are often envisioned to be destroyed. This creates a powerful, theologically motivated political lobby (especially in the United States) that reinforces Israeli state policy.
Global Export of “Security” Models: Israel has leveraged its experience controlling Palestinian populations to become a leading global exporter of surveillance technology, weapons, and counter-insurgency tactics. This “laboratory” of repression markets its products to other states and regimes, embedding Zionist-derived models of population control into global security infrastructures.
Conflating Critique with Antisemitism: A potent defensive mechanism has been the strategic effort to equate criticism of Zionism or Israeli state policy with antisemitism, as seen in debates over definitions like the IHRA working definition. This conflation seeks to immunise the ideology from political critique by framing opposition as a form of racial or religious hatred.
Conclusion: A Tale That Found a Home
Zionism is indeed “a tale that found a home.” It is a modern European nationalist tale, constructed from the ancient lexicon of Jewish prophecy and the contemporary grammar of 19th-century racial and colonial thought. It found a home through a deliberate and violent process of settlement and state-building, necessitating the displacement and continued subjugation of another people.
Its “pathogenic” quality lies in its resilience and adaptability – its ability to graft itself onto different host ideologies, from socialist pioneering to evangelical Christian millennialism, and to replicate its core logic of ethnic dominance in new contexts. The language that shaped it provided a bridge between deep history and political modernity, creating an ideology of immense persuasive power and tragic consequence. To understand the ongoing conflict and its global resonances, one must first understand this foundational synthesis of word, idea, and power.
References…………………………..
This Nuclear Renaissance Has a Waste Management Problem

12 Jan, 26, https://energyathaas.wordpress.com/2026/01/12/this-nuclear-renaissance-has-a-waste-management-problem/
Three sobering facts about nuclear waste in the United States.
Americans are getting re-excited about nuclear power. President Trump has signed four executive orders aiming to speed up nuclear reactor licensing and quadruple nuclear capacity by 2050. Big tech firms ( e.g. Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Meta) have signed big contracts with nuclear energy producers to fuel their power-hungry data centers. The federal government has signed a deal with Westinghouse to build at least $80 billion of new reactors across the country. Bill Gates has proclaimed that the “future of energy is sub-atomic”.
It’s easy to see the appeal of nuclear energy. Nuclear reactors generate reliable, 24/7 electricity while generating no greenhouse gas emissions or local air pollution. But these reactors also generate some of the most hazardous substances on earth. In the current excitement around an American nuclear renaissance, the formidable challenges around managing long-lived radioactive waste streams are often not mentioned or framed as a solved problem. This problem is not solved. If we are going to usher in a nuclear renaissance in this country, I hope we can keep three sobering facts top-of-mind.
Fact 1: Nuclear fission generates waste that is radioactive for a very long time.
After 4-6 years of hard work in a commercial fission reactor, nuclear fuel can no longer generate energy efficiently and needs to be replaced. When this “spent” fuel comes out of the reactor it is highly radioactive and intensely hot, so it must be carefully transferred into deep pools where it spends a few years cooling off…

Once cooled, this spent fuel is still not something you want to spend time with because direct exposure is lethal. While most of the radioactivity decays after about 1000 years, some will persist for over a million years. U.S. efforts to site and build a permanent repository for nuclear waste have failed (more on this below). After spending time in the pool, spent fuel is stored on sites of operating or retired reactors in steel canisters or vaults.

Across the country, more than 90,000 metric tons of radioactive fuel is sitting in pools or dry storage at over 100 sites in 39 states. These sites are licensed by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) and regulated by the EPA. They are designed to be safe! But experts agree that this is an unacceptable long-term waste management situation (see, for example, here, here, and here).
Fact 2: The U.S. has no permanent nuclear waste disposal plan
For more than half a century, the United States has tried—and failed—to find a forever-home for its nuclear waste. Early efforts in the 1960s and 1970s went nowhere. In 1982, Congress passed the Nuclear Waste Policy Act which laid out a comparative siting process that was designed to be technically rigorous and politically fair. But this process was slow, expensive, and politically exhausting.
By 1987, Congress lost patience, scrapped its own framework, and tried to force the issue by designating Yucca Mountain in Nevada as the chosen one. Nevada’s resistance was relentless. After roughly $15 billion in spending on site development, the Yucca Mountain proposal was finally withdrawn in 2010. As I understand it, these siting efforts did not fail because the location was declared unsafe. They failed because nuclear waste storage siting was being forced on an unwilling community.
In the years since, Blue Ribbon panels, expert advisory groups, and national research councils have been convened. All have reached the same conclusion. The U.S. needs to break the impasse over a permanent solution for commercial spent nuclear fuel and this will require a fair, transparent, and consent-based process.
You might be thinking that spent fuel reprocessing, which is also enjoying an American renaissance right now, could eliminate the need for a geological repository. It’s true that reprocessing breaks spent fuel down to be used again. But in that process, new types of radioactive wastes are created that need to be managed in deep repositories or specialized landfills. This creates a potentially more (versus less) challenging mess to clean up (reprocessing leaders like France are pursuing costly geological repositories for these wastes).
Fact 3: We are actively undermining public trust in the nuclear waste management process
Convincing a community to host thousands of tons of radioactive waste for thousands of years is not easy. But it’s not impossible. Efforts in Sweden, Finland, France, Switzerland, and Canada are starting to find some success.
All of these international success stories share one important feature: a sustained commitment to building public trust in both nuclear industry regulation and the nuclear waste storage siting process. Alas, here in the United States, we seem to be moving in the opposite direction.
A series of recent developments make it hard to feel hakuna matata about our nuclear waste management protocols:
- In May, an executive order called for a “wholesale revision” of the NRC directing it to accelerate reactor licensing, reconsider radiation standards, and reduce staffing.
- In June, an NRC commissioner was abruptly fired, prompting a letter from concerned career staff .
- The Department of Energy has pledged to “use all available authorities to eliminate or expedite its environmental reviews for authorizations, permits, approvals, leases, and any other activity requested” by nuclear reactor projects under its supervision.
- The Supreme Court recently ruled that Texas lacks legal standing to challenge NRC approval of a privately operated interim nuclear waste facility, raising questions about state’s abilities to challenge nuclear waste siting decisions.
These developments may ultimately succeed in accelerating nuclear deployment across the United States. But they also undermine the public trust and independent governance that are essential inputs into the building of a long-term nuclear waste management strategy.
Weighing our nuclear options
Taking a step back, it is worth asking why nuclear energy is enjoying such a resurgence in this country right now. The growing availability of low-cost renewables and storage, together with an increasingly flexible demand-side, complicates the claim that nuclear power is some kind of moral climate necessity. There are cheaper ways to decarbonize the grid.
The renewed push for nuclear energy is not really about climate necessity. It seems to be driven by anxiety about reliability in a strained power system, industrial policy aimed at rebuilding domestic manufacturing capacity, and the commercial interests of firms chasing revenue streams tied to data centers and federal support. This nuclear revival trades off today’s politically urgent reliability concerns for a long-term obligation to manage radioactive waste (along with some low-probability risk of catastrophic failure). If that’s the trade off we want to make, we should understand that a nuclear renaissance without a viable long-term waste management plan saddles future generations with the messy consequences of our policy choices.
US 21st Century regime change ops: Failure, Failure, Failure, Failure, Failure… To Be Determined

5 January 2026 AIMN Editorial , By Walt Zlotow, West Suburban Peace Coalition, Glen Ellyn, IL, https://theaimn.net/us-21st-century-regime-change-ops-failure-failure-failure-failure-failure-to-be-determined/
The US has spent the entire 21st century toppling regimes it hates. Every one up to Saturday’s removal of Venezuelan president Nicholas Maduro has ended in failure.
2001 Afghanistan
President George W. Bush kicked off the 21st century by changing out the Taliban regime in Afghanistan. America could not confront the real culprit of 911, ally Saudi Arabia, so we picked an easy scapegoat to extract our revenge. It only took 5 weeks to topple the Taliban, allowing installation of a US puppet government. Result? Taliban regrouped to win their country back. Took 20 years but this time it was the hated Yankees ousted, killing 2,461 Americans in the process. America left the failed state of Afghanistan with over 150,000 dead and Afghanistan’s 42 million people worse off than before American’s criminal regime change operation.
2003 Iraq
Bush turned next to hated Iraq to one up Poppy Bush’s failure to oust Saddam Hussein 1991. His regime change turned Iraq into a failed state with over 500,000 Iraqis and 5,984 American soldiers and contractors killed. Over 100,000 Americans were injured in body and mind from in a totally made up, senseless war. Twenty-three years later the US is still defiling Iraqi sovereignty with a couple of thousand soldiers stuck in the Iraq war roach motel.
2011 Libya
George W. Bush’s successor Barack Obama got into regime change business to knock off Libyan strongman Muammar Gaddafi. He employed so called defense alliance NATO to bomb Libby during the Libyan civil war to tip the scales against Gaddafi. Obama’s Secretary of State Hillary Clinton gloated, “We came, we saw, he died”, failing to mention this death resulted from a bayonet to the butt. The US achieved the complete opposite of its intended goal of Libyan and regional stability by turning Libya into one of the most chaotic, failed states on the planet.
2013 Syria
Just 2 years later Obama was at it again, this time intervening in the Syrian civil war, supporting jihadist terrorists to depose hated Syrian President Bashar Assad. Neither Obama nor successor Trump could complete the task finally achieved by President Joe Biden in his last 2 months. US intervention was primarily designed to rid puppet master Israel of one of its regional hegemonic rivals. By prolonging the Syrian civil war for 11 years, the US contributed mightily to the civil war’s half million deaths. Led by new US pal, former US designated al-Qaeda terrorist Ahmed al-Sharaa, Christians, Druze and Alawites are being systematically hunted down and killed by the US backed al-Sharaa regime.
2022 Russia
The US and NATO spent 14 years under 4 presidents provoking Russia to invade Ukraine to keep Ukraine out of NATO. The US knew Russia would eventually invade; indeed, also knew Ukraine could not prevail against the Russian goliath. Didn’t matter. The US believed the war would so weaken Russia it might topple despised President Vladimir Putin, bringing in a Russian puppet amenable to US influence. Four years on Russia and Putin are stronger than ever, pivoting away from Europe to the non-aligned world seeking independence from a war and sanctions crazed America. Ukraine is now a failed state near totally dependent on US, NATO treasure to survive. A fifth of its land is gone forever, soon to be joined by its last warm water port. Looks like the only regime to be removed is Ukraine’s, not Russia’s.
2026 Venezuela
In his first solo adventure in regime change, President Trump kicked off 2026 with a lightning assault that snatched Venezuelan President Nicholas Maduro out of Venezuela to face a Trump style show trial in the US. Trump and his war cabinet are positively ecstatic about completing America’s two decade crusade to snuff out socialism in Venezuela and gobble up its 300 billion barrels of heavy crude in the process. But they might look back at America’s 21st century regime change failures in Afghanistan, Iraq, Libya, Syria, Russia, and ponder whether they’re simply following previous administrations down the rabbit hole of regime change failure.
How are geological repository projects progressing?


COMMENT. This story is from the nuclear industry’s online publication “World Nuclear News”, so important to recognize that there is a bias throughout. And errors. For example, it erroneously describes the Nuclear Waste Management Organization as a government agency.
By Alex Hunt, World Nuclear News, in Vienna, Sunday, 28 December 2025
A growing number of countries are planning a permanent solution to the issue of radioactive waste by burying it deep underground. Schemes take many years to plan, and many more years to build, but progress is being made.
Setting the scene: Why deep geological repository projects matter
A deep geological repository comprises a network of highly-engineered underground vaults and tunnels built to permanently dispose of higher activity radioactive waste so that no harmful levels of radiation ever reach the surface environment. They need to be located deep enough, and in suitable geological conditions, to ensure they will be safely secured for thousands of centuries.
The disposal of used nuclear fuel and other high-level waste has long been a pressing issue in terms of the perceived sustainability of nuclear energy programmes. For many decades this material has been stored [?]safely in pools or special containers and facilities at surface, or near-surface, locations, often close by nuclear power plants. These are seen as interim storage measures pending a permanent solution.
Hildegarde Vandenhove, Director of the IAEA Division of Radiation Safety, Transport and Waste Safety…………..” developing these facilities is a long and a complex process. It requires rigorous studies and extensive safety demonstrations. These are all first-of-a-kind facilities, and their construction takes time.“
The process of selecting a site, and getting approval for it, takes decades, with Anna Clark, head of the Waste and Environmental Safety Section in the Division of Radiation Transport and Waste Safety at the IAEA, saying that “before operations can begin, there’s a lengthy pre-operational phase with conceptual design, the planning, the surveys, the site investigations, site selection, narrowing down the number of sites, doing detailed characterisation of your preferred site, it’s a long process before you even begin with the licensing of construction. And throughout that period, the safety case evolves and the role of the regulator also evolves, and the regulators have to adapt their expertise and knowledge as they go”.
Canada
Colin Moses, Vice-President, Regulatory Affairs, and Chief Communications Officer at the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission, outlined the status of the country’s deep geological repository which, he noted, started being discussed in the 1970s. It is being taken forward by the Nuclear Waste Management Organization, a government agency fully funded by the producers of waste with a mandate to determine and find and build and operate a long-term solution for disposal of used fuel in Canada.
Its concept is for a “geosphere which forms a natural barrier of rock to protect the waste from disruptive natural events, water flow and human intrusion”.
The current status is that Wabigoon Lake Ojibway Nation and the Township of Ignace were selected in November 2024 as the host communities for the proposed repository, following a consent-based siting process that had begun some 14 years earlier. Pre-licensing activities, including stakeholder engagement, pre-environmental assessment and technical reviews, have been taking place.
Construction of the facility will only begin once the deep geological repository has successfully completed the federal government’s multi-year regulatory process and the Indigenous-led Regulatory Assessment and Approval Process, a sovereign regulatory process that will be developed and implemented by Wabigoon Lake Ojibway Nation.
The Nuclear Waste Management Organization explored more than 20 different potential locations in Canada looking for local communities to raise their hand and express an interest in potentially hosting the repository, with the last decade spent refining that list down to the one preferred site.
Moses said he was expecting the formal regulatory process to begin this year and “will play out over several years, looking to give an initial decision in 2030. That will allow them to advance construction in 2032, move into operation in 2042 and ultimately to operate that facility for many decades, expecting a current closure date of 2092”.
and ultimately to operate that facility for many decades, expecting a current closure date of 2092″.
“So this is a project that’s playing out over multiple decades and has spent multiple decades getting ready.”
Finland
Progress is furthest advanced with Finland’s Onkalo project. Petteri Tiippana, Director General of the Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority of Finland (STUK) outlined the concept, which is a repository in crystalline rock with used fuel in copper canisters surrounded by a bentonite buffer at a depth of 400-430 metres.
For Finland, which is currently in the process of commissioning the deep geological repository, the process began in the 1980s with the then government setting a target for operation in the 2020s. Pre-licensing activities started almost immediately, Tiippana said, in terms of research and design and for the concept, with actual licensing steps beginning in the early 2000s with a site selection. A construction licence was issued in 2015.
Currently the encapsulation plant has been commissioned and tested the dummy fuel elements in five canisters and transported them to the underground facility. The next phase will be to “test the underground facility and the final disposal of those five copper cases”. He said that the reviewing of safety documentation is approaching its final stages and the aim is for a decision next year, with operations then starting.
See how Finland’s project will work:
France
France plans to construct the Centre Industriel de Stockage Géologique (Cigéo) repository – an underground system of disposal tunnels – in a natural layer of clay near Bure, to the east of Paris in the Meuse/Haute Marne area. The plan is to dispose of 10,000 cubic metres of high level waste and 75,000 cubic metres of intermediate-level waste.
Jean-Luc Lachaume, Commissioner of the French Authority for Nuclear Safety and Radiation Protection (ASNR), said that, as with other countries, there had been decades of work already on developing the repository, with parliamentary debates about it beginning in the 1980s, before a decision 20 years ago to go ahead with a deep geological repository.
The milestone of the construction licence application being submitted happened in 2023, since when it has been under review. A technical review was completed in June and ASNR issued a favourable opinion on the application earlier this month.
This will be followed by the consultation phase and public inquiry in 2026 and a potential licence granting in 2027 or 2028, with a target first operation of the pilot phase in 2035.
Sweden
A site has been selected at Fosmark, 150 kilometres north of Stockholm. Surface works have been taking place and the application to start underground excavation was submitted in January 2025 and is currently being considered. The concept for Sweden is the repository to be at a depth of 500 metres, in crystalline rock, with copper canisters each surrounded by bentonite clay to keep groundwater away from the canister and to provide a barrier to any potential leakage of radioactive material.
As with all countries, there has been decades of preparation and discussion, with regulatory licensing reviews and court hearings from 2011 to 2018 prior to government approval being issued in 2022……………………………..
Switzerland
Switzerland is in the final stage of the site selection process, which began in 2008, with national and international participation. The plan is for a combined repository for high- low- and Intermediate-level waste, with a general licence application submitted and due to be considered by 2027 with a government decision targeted for 2029.
Marc Kenzelmann, Director General of the Swiss Federal Nuclear Safety Inspectorate, outlined the background to the site selection, noting that Switzerland was a country about 7% the size of Texas, with two thirds of its area covered in mountains, so unusable for a high-level waste repository because the Alps could rise by a kilometre over the next million years, which is “the time frame that we have set for a safe, deep geological repository. So the Alps have an active geology, but what we need is a boring geology”.
This has meant that the location search was focused on the area near to the German border, so “we have involved Germany from the very start of the selection process”. He said that one issue was making sure to take the time and effort to build up stakeholder trust. In their case there have also been some unique differences of public opinion, with “Swiss people generally less concerned than German people” about the issue.
In November 2024 Switzerland’s national radioactive waste disposal cooperative Nagra applied to the Swiss Federal Office of Energy for a general permit for the construction of the planned deep geological repository for radioactive waste at Nördlich Lägern in northern Switzerland, and a used nuclear fuel encapsulation plant at the existing Zwilag interim storage facility in Würenlingen in the canton of Aargau.
According to current planning, the Federal Council will decide on the application in 2029 and Parliament in 2030. A national referendum is expected to take place in 2031.
Once the general authorisation for the repository comes into force, geological studies will be carried out underground in the area of implantation (through the creation of an underground laboratory), with the aim of acquiring more in-depth knowledge with a view to the construction of the repository. The application for a building permit, then later the application for an operating permit, can then be submitted. According to current planning, the repository could come into operation and the first radioactive waste could be stored there from 2050.
The USA
Yucca Mountain has since 1987 been named in the US Nuclear Waste Policy Act as the sole initial repository for disposal of the country’s used nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive wastes. The DOE submitted a construction licence application to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission in 2008, but the Obama Administration subsequently decided to abort the project and there have been various twists and turns since then, with the upshot that it has not been built.
Mike King, Executive Director for Operations at the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission, said the current status of its high-level waste disposal programme is that NRC staff had reviewed the US Department of Energy’s application for a repository at Yucca Mountain and staff completed its Safety Evaluation Report more than a decade ago and concluded it met safety standards “however there were two remaining environmental and programmatic pull points that prevented the final authorisation” and since 2016 funding has been halted and there are no activities taking place on it other than record-keeping, and the licensing process is currently suspended.
The general thrust of the discussion was that there needs to be a clear delineation of responsibilities for the project, with long-term planning and clear public consultation and decision-making processes to ensure there is community trust in the decision making process……………………………………………https://www.world-nuclear-news.org/articles/how-are-geological-repository-projects-progressing
The Real Story Behind the Russia–Ukraine War—and What Happens Next
local Ukrainian nationalists joined Hitler’s Wehrmacht in its depredations against Jews, Poles, Roma and Russians when it first swept through the country from the west on its way to Stalingrad; and then, in turn, the Russian populations from the Donbas and south campaigned with the Red Army during its vengeance-wreaking return from the east after winning the bloody 1943 battle of Stalingrad that turned the course of WWII.
As Washington sleepwalks deeper into conflicts that have nothing to do with genuine US security, the stakes for ordinary Americans grow higher by the day.
by David Stockman, Doug Casey’s International Man , 27 Dec 25
Notwithstanding the historic fluidity of borders, there is no case whatsoever that Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 was “unprovoked” and unrelated to NATO’s own transparent provocations in the region.
The details are arrayed below, but the larger issue needs be addressed first.
Namely, is there any reason to believe that Russia is an expansionist power looking to gobble up neighbors which were not integral parts of its own historic evolution, as is the case with Ukraine?
After all, if despite Rubio’s treachery President Trump does manage to strike a Ukraine peace and partition deal with Putin you can be sure that the neocons will come charging in with a false Munich appeasement analogy.
The answer, however, is a resounding no!
Our firm rebuke of the hoary Munich analogy as it has been falsely applied to Putin is based on what might be called the double-digit rule. To wit, the true expansionary hegemons of modern history have spent huge parts of their GDP on defense because that’s what it takes to support the military infrastructure and logistics required for invasion and occupation of foreign lands.
For instance, here are the figures for military spending by Nazi Germany from 1935–1944 expressed as a percent of GDP. This is what an aggressive hegemon looks like in the ramp-up to war: German military spending had already reach 23% of GDP, even before its invasion of Poland in September 1939 and its subsequent commencement of actual military campaigns of invasion and occupation.
Not surprisingly, the same kind of claim on resources occurred when the United States took it upon itself to counter the aggression of Germany and Japan on a global basis. By 1944 defense spending was equal to 40% of America’s GDP, and would have totaled more than $2 trillion per year in present day dollars of purchasing power.
Military Spending As A Percent Of GDP In Nazi Germany
- 1935: 8%.
- 1936: 13%.
- 1937: 13%.
- 1938: 17%.
- 1939: 23%.
- 1940: 38%.
- 1941: 47%.
- 1942: 55%.
- 1943: 61%.
- 1944: 75%
By contrast, during the final year before Washington/NATO triggered the Ukraine proxy war in February 2022, the Russian military budget was $65 billion, which amounted to just 3.5% of its GDP.
Moreover, the prior years showed no build-up of the kind that has always accompanied historic aggressors. For the period 1992 to 2022, for instance, the average military spending by Russia was 3.8% of GDP– with a minimum of 2.7% in 1998 and a maximum of 5.4% in 2016.
Needless to say, you don’t invade the Baltics or Poland—to say nothing of Germany, France, the Benelux and crossing the English Channel—on 3.5% of GDP! Not even remotely.
Since full scale war broke out in 2022 Russian military spending has increased significantly to 6% of GDP, but all of that is being consumed by the Demolition Derby in Ukraine—barely 100 miles from its own border.
That is, even at 6% of GDP Russia has not yet been able to subdue its own historic borderlands. So if Russia self-evidently does not have the economic and military capacity to conquer its non-Ukrainian neighbors in its own region, let alone Europe proper, what is the war really about?
Continue readingThe first Zionist targeted assassination – 1924

Eli Ku, Aug 25, 2025, https://lenabloch.medium.com/the-first-zionist-targeted-assassination-was-of-the-orthodox-jewish-peace-negotiator-jaacob-israel-de5b0eb7844b
The first Zionist targeted assassination was of the Orthodox Jewish peace negotiator, Jaacob Israel De Haan, in 1924. Jewish terrorists unleashed a brutal terror campaign on Palestinians and the British, with bombings, assassinations, pogroms of Arab businesses and villages, destruction of civilian places of commonality, sabotaging railroads.
“By the time the Balfour Declaration was finalised, thirty-plus years of Zionist settlement had made clear that the Zionists intended to ethnically cleanse the land for a settler state based on racial superiority; and it was the behind-the-scenes demands of the principal Zionist leaders, notably Chaim Weizmann and Baron Rothschild.
First-hand accounts of Zionist settlement in Palestine had already painted a picture of violent racial displacement. I will cite one of the lesser known reports, by Dr. Paul Nathan, a prominent Jewish leader in Berlin, who went to Palestine on behalf of the German Jewish National Relief Association. He was so horrified by what he found that he published a pamphlet in January, 1914, in which he described the Zionist settlers as carrying on
“a campaign of terror modelled almost on Russian pogrom models [against settlers refusing to adopt Hebrew].”
A few years later, the Balfour Declaration’s deliberately ambiguous wording was being finalized. Sceptics—and the British Cabinet—were assured that it did not mean a Zionist state. Yet simultaneously, Weizmann was pushing to create that very state immediately. He demanded that his state extend all the way to the Jordan River within three or four years of the Declaration—that is, by 1921—and then expand beyond it.
In their behind-the-scenes meetings, Weizmann and Rothschild treated the ethnic cleansing of non-Jewish Palestinians as indispensable to their plans, and they repeatedly complained to the British that the settlers were not being treated preferentially enough over the Palestinians. And they insisted that the British must lie about the scheme until it is too late for anyone to do anything about it.
In correspondence with Balfour, Weizmann justified his lies by slandering the Palestinians and Jews—that is, the Middle East’s indigenous Jews, who were overwhelmingly opposed to Zionism and whom Weizmann smeared with classic anti-Semitic stereotypes. The Palestinians he dismissed as, in so many words, a lower type of human, and this was among the reasons he and other Zionist leaders used for refusing democracy in Palestine—if the “Arabs” had the vote, he said, it would lower the Jew down to the level of a “native”.
With the establishment of the British Mandate, four decades of peaceful Palestinian resistance had proved futile, and armed Palestinian resistance—which included terrorism—began. Zionist terror became the domain of formal organizations that attacked anyone in the way of its messianic goals—Palestinian, Jew, or British. These terror organizations operated from within the Zionist settlements and were actively empowered and shielded by the settlements and the Jewish Agency, the recognized semi-autonomous government of the Zionist settlements, what would become the Israeli government.
There was no substantive difference between the acknowledged terror organizations—most famously, the Irgun, and Lehi, the so-called Stern Gang—and the Jewish Agency, and its terror gang, the Hagana. The Agency cooperated, collaborated, and even helped finance the Irgun.
The relationship between the Jewish Agency, and the Irgun and Lehi, was symbiotic. The Irgun in particular would act on behalf of the Hagana so that the Jewish Agency could feign innocence. The Agency would then tell the British that they condemn the terror, while steadfastly refusing any cooperation against it, indeed doing what they could to shield it.
The fascist nature of the Zionist enterprise was apparent both to US and British intelligence. The Jewish Agency tolerated no dissent and sought to dictate the fates of all Jews. Children were radicalised as part of the methodology of all three major organizations, and by extension, the Jewish Agency.”
Thomas Suarez, London House of Lords, December 2016.
Fire at Windscale piles

Does Britain Really Ned Nuclear Power? by Ian Fairlea, beyondnuclearinternational
“…………………………………………………………….In 1957, a major fire occurred at Windscale nuclear site (what is now known as Sellafield). The effects of the Windscale fire were hushed up at the time but it is now recognised as one of the world’s worst nuclear accidents. An official statement in 1957 said: ‘There was not a large amount of radiation released. The amount was not hazardous and in fact it was carried out to sea by the wind.’ The truth, kept hidden for over thirty years, was that a large quantity of hazardous radioactivity was blown east and south east, across most of England.
After years of accidents and leaks, several of them serious, and regular cover-up attempts by both the management and government, it was decided to change the plant’s name in 1981 to Sellafield, presumably in the hope that the public would forget about Windscale and the accident.
When, in 1983, Greenpeace divers discovered highly radioactive waste being discharged into the sea through a pipeline at Sellafield and tried to block it, British Nuclear Fuels Ltd (BNFL), who then operated the site, repeatedly took Greenpeace to the High Court to try to stop them and to sequestrate its assets. The first generation of British Magnox nuclear power stations were all secretly designed with the dual purpose of plutonium and electricity production in mind.
Some people think that because plutonium is no longer needed by the UK to make weapons as it already has huge stocks of weapons grade plutonium, there no longer is any connection between nuclear weapons and nuclear energy. This is incorrect: they remain inextricably linked. For example:
- All the processes at the front of the nuclear fuel cycle, i.e. uranium ore mining, uranium ore milling, uranium ore refining, and U-235 enrichment are still used for both power and military purposes.
- The UK factory at Capenhurst that makes nuclear fuel for reactors also makes nuclear fuel for nuclear (Trident and hunter-killer) submarines.
- Nuclear reactors are used to create tritium (the radioactive isotope of hydrogen) necessary for nuclear weapons.
………………………………………………………………………………………………… https://beyondnuclearinternational.org/2025/12/14/does-britain-really-need-nuclear-power/
Radioactive fertilizer and the nuclear industry

Gordon Edwards. 14 Dec 25
CORRECTION
I wrote that
“…selling raffinate as fertilizer goes on all the time from the world’s largest uranium refinery owned by Cameco, situated at Blind River on the north shore of Georgian Bay.”
This sentence is incorrect. Raffinate from Blind River is not used as fertilizer. I apologize for the error.
Radioactive fertilizer from the Canadian uranium industry does not come from the Cameco Blind River refinery but from two other sources – the Cameco Key Lake uranium mill in Northern Saskatchewan, and the Cameo uranium dioxide conversion facility at Port Hope Ontario.
Moreover, the material that is being used in radioactive fertilizer is not raffinate (i.e. refinery waste). It is ammonium sulphate that is recovered from the Key Lake uranium processing circuits and sold as fertilizer, together with a liquid by-product of Cameco’s Port Hope uranium dioxide conversion plant – an ammonium nitrate solution – that is sold to a local agricultural supply company for use in fertilizer production.
The use of similar waste solutions from nuclear fuel facilities as fertilizer has been a concern in other jurisdictions as well. So at the present time, it is not raffinate but ammonium compounds that have been used in uranium processing that ends up in fertilizer. I apologize for not checking the facts much more carefully..
About radioactive fertilizer and the nuclear industry.
A lot of the phosphate used for fertilizer comes from Florida where the phosphate ore is mined. That ore is contaminated with uranium and its decay products, especially radium. Radium disintegrates to produce radon gas Radon-222) and this builds up in an enclosed space, without adequate ventiliation, reaching an “equilibrium” in about one month.
That’s why Florida was the first “hot spot” that alerted the US government to the major public health hazard posed by radon, which is estimated to kill about 20-30 thousand Americans every year. Every atom of radon comes from the disintegration of a radium atom, and in turn, every atom of radium started out as an atom of uranium.
Radioactive quilibrium means #becquerels of radium = #becquerels of radon. One becquerel being one disintegration per second. In a simiar way, if pure radon gas is in an enclosed container, it will reach equilibrium with its four short-lived decay products in a couple of hours – so the radioactivity in the container is about five times greater than it was originally, as all the short-lived decay products have attained roughly the same level of radioactivity as the radon.
When this radioactive fertilizer is used on tobacco crops, the radon from the soil and the fertilizer builds up under the thick canopy of tobacco leaves and hangs there for a time (radon being 7-8 times heavier than air). The radon atoms disintegrate to produce four airborne solid short lived decay products – polonium-218, bismuth-214, lead-214, polonium-214, all of which decay into lead-210 and polonium-210. [Note: the last two nuclides never reach equilibrium, unlike the first four.]
These radon decay products stick to the resinous (sticky) hairs on the undersides of the tobacco leaves and when the tobacco is harvested these radioactive materials are harvested along with the tobacco. By the time the tobacco is cured, rolled, and packaged, small quantities of lead-210 (22-year half-life) and its immediate successor polonium-210 are left in the tobacco/cigarettes for the unwitting smoker (or second-hand-smoke inhaler) to encounter.
When the cigarette is lit and the smoker draws on it, the temperature at the tip increases dramatically and it vaporizes the lead-210 and polonium-210 which is inhaled deep into the lungs, where polonium-210 sticks to and attacks the sensitive lung tissue with its very energetic alpha particles.
Polonium-210 is a very damaging radionuclide which Los Alamos Labs reckons is about 250 billion time more toxic than hydrogen cyanide. (It’s what was used to murder Alexander Litvenenko in London at the “request” of Putin who was openly criticized by Litvenenko).
Polonium-210 adds greatly to the cancer-causing characteristic of the tobacco residues lodged in the lung, making cigarettes smoke significantly more carcinogenic than it would otherwise be. (When the smoker is not inhaling, the lead-210/polonium-210 is wafted into the second-hand cigarette smoke as a respirable aerosol to endanger the health of those within sniffing distance,)
Inside the lung, some of the inhaled polonium-210 crosses the blood-air barrier end enters the bloodstream. Being solid, it attaches to pre-existing plaque build-up in the arteries of the smoker, usually near the arterial valves, where the alpha particle bombardment causes fibrosis of the arterial wall and valve, thus exacerbating the plaque build-up and increasing the restriction of blood flow, thereby contributing substantially to the incidence of heart attacks and strokes among smokers because of the alpha emitting polonium-210 in the plaque.
What you may not have heard is that voluminous sand-like radioactive waste from the uranium industry, called “raffinate” (leftovers from uranium refining), is also sold as fertilizer on the open market without any warnings about the radioactive content. The justification for this nefarious practice seems to be, that since “natural” phosphate from Florids is used to make fertilizer, and it is clearly radioactive (due to the radium-radon chain), and since raffinate from a uranium refinery is not much higher in radioactive content, then what the heck, we (the uranium industry) may as well turn this sow’s ear into a silk purse by selling the radioactive raffinate waste as fertilizer.
Extensive radioactive contamination – involving uranium raffinate – of the homes, schools, roadways, ravines, and the public beach in the town of Port Hope (prior to 1985) – has led to a $2.6 billion radioactive environmental cleanup of the town (by the federal government) resulting in over a million cubic metres (about a million tonnes) of radioactibve waste to be stored for 500 years in a gigantic earthen mound just north of the town. The subsequent fate of the still-radioactive waste will be decided at that time.
This practice of selling raddinate as fertilizer goes on all the time from the world’s largest uranium refinery owned by Cameco, situated at Blind River on the north shore of Georgian Bay. The Blind RIver plant turns uranium mill concentrates from Saskatchewan, Australia and South Africa, called “yellowcake” (mostly U3O8), into a product called “uranium trioxide” UO3. At that point the raffinate is the waste product, contaminated with radium. That’s what’s sold for fertilizer.
The trioxide then goes to Port Hope Ontario, where it is chemically converted into UO2 (uranium dioxide) for domestic use, about 15% of the total, and into UF6 (uranium hexafluoride or “hex”) for export to enrichment plants outside of Canada where the concentration of U-235 is increased to the level required by the customer.
At the enrichment plant, the “hex” is turned into a gas at a fairly low temperature so that the heavier U-238 atoms can be separated from the lighter U-235 atoms, resulting in an enriched uranium product that goes out the front door while the voluminous discarded U-238 (called depleted uranium or “DU”) goes out the back door.
For low enrichment in light water nuclear power plants, about 85% of the refined uranium is discarded as depleted uranium. The DU has important military uses, and a few civilian uses, but for the most part DU is part of the radioactive legacy of the nuclear age wth a half-life of 4.5 billion years.
Besides using DU in conventional bullets, shells, missiles, tanks, et cetera, used in the former Yugoslavia and in other conflicts, resulting in a battlefield litters with radioactive waste, the military also uses DU as “target rods” in plutonium production reactors to breed plutonium for nuclear warheads. In addition, the military uses DU metal in almost all nuclear warheads as a way of significantly multiplying the explosive power of the warhead by a sizable factor. These weapons are called “fission-fusion-fission” weapons,
The first fission is from a small ball of plutonium (usually with a tritium “spark-plug” inside) whose sole purpose is to ignite the fusion reaction by raising it to a temperature of about 100 million degrees. When fusion occurs, extremely energetic neutrons are goven off which fission the U-238 that has been used for that exact purpose in the construction of the warhead. That third stage, the fission of U-238, provides the bulk of the explosive power and the lion’s share of the radioactive fallout.
It is a sad story from beginning to end.
And, to add to this tale of woe, Canada currently has about 220 million tonnes of radioactive waste (tailings) stored at or near the surface from uranium milling (the operation that produces yellowcake) along with about 167 million tonnes of radioactive “waste rock”. Yet the Canadian authorities and others routinely and unabashedly declare that nuclear power is a “clean” source of energy and for the most part, Canadian academic scientists and sientific bodies say not a peep to the contrary.
What to do with Britain’s radioactive waste?

by Ian Fairlea, beyondnuclearinternational .
“………………………………………………………………………………… Radioactive nuclear waste is produced by all nuclear activities. For example, uranium mining produces a great deal of waste in the form of ore spoil like all mining. Since uranium is radioactive, so are its ore wastes. So also are all the processes of refining the ore, enriching the uranium, turning it into fuel for reactors, transportation, burning it in nuclear power stations, processing the used fuel, and its handling and storage. They all create more nuclear waste.
The reason is that everything that comes into contact with radioactive materials, including the containers in which they are stored or moved and even the buildings in which they are handled, become contaminated with radioactivity or are activated by radiation
All radioactive waste is dangerous to human life as exposure to it can cause leukaemia and other cancers. It is usually categorised as low, intermediate or high-level waste. As the radioactivity level increases, so does the danger. Extremely high levels of radioactivity can kill anyone coming into contact with it – or just getting too close to it – within a matter of days or weeks.
Radioactive materials slowly lose their radioactivity and so can become in theory safe to handle but in most cases this is a very slow process. Plutonium-239, for instance, has a half-life of over 24,000 years which means it will remain lethal for over 240,000 years. Other radio-isotopes remain radioactive for millions or even billions of years.
The safe, long-term storage of nuclear waste is a problem that is reaching crisis point for both the civil nuclear industry and for the military.
During the Cold War years of the 1950s and 1960s, the development of the British atomic bomb was seen as a matter of urgency. Dealing with the mess caused by the production, operating and even testing of nuclear weapons was something to be worried about later, if at all.
For example, the Ministry of Defence does not really have a proper solution for dealing with the highly radioactive hulls of decommissioned nuclear submarines, apart from storing them for many decades. As a result, 19 nuclear-powered retired submarines are still waiting to be dismantled, with more expected each year. Yet Britain goes on building these submarines.
This callous disregard for the future has spilled over to the nuclear power industry. For example, at Dounreay, in the north of Scotland, nuclear waste and scrap from the experimental reactor and reprocessing plants were simply tipped down a disused shaft for over 20 years. No proper records of what was dumped were kept and eventually, in 1977, an explosion showered the area with radioactive debris. In April 1998, it was finally announced that excavation and safe removal of the debris had cost £355 million.
The problems of long term, secure storage of nuclear waste are unsolved and growing more acute year by year. Earlier attempts by the nuclear industry to get rid of it by dumping it in the sea were stopped by environmental direct action, trades union protests and now by law.
All details concerning military nuclear waste are regarded as official secrets. However, large and growing quantities of radioactive waste exist at the Rosyth and Devonport dockyards and in particular at the Aldermaston and Burghfield Atomic Weapons Establishments.
One feature of Aldermaston and Sellafield in particular is that they are old sites, and have grown up in an unplanned, haphazard way. New buildings are fitted in between old, sometimes abandoned, buildings. Some areas and buildings are sealed off and polluted by radioactivity. Local streams, and in the case of Sellafield the sea shore, are polluted. The demolition of old radioactive buildings is a delicate, slow and dangerous process. In the circumstances it is hardly surprising that the amount of nuclear waste can only be estimated.
Civil intermediate level solid waste is mainly stored at Sellafield awaiting a decision on a national storage facility.
Military intermediate level solid waste is stored where it is created: dockyards, AWE plants etc. Both civil and military high level solid waste is generally moved to Sellafield for temporary storage.
The major problems are with the long-term storage of intermediate and in particular high-level wastes. Since these are very dangerous and very long-lived, any storage facility has to be very secure (i.e. well-guarded) and safer over a longer period – some tens of thousands of years – than anything yet designed and built by humanity.
Because of this very long time scale, it can never be sealed up and forgotten. Containers corrode with time. There are earth movements. Water seeps through rocks. The waste will have to be stored in such a form that it cannot be stolen and misused and in such a way that it can be inspected and if necessary retrieved and moved.
Plans to dig a trial deep storage facility under the Sellafield site were thrown out in 1997. Geological evidence suggested that the local rock is too fissured and liable to be affected by water seepage.
This threw all the nuclear industry’s plans into confusion. Instead of having a storage site ready by 2010, the date has been put back more or less indefinitely. No alternative site has even been identified.
Apart from the technical, geological problems, few communities seek a huge, long-term nuclear waste storage site in their neighbourhood. Indeed the original choice of Sellafield was as much political as technical. With most local jobs depending on nuclear industry already, there would have been less local opposition than elsewhere.
Nuclear waste is a problem that the nuclear industry has failed to consider seriously for over sixty years but one that can no longer be put off for future generations to cope with.
The effects of any nuclear accidents, such as those at Chernobyl in 1986 and Fukushima in 2011, are also very long-lasting and will affect future generations. The problems of nuclear waste are nowhere near solution. The history of the nuclear industry does not inspire confidence………………………………………………………. https://beyondnuclearinternational.org/2025/12/14/does-britain-really-need-nuclear-power/
-
Archives
- March 2026 (99)
- February 2026 (268)
- January 2026 (308)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (376)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS




