China’s Retaliation: when will it happen?

And more appropriately, what form will it take?
Jerrys take on China, Feb 18, 2026, https://jerrygrey2002.substack.com/p/chinas-retaliation-when-will-it-happen?utm_source=post-email-title&publication_id=1744413&post_id=188346536&utm_campaign=email-post-title&isFreemail=true&r=ln98x&triedRedirect=true&utm_medium=email
A few comments about why China is like it is – first of all, in the last 45 years, there has been no invasions, despite what people like little Marco Rubio of the US and Richard Marles the Australian Defence Minister might say, China is not and does not pose a threat to any of these countries – Japan might think there is a threat, China does not agree, in fact the opposite is true, Japan poses a much larger threat to China than China has ever posed to Japan.
China is concerned about, and in fact does feel threatened by Japan’s military expansion because the last time it happened literally millions of Chinese were murdered by the Japanese. Australia’s defence minister, Marles, asks us to consider why China has the world’s largest military expansion but he’s wrong – we have to hope he’s wrong because he’s been misinformed and is too dim to check out for himself, but more likely he knows he’s lying about this as China spends considerably less money than the US, in terms of not only its population but its geographical size, it’s quite entitled to spend more cash, when on a per capita basis, the amount is tiny compared to the US, on a ratio to GDP, it’s smaller than the US, it’s one third or less than NATO has been required to spend in terms of percentage of GDP and there’s one more very important factor that the US with only two neighbouring countries doesn’t have – that is 14 neighbouring countries with a shared land border.
Here’s another thing. China was invaded when they were weak, the British did it, the Americans did it, the eight nations alliance did it, Britain carved up part of Burma and took away some of China, it carved up India and took away parts of China, the Russians carved up Mongolia and Heilongjiang, taking away parts of China, the Japanese invaded and occupied China for 14 years. The classic twists and mental gymnastics people like Marles make would have us believe that the hundreds of US bases around China are to prevent China from doing what they’ve NEVER done – going out to invade other countries.
He, and several pundits would like us all to believe is that the US is keeping the world safe from China by arming their neighbours, interfering in the Provinces, Regions and the SARs but the reality is, China is building a military that will defend Chinese people inside China and Chinese land that belongs to China now – it’s not looking to reclaim land back, except in disputed regions.
Those disputed regions include parts of Tibet that the British took away and gave to India, parts of the South China Seas that the Japanese took away and both the US and UK, at the end of the Second World War, agreed would come back to China. There’s one military base in Africa, which is in a region shared with many other countries, including the USA, Japan, France, Italy, Germany Spain and even Saudi Arabia. Taiwan is NOT one of these disputed regions – the entire world whether they recognise Beijing or Taipei as the capital, recognises that there is one China and Taiwan is part of it – anyone who suggests that Taiwan is a country is either a liar, deliberately misleading us, or is far too dim to read the Constitution of the Republic of China, which not only claims all of the Chinese Mainland, it also wants those disputed regions back too.
China has something else which its detractors hate to admit and will lie about – that’s a policy of non-interference in the affairs of a sovereign nation – when it invests in another nation, it doesn’t call for democracy or elections, it doesn’t even ask that Communism or Socialism are accepted, it doesn’t send military to protect its assets, it won’t send missionaries to convert their subjects and it won’t impose conditions that force countries to give up their national assets or utilities if they can’t make the payments – if that sounds familiar and if it’s because you’ve been hearing that China will do all of those things and, if you think they have, I’d implore you to find me an example of where it’s happened, outside of opinion pieces written by people who want you to believe they have, almost every incident where we can find any of these things alleged, will be speculative – they’ll tell us what China might do, what China could do, what China may be doing, is alleged to have done or suspected to be involved in.
We might find individual cases of rogue Chinese people, Chinese criminals even and they use these tiny individual examples to tell you that this is “what China does” when that person who has broken the law has usually already been punished by the time they report it in western media and, if they mention that at all, it’ll be after the third paragraph where most of us have stopped reading.
On the other hand, I can find literally hundreds of examples where the USA is doing these things, where the UK and France have done these things, where Germany, Belgium, even Spain and Portugal have done them.
So then some of the comments I have been getting relate to the Port in Darwin, the ports in Panama and the Pirelli saga in Italy. Just for some background here, Sinochem owns 37% of Pirelli, the big Italian tyre company which wants to expand into the USA, of course the US won’t allow that while China has such a controlling interest. The share of Sinochem hasn’t changed, the only change is that the board, and remember Sinochem had controlling interest being the largest single shareholder, has declared that Sinochem no longer has control, giving the board more autonomy, – Sinochem agreed to this, so this isn’t a situation where anything has been taken from China, merely an agreement that the board retains control which a Chinese corporation retains more shares.
Erich, one of my followers said this: “if China doesn’t protect its assets it will lose them like Pirelli in Italy, the Ports in Panama, etc. Maybe at some point China will start caring about these things.”
My response is that it’s not just Erich, it’s literally hundreds of people, probably thousands but many in my responses who are misunderstanding China. China cares very deeply about the assets its people and corporations invest in, particularly overseas, but it will not break international laws, or contractual Agreements in order to protect them from people or governments which do break laws.
China will react to this in the same way it reacts to every other illegal action against it, by negotiations, and where they fail, arbitration, it will, when all else fails, take the appropriate legal action, which might be appeals to the WTO and perhaps even the UN or more likely the local courts – it knows there will be no satisfaction from those appeals but they are the legal mechanisms open to Chinese corporation. China as a government participates in legal and lawful bodies and does not want to overthrow them, to do so, makes China another USA – so the actions China takes, which will definitely be retaliatory, will be legal, they can, and probably will reduce purchases from offending countries, and of course, they will be much more careful in the decisions when investing in those countries both of which are well within their legal rights.
What China will not do is: unilaterally sanction anyone, any country or even any organisation within the country, it will not militarily defend its assets, it will not interfere in the internal affairs of another country but there is no doubt in my mind that if any country persists and acts on threats to China’s investments, there will be repercussions, probably it’s best not to call them retaliations, they are simply normal responses to a situation of risk.
In Australia for example, if they persist with this challenge to the legal investments Landbridge has made, investments that are compliant in every way and even beneficial to the people of the Northern Territory in jobs and payroll taxes, as well as increased business going through it’s port and beneficial to the people of Australia in 4.5 million income tax paid last year, those are the people who will suffer – China will find other suppliers for the things Australia sends – so far, the only one which is not directly sourced elsewhere is iron ore and, if China stops buying that in any great quantity, it will kill Australia’s economy.
Just continuing to use Darwin Port as an example, it is a critical trade hub in Northern Australia, handling minerals, agriculture, and livestock, with 2,295 vessel visits recorded in 2024-25, marking a 31.07% increase on the previous year. Darwin serves as a key gateway to Asia, managing significant exports of manganese, titanium, iron ore, and livestock. Given that China is the major trading partner of Australia, a huge proportion, unfortunately, there’s no way I can find out, would be Chinese owned, flagged, operated or destined ships, they would be travelling between China and Darwin – that’s 44 ships a week, many of which will simply divert to other ports, or, if the asset has been seized they’re more likely to simply stop coming altogether – how can that possibly benefit the warehouses, the truckers, the waste management, the catering and hospitality venues that the sailors use, the customs brokers, the security and surveillance companies – there’s an entire eco-system of industries deriving their income from a well-operated port and Darwin, which is a small city will feel a very heavy impact from no Chinese ships arriving and departing there. There will also be a lot of farmers, miners and other suppliers using that port to ship to China – it will all stop.
So, to think China will just sit back and do nothing is wrong, they are very mindful that their investments are not just at risk but under threat – business leaders in China understand this and are already taking action – there’s an April 2024 KPMG report, that’s almost 2 years old now showing that China’s investments in Australia have declined from a peak in 2016, just after the Free Trade Agreement was signed to the lowest level since 2006. It’s well worth a read if you’re interested, the report defines all kinds of factors but fails to mention the obvious one – Australia simply doesn’t want Chinese investment, they feel threatened by perceptions given to them by media which are completely false.
In keeping with the maxim that one person’s loss is another’s gain, the vast majority of China’s Overseas Direct Investment is now going to One Belt One Road countries – these are safe destinations, they are countries that welcome trade with and investments from China. In the Western world, that’s not many countries. Leaders of Canada and the UK were recently in China seeking investment opportunities, in both cases, they returned to their home countries to media criticism. It remains to be seen how they will handle this but they, as leaders, and their business leaders all know the truth – the media is lying, a few politicians who are actually paid by Washington to further lie about China are losing influence. Some people will assume that I’m either exaggerating about this but the reality is there for all to see, if you don’t believe me, go look up who are the main funders of the Inter Parliamentary Alliance on China (IPAC). It states clearly on its website that it does not accept funds from governments. But then lists the Taiwan Foundation for Democracy, the National Endowment for Democracy, the International Republican movement, Hello Taiwan the National Democratic Institute and others, all of which are government funded and almost all of which can trace their funds back to Washington DC and congressionally approved expenditure.
The vast majority of the Non-US aligned world realises – there is no threat from China and, once again I reiterate something I’ve said many times, the people telling you China is a threat are more likely to damage your economy and your global standing than China ever will – China isn’t a threat, it’s those people telling you it is, who are.
No evidence to support US claim China conducted nuclear blast test: Monitor

Robert Floyd, executive secretary of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization, said in a statement on Friday that the body’s monitoring system “did not detect any event consistent with the characteristics of a nuclear weapon test explosion” at the time of the alleged Chinese test, adding that that assessment remains unchanged after further detailed analyses.
Washington wants Beijing to join a new nuclear weapons treaty after expiration of the New START accord between the US and Russia.
By Al Jazeera and News Agencies, 6 Feb 26, https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2026/2/7/no-evidence-to-support-us-claim-china-conducted-nuclear-blast-test-monitor
An international monitor said it has seen no evidence to support the claim by a senior United States official who accused China of carrying out a series of clandestine nuclear tests in 2020 and concealing activities that violated nuclear test ban treaties.
US Under Secretary of State for Arms Control and International Security Thomas DiNanno made the assertions about China at a United Nations disarmament conference in Geneva, Switzerland, on Friday, just days after a nuclear treaty with Russia expired.
“I can reveal that the US government is aware that China has conducted nuclear explosive tests, including preparing for tests with designated yields in the hundreds of tonnes,” DiNanno said at the conference.
China’s military “sought to conceal testing by obfuscating the nuclear explosions because it recognised these tests violate test ban commitments,” he said.
“China conducted one such yield-producing nuclear test on June 22 of 2020,” he said.
DiNanno also made his allegations on social media in a series of posts, making the case for “new architecture” in nuclear weapons control agreements following the expiration of the New START treaty with Russia this week.
“New START was signed in 2010 and its limits on warheads and launchers are no longer relevant in 2026 when one nuclear power is expanding its arsenal at a scale and pace not seen in over half a century and another continues to maintain and develop a vast range of nuclear systems unconstrained by New START’s terms,” he said.
Robert Floyd, executive secretary of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization, said in a statement on Friday that the body’s monitoring system “did not detect any event consistent with the characteristics of a nuclear weapon test explosion” at the time of the alleged Chinese test, adding that that assessment remains unchanged after further detailed analyses.
China’s ambassador on nuclear disarmament, Shen Jian, did not directly address DiNanno’s charge at the conference but said Beijing had always acted prudently and responsibly on nuclear issues while the US had “continued to distort and smear China’s national defence capabilities in its statements”.
We firmly oppose this false narrative and reject the US’s unfounded accusations,” Shen said.
“In fact, the US’s series of negative actions in the field of nuclear arms control are the biggest source of risk to international security,” he said.
Later on social media, Shen said, “China has always honored its commitment to the moratorium on nuclear testing”.
Diplomats at the conference said the US allegations were new and concerning.
China, like the US, has signed but not ratified the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (CTBT), which bans explosive nuclear tests. Russia signed and ratified it, but withdrew its ratification in 2023.
US President Donald Trump has previously instructed the US military to prepare for the resumption of nuclear tests, stating that other countries are conducting them without offering details.
The US president said on October 31 that Washington would start testing nuclear weapons “on an equal basis” with Moscow and Beijing, but without elaborating or explaining what kind of nuclear testing he wanted to resume.
He has also said that he would like China to be involved in any future nuclear treaty, but authorities in Beijing have shown little interest in his proposal.
Leaked Nuclear Secrets: China Arrests Top Military Leader Close to Xi Jinping
Vladislav V., January 25, 2026, https://militarnyi.com/en/news/leaked-nuclear-secrets-china-arrests-top-military-leader-close-to-xi-jinping/
China’s top general has been accused of leaking information about the country’s nuclear program to the United States and of accepting bribes to facilitate official promotions, including that of an officer to the post of defense minister.
This was reported by The Wall Street Journal, citing attendees of a closed briefing on the case.
The briefing, attended by some of China’s senior military commanders, took place shortly before the Ministry of National Defense of the People’s Republic of China issued a statement announcing an investigation into General Zhang Youxia.
He had previously been considered one of Chinese leader Xi Jinping’s closest military allies.
The official statement provided minimal details, only noting that Zhang was under investigation for serious violations of party discipline and state law.
Sources familiar with the undisclosed briefing said Zhang is suspected of forming political cliques — a term in the Chinese system that refers to informal networks undermining the Communist Party’s unity.
He is also accused of abusing his authority in the Central Military Commission, the top body overseeing the PLA’s administration.
Investigators are focusing on the period when Zhang headed the influential department responsible for military research, development, and procurement.
According to sources, the general allegedly received large sums in exchange for official appointments and promotions within the military procurement system, which operates with multi-billion-dollar budgets.
Zhang Youxia’s Removal and Its Consequences
Zhang’s removal makes the purge of the PRC general staff one of the largest personnel reshuffles in the Chinese military since the dispersal of protests in Tiananmen Square in 1989.
Control over the armed forces is widely seen as critical to the power and political survival of Chinese leaders. Historically, internal party struggles have often been won by those with authority and influence over the military.
Zhang’s dismissal highlights Xi’s drive for absolute concentration of power.
As first vice chairman of the Central Military Commission, a role combining responsibilities similar to those of a US defense minister, chairman of the Joint Chiefs, and national security adviser, Zhang held exceptionally broad authority.
He oversaw strategy, promotions, and budgets, and reported directly to Xi. Analysts had considered him virtually untouchable due to his combat experience and personal ties to Xi.
Zhang had survived previous purges among the generals, retained significant loyalty within the military, and remained in his top post well past the normal retirement age.
Analysts say his removal reflects Xi’s urgent effort to “restore order” in the military leadership, despite Zhang’s planned retirement at the next party congress in 2027.
Xi’s unprecedented consolidation of military power also narrows the circle of decision-makers on Taiwan and other strategic issues, including control of China’s nuclear arsenal.
Analysts note that the older generation of PLA leaders has historically acted as a moderating influence in military planning.
The reshuffle comes as Xi seeks to rapidly modernize the military and achieve strategic objectives, including the declared ability to conduct operations against Taiwan by 2027.
Spectral Threats: China, Russia and Trump’s Greenland Rationale

Were Russia or China to attempt an occupation of Greenland through military means, Article V of the North Atlantic Treaty would come into play, obliging NATO member states, including the United States, to collectively repel the effort.
“There are no Russian and Chinese ships all over the place around Greenland,”
“Russia and/or China has no capacity to occupy Greenland or to take control over Greenland.”
14 January 2026 Dr Binoy Kampmark, https://theaimn.net/spectral-threats-china-russia-and-trumps-greenland-rationale/
The Trump administration’s mania about Greenland, a self-governing territory of Denmark, is something to behold. Its untutored thuggery, its brash assertiveness, and the increasingly strident threats to either use force, bully Denmark into a sale of the island, or simply annex the territory, have officials and commentators scrambling for theories and precedents. The Europeans are terrified that the NATO alliance is under threat from another NATO member. The Greenlanders are anxious and confused. But the ground for further action by Washington is being readied by finding threats barely real and hardly plausible.
The concerns about China and Russia seizing Greenland retells the same nonsense President Donald Trump promoted in kidnapping the Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro and his wife. Looking past the spurious narcoterrorism claims against the former leader, it fell to the issue of who would control the natural resources of the country. If we don’t get Venezuelan oil now and secure it for American companies, the Chinese or the Russians will. he gangster’s rationale is crudely reductionist, seeing all in a similar veinThe obsession with Beijing and Moscow runs like a forced thread through a dotty, insular rationale that repels evidence and cavorts with myth: “We need that [territory],” reasons the President, “because if you take a look outside Greenland right now, there are Russian destroyers, there are Chinese destroyers and, bigger, there are Russian submarines all over the place. We are not gonna have Russia or China occupy Greenland, and that’s what they’re going to do if we don’t.” On Denmark’s military capabilities in holding the island against any potential aggressor, Trump could only snort with macho dismissiveness. “You know what their defence is? Two dog sleds.”
This scratchy logic is unsustainable for one obvious point. Were Russia or China to attempt an occupation of Greenland through military means, Article V of the North Atlantic Treaty would come into play, obliging NATO member states, including the United States, to collectively repel the effort. With delicious perversity, any US effort to forcibly acquire the territory through use of force would be an attack on its own security, given its obligations under the Treaty. In such cases, it becomes sound to assume, as the Danish Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen does, that the alliance would cease to exist.
Such matters are utterly missed by the rabidly hawkish Deputy Chief of Staff Stephen Miller, who declared that, “Nobody’s going to fight the United States militarily over the future of Greenland.” It was up to the US “to secure the Arctic region, to protect and defend NATO and NATO interests” in incorporating Greenland. To take territory from a NATO ally was essentially doing it good.
Given that the United States already has a military presence on the island at the Pituffik Space Base, and rights under the 1951 agreement that would permit an increase in the number of bases should circumstances require it, along with the Defence Cooperation Agreement finalised with Copenhagen in June 2025, much of Miller’s airings are not merely farcical but redundant. Yet, Trump has made it clear that signatures and understandings reflected in documents are no substitute for physically taking something, the thrill of possession that, by its act, deprives someone else of it. “I think ownership gives you a thing that you can’t do, whether you’re talking about a lease or a treaty,” he told the New York Times. “Ownership gives you things and elements that you can’t get from just signing a document.”
What, then, of these phantom forces from Moscow and Beijing, supposedly lying in wait to seize the frozen prize? “There are no Russian and Chinese ships all over the place around Greenland,” states the very convinced research director of the Oslo-based Fridtjof Nansen Institute, Andreas Østhagen. “Russia and/or China has no capacity to occupy Greenland or to take control over Greenland.”
Danish Foreign Minister Lars Lokke Rasmussen is similarly inclined. “The image that’s being painted of Russian and Chinese ships right inside the Nuuk fjord and massive Chinese investments being made is not correct.” Senior “Nordic diplomats” quoted in the Financial Times add to that version, even if the paper is not decent enough to mention which Nordic country they come from. “It is simply not true that the Chinese and Russians are there,” said one. “I have seen the intelligence. There are no ships, no submarines.” Vessel tracking data from Marine Traffic and LSEG have so far failed to disclose the presence of Chinese and Russian ships near the island.
Heating engineer Lars Vintner, based in Greenland’s capital, Nuuk, wondered where these swarming, spectral Chinese were based. “The only Chinese I see,” he told Associated Press,“ is when I go to the fast food market.” This sparse presence extends to the broader security footprint of China in the Arctic, which remains modest despite a growing collaboration with Russia since the 2022 invasion of Ukraine. These have included Arctic and coast guard operations, while the Chinese military uses satellites and icebreakers equipped with deep-sea mini submarines, potentially for mapping the seabed.
However negligible and piffling the imaginary threat, analysts, ever ready with a larding quote or a research brief, are always on hand to show concern with such projects as Beijing’s Polar Silk Road, announced in 2018, which is intended as the Arctic extension of its transnational Belt and Road initiative. The subtext: Trump should not seize Greenland, but he might have a point. “China has clear ambitions to expand its footprint and influence in the region, which it considers… an emerging arena for geopolitical competition.” Or so says Helena Legarda of the Mercator Institute for China Studies in Berlin.
The ludicrous nature of Trump’s claims and acquisitive urges supply fertile material for sarcasm. A prominent political figure from one of the alleged conquerors-to-be made an effort almost verging on satire. “Trump needs to hurry up,” mocked the Deputy Chairman of the Russian Security Council and former President Dmitry Medvedev. “According to unverified information, within a few days, there could be a sudden referendum where all 55,000 residents of Greenland might vote to join Russia. And that’s it!” With Trump, “that’s it” never quite covers it.
Faslane nuclear base tugboats may be built in China
UK Defence Journal By George Allison, January 12, 2026
New tugboats intended to support operations at HM Naval Base Clyde, the UK’s nuclear submarine hub at Faslane, may be constructed in China under a major fleet replacement programme, depending on how the contractor applies its global production model.
The vessels form part of the Defence Maritime Services Next Generation programme, under which Serco is replacing a wide range of Royal Navy harbour and support craft. The programme covers tugs, pilot boats and barges used at naval bases across the UK, including Faslane, which hosts the UK’s continuous at-sea nuclear deterrent.
Under the current arrangements, the Ministry of Defence pays Serco to provide support services at the Royal Navy’s principal bases, and allows Serco, as the prime contractor, to determine its own supply chain for vessel replacement.
Build locations and Damen’s production model
Damen operates a distributed shipbuilding model, with construction spread across a network of yards in Europe and Asia depending on vessel type and production capacity. The company has historically built a range of smaller commercial and support vessels at yards in China and Vietnam, including certain classes of tugboats, while other workboat types are constructed at European facilities in countries such as Poland and Romania. Final outfitting, integration and delivery preparation are often carried out in the Netherlands or at European partner yards, depending on the contract.
Neither Serco nor Damen has publicly confirmed the specific build locations for individual vessels within the programme. However, Damen’s established production model suggests that some tugboats could be built outside Europe, including at shipyards in China that form part of Damen’s wider manufacturing network……………………………………………………………………………………………….
Not the first time
A similar issue emerged in Australia in 2025, when the national broadcaster ABC reported that a new fleet of tugboats ordered for the Royal Australian Navy had been built in China under a contract awarded to Dutch shipbuilder Damen. The report said certification documents showed the vessels were constructed at Damen’s Changde shipyard in China, before being delivered to Australia under a civilian-operated support arrangement.
In response to the reporting, Australia’s Department of Defence confirmed that the tugboats had been built in China, while stating that they were not commissioned naval vessels and would be operated by a civilian contractor. Defence officials emphasised that sustainment activity would take place domestically and that the vessels were intended for harbour support roles rather than frontline operations…………………….
Wider security context
In a separate but related context, the Ministry of Defence has in recent months issued internal guidance concerning the use of vehicles containing Chinese-manufactured components, amid broader concerns about information security and connected systems. Media reporting has said warning notices were placed in some MoD-leased vehicles advising personnel not to discuss sensitive matters inside them or connect official devices, and that certain vehicles were restricted from accessing sensitive military sites. The measures were described as precautionary, with no publicly confirmed security breach.
Parliamentary questions have also raised wider issues about reliance on overseas-manufactured systems within defence and government operations. Ministers have acknowledged the need to assess potential vulnerabilities linked to global supply chains, while maintaining that decisions are taken on a case-by-case basis and that there has been no evidence of compromise.
Competing views on cost, transparency and social value
Those defending the programme argue that the arrangements reflect commercial shipbuilding norms rather than a deliberate policy decision. They note that hull construction in Asia can reduce costs and production timelines, with final outfitting, systems integration and acceptance carried out later in Europe under established regulatory oversight. Critics argue that the lack of transparency over build locations risks undermining confidence, especially where vessels operate at nuclear sites. They contend that clearer public disclosure is needed on where vessels are constructed and what safeguards apply during the build process.
Louise Gilmour, secretary of GMB Scotland, said the decision to source the workboats overseas represented a missed opportunity to support domestic shipbuilding capacity, particularly at Ferguson Marine, where the union represents the largest section of the workforce. She said the vessels were well suited to the type of work the yard had carried out for generations and argued that contracts of this scale could play a role in sustaining skills and employment in Scotland.
https://ukdefencejournal.org.uk/faslane-nuclear-base-tugboats-may-be-built-in-china/
Plunging Toward Armageddon: U.S. and Russia on the Brink of a New Nuclear Arms Race

Beginning on February 6th, Russian and American leaders will face no barriers whatsoever to the expansion of those arsenals or to any other steps that might increase the danger of a thermonuclear conflagration.
Both the United States and Russia have already committed vast sums to the “modernization” of their nuclear delivery systems
By Michael Klare. 8 Jan 26, https://tomdispatch.com/plunging-into-the-abyss/
Plunging Into the Abyss. Will the U.S. and Russia Abandon All Nuclear Restraints?
For most of us, Friday, February 6, 2026, is likely to feel no different than Thursday, February 5th. It will be a work or school day for many of us. It might involve shopping for the weekend or an evening get-together with friends, or any of the other mundane tasks of life. But from a world-historical perspective, that day will represent a dramatic turning point, with far-reaching and potentially catastrophic consequences. For the first time in 54 years, the world’s two major nuclear-weapons powers, Russia and the United States, will not be bound by any arms-control treaties and so will be legally free to cram their nuclear arsenals with as many new warheads as they wish — a step both sides appear poised to take.
It’s hard to imagine today, but 50 years ago, at the height of the Cold War, the U.S. and Russia (then the Soviet Union) jointly possessed 47,000 nuclear warheads — enough to exterminate all life on Earth many times over. But as public fears of nuclear annihilation increased, especially after the near-death experience of the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis, the leaders of those two countries negotiated a series of binding agreements intended to downsize their arsenals and reduce the risk of Armageddon.
The initial round of those negotiations, the Strategic Arms Limitation Talks I, began in November 1969 and culminated in the first-ever nuclear arms-limitation agreement, SALT-I, in May 1972. That would then be followed in June 1979 by SALT-II (signed by both parties, though never ratified by the U.S. Senate) and two Strategic Arms Reduction Treaties (START I and START II), in 1991 and 1993, respectively. Each of those treaties reduced the number of deployed nuclear warheads on U.S. and Soviet/Russian intercontinental ballistic missiles, submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and long-range bombers.
In a drive to reduce those numbers even further, President Barack Obama and Russian President Dmitry Medvedev signed a New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (New START) in April 2010, an agreement limiting the number of deployed nuclear warheads to 1,550 on each side — still enough to exterminate all life on Earth, but a far cry from the START I limit of 6,000 warheads per side. Originally set to expire on Feb. 5, 2021, New START was extended for another five years (as allowed by the treaty), resetting that expiration date for February 5, 2026, now fast approaching. And this time around, neither party has demonstrated the slightest inclination to negotiate a new extension.
So, the question is: What, exactly, will it mean for New START to expire for good on February 5th?
Most of us haven’t given that a lot of thought in recent decades, because nuclear arsenals have, for the most part, been shrinking and the (apparent) threat of a nuclear war among the great powers seemed to diminish substantially. We have largely escaped the nightmarish experience — so familiar to veterans of the Cold War era — of fearing that the latest crisis, whatever it might be, could result in our being exterminated in a thermonuclear holocaust.
A critical reason for our current freedom from such fears is the fact that the world’s nuclear arsenals had been substantially diminished and that the two major nuclear powers had agreed to legally binding measures, including mutual inspections of their arsenals, meant to reduce the danger of unintended or accidental nuclear war. Together, those measures were crafted to ensure that each side would retain an invulnerable, second-strike nuclear retaliatory force, eliminating any incentive to initiate a nuclear first strike.
Unfortunately, those relatively carefree days will come to an end at midnight on February 5th.
Beginning on February 6th, Russian and American leaders will face no barriers whatsoever to the expansion of those arsenals or to any other steps that might increase the danger of a thermonuclear conflagration. And from the look of things, both intend to seize that opportunity and increase the likelihood of Armageddon. Worse yet, China’s leaders, pointing to a lack of restraint in Washington and Moscow, are now building up their own nuclear arsenal, only adding further fuel to the urge of American and Russian leaders to blow well past the (soon-to-be-abandoned) New START limits.
A Future Nuclear Arms Race?
Even while adhering to those New START limits of 1,550 deployed nuclear warheads, both Russia and the United States had taken elaborate and costly steps to enhance the destructive power of their arsenals by replacing older, less-capable intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs), and nuclear bombers with newer, even more capable ones. As a result, each side was already becoming better equipped to potentially inflict catastrophic damage on its opponent’s nuclear retaliatory forces, making a first strike less inconceivable and so increasing the risk of precipitous escalation in a crisis.
The Russian Federation inherited a vast nuclear arsenal from the former Soviet Union, but many of those systems had already become obsolete or unreliable. To ensure that it maintained an arsenal at least as potent as Washington’s, Moscow sought to replace all of the Soviet-era weapons in its inventory with more modern and capable systems, a process still underway. Russia’s older SS-18 ICBMs, for example, are being replaced by the faster, more powerful SS-29 Sarmat, while its remaining five Delta-IV class missile-carrying submarines (SSBNs) are being replaced by the more modern Borei class. And newer ICBMs, SLBMs, and SSBNs are said to be in development.
At present, Russia possesses 333 ICBMs, approximately half of them deployed in silos and the other half on road-mobile carriers. It also has 192 SLBMs on 12 missile-carrying submarines and possesses 67 strategic bombers, each capable of firing multiple nuclear-armed missiles. Supposedly, those systems are currently loaded with no more than 1,550 nuclear warheads (enough, of course, to destroy several planets), as mandated by the New START treaty. However, many of Russia’s land- and sea-based ballistic missiles are MIRVed (meaning they’re capable of launching multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles) but not fully loaded, and so could carry additional warheads if a decision were ever made to do so. Given that Russia possesses as many as 2,600 nuclear warheads in storage, it could rapidly increase the number of deployed nuclear weapons at its disposal beginning on February 6, 2026.
Rather than confront such challenges, the leaders of both countries may instead choose to retain the New START limits voluntarily. Indeed, Vladimir Putin has already agreed to a one-year extension of this sort, if the United States is willing to do likewise. But pressures (which are bound to increase after February 5th) are also building to abandon those limits and begin deploying additional warheadsmost missile-tracking radars.
The United States is engaged in a comparable drive to modernize its arsenal, replacing older weapons with more modern systems. Like Russia, the U.S. maintains a “triad” of nuclear delivery systems — land-based ICBMs, submarine-launched SLBMs, and long-range bombers, each of which is now being upgraded with new warheads at an estimated cost over the next quarter century of approximately $1.5 trillion.
The existing New START-limited U.S. nuclear triad consists of 400 silo-based Minuteman-III ICBMs, 240 Trident-II SLBMs carried by 14 Ohio-class submarines (two of which are assumedly being overhauled at any time), and 96 strategic bombers (20 B-2s and 76 B-52s) armed with a variety of gravity bombs and air-launched cruise missiles. According to current plans, the Minuteman-IIIs will be replaced by Sentinel ICBMs, the Ohio-class SSBNs by Columbia-class ones, and the B-2s and B-52s by the new B-21 Raider bomber. Each of those new systems incorporates important features — greater accuracy, increased stealth, enhanced electronics — that make them even more useful as first-strike weapons, were a decision ever made to use them in such a fashion.
When initiated, the U.S. nuclear modernization project was expected to abide by the New START limit of 1,550 deployed nuclear warheads. After February 5th, however, the U.S. will be under no legal obligation to do so. It could quickly begin efforts to exceed that limit by loading all existing Minuteman-IIIs and future Sentinel missiles on MIRVed rather than single-warhead projectiles and loading the Trident missiles (already MIRVed) with a larger number of warheads, as well as by increasing production of new B-21s. The United States has also commenced development of a new delivery system, the nuclear-armed sea-launched cruise missile (SLCM-N), supposedly intended for use in a “limited” regional nuclear conflict in Europe or Asia (though how such a conflagration could be prevented from igniting a global holocaust has never been explained).
In short, after the expiration of the New START agreement, neither Russia nor the United States will be obliged to limit the numbers of nuclear warheads on their strategic delivery systems, possibly triggering a new global nuclear arms race with no boundaries in sight and an ever-increasing risk of precipitous nuclear escalation. Whether they choose to do so will depend on the political environment in both countries and their bilateral relations, as well as elite perceptions of China’s nuclear buildup in both Washington and Moscow.
The Political Environment
Both the United States and Russia have already committed vast sums to the “modernization” of their nuclear delivery systems, a process that won’t be completed for years. At present, there is a reasonably broad consensus in both Washington and Moscow on the need to do so. However, any attempt to increase the speed of that process or add new nuclear capabilities will generate immense costs along with significant supply-chain challenges (at a time when both countries are also trying to ramp up their production of conventional, non-nuclear arms), creating fresh political disputes and potential fissures.
Rather than confront such challenges, the leaders of both countries may instead choose to retain the New START limits voluntarily. Indeed, Vladimir Putin has already agreed to a one-year extension of this sort, if the United States is willing to do likewise. But pressures (which are bound to increase after February 5th) are also building to abandon those limits and begin deploying additional warheads.
In Washington, a powerful constellation of government officials, conservative pundits, weapons industry leaders, and congressional hawks is already calling for a nuclear buildup that would exceed the New START limits, claiming that a bigger arsenal is needed to deter both a more aggressive Russia and a more powerful China. As Pranay Vaddi, a senior director of the National Security Council, put it in June 2024, “Absent a change in the trajectory of the adversary arsenal, we may reach a point in the coming years where an increase from current deployed numbers is required, and we need to be fully prepared to execute if the president makes that decision.”
Those who favor such a move regularly point to China’s nuclear buildup. Just a few years ago, China possessed only some 200 nuclear warheads, a small fraction of the 5,000 possessed by both Russia and the U.S. Recently, however, China has expanded its arsenal to an estimated 600 warheads, while deploying more ICBMs, SLBMs, and nuclear-capable bombers. Chinese officials claim that such weaponry is needed to ensure retaliation against an enemy-first strike, but their very existence is being cited by nuclear hawks in Washington as a sufficient reason for the U.S. to move beyond the New START limits.
Russian leaders face an especially harsh quandary. At a moment when they are devoting so much of the country’s state finances and military-industrial capacities to the war in Ukraine, they face a more formidable and possibly expanded U.S. nuclear arsenal, not to mention the (largely unspoken) threat posed by China’s growing arsenal. Then there’s President Trump’s plan for building a “Golden Dome” missile shield, intended to protect the U.S. from any type of enemy projectile, including ICBMs — a system which, even if only partially successful, would threaten the credibility of Russia’s second-strike retaliatory capability. So, while Russia’s leaders would undoubtedly prefer to avoid a costly new arms buildup, they will probably conclude that they have little choice but to undertake one if the U.S. abandons New START.
Racing to Armageddon
Many organizations, individuals, and members of Congress are pleading with the Trump administration to accept Vladimir Putin’s proposal and agree to a voluntary continuation of the New START limits after February 5th. Any decision to abandon those limits, they argue, would only add hundreds of billions of dollars to the federal budget at a time when other priorities are being squeezed. Such a decision would also undoubtedly provoke reciprocal moves by Russia and China. The result would be an uncontrolled arms race and a rising risk of nuclear annihilation.
But even if Washington and Moscow were to agree to a one-year voluntary extension of New START, each would be free to break out of it at any moment. In that sense, February 6th is likely to bring us into a new era — not unlike the early years of the Cold War — in which the major powers will be poised to ramp up their nuclear war-fighting capabilities without any formal restrictions whatsoever. That comfortable feeling we once enjoyed of relative freedom from an imminent nuclear holocaust will also then undoubtedly begin to dissipate. If there is any hope in such a dark prognosis, it might be that such a reality could, in turn, ignite a worldwide anti-nuclear movement like the Ban the Bomb campaigns of the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s. If only.
The Unbroken Thread: China’s Civilisational-State vs. The West’s Contractual Empire – A Study in Divergent Destinies

10 January 2026 Andrew Klein, PhD, https://theaimn.net/the-unbroken-thread-chinas-civilisational-state-vs-the-wests-contractual-empire-a-study-in-divergent-destinies/
Abstract
This article contrasts the developmental trajectories of China and the United States (representing the modern West) by examining their foundational civilisational codes, historical experiences, and political philosophies. It argues that while the U.S. follows the extractive, individual-centric model of a classic maritime empire (extending the Roman pattern), China operates as a continuous civilisational-state, its policies shaped by a deep memory of collapse and humiliation and a Confucian-Legalist emphasis on collective resilience. The analysis critiques the Western failure to comprehend China through the reductive lens of “Communism,” ignoring the profound impact of the “Century of Humiliation” and China’s subsequent focus on sovereignty, infrastructure, and social stability as prerequisites for development. The paper concludes that China’s model, focused on long-term societal flourishing over short-term extraction, presents a fundamentally different, and perhaps more durable, imperial paradigm.
Introduction: The Mandate of History vs. The Mandate of Capital
The rise of China is often analysed through the prism of Western political theory, leading to a fundamental category error. To compare China and the United States is not to compare two nation-states of similar ontological origin. It is to compare a civilisational-state – whose political structures are an outgrowth of millennia of unified cultural consciousness and bureaucratic governance – with a contractual empire – a relatively recent construct built on Enlightenment ideals, but ultimately sustained by global financial and military hegemony (Jacques, 2009). Their paths diverge at the root of their historical memory and their core objectives.
China’s Catalysing Trauma: Modern China’s psyche is indelibly shaped by the “Century of Humiliation” (c. 1839-1949), beginning with the Opium Wars – a stark example of Western imperial extraction enforced by gunboats (Lovell, 2011). This was compounded by the collapse of the Qing dynasty, civil war, and the horrific suffering during the Second World War. The foundational drive of the People’s Republic, therefore, was not merely ideological victory but the restoration of sovereignty, stability, and dignity (Mitter, 2013). Every policy is filtered through the question: “Will this prevent a return to fragmentation and foreign domination?”
America’s Founding Myth: The U.S. narrative is one of triumphant exceptionalism. Born from anti-colonial revolution, it expanded across a continent it saw as empty (ignoring Native nations) and engaged with the world primarily from a position of growing strength. Its traumas (Civil War, 9/11) are seen as interruptions to a forward progress, not as defining, humiliating collapses. This fosters an optimistic, forward-looking, and often abistorical mindset (Williams, 2009).
2. Political Philosophy: Meritocratic Collectivism vs. Individualist Democracy
China’s System: The “Exam Hall” State. China’s governance synthesises Confucian meritocracy and Legalist institutionalism. The modern manifestation is a rigorous, multi-decade screening process for political advancement, emphasising administrative competence, economic performance, and crisis management (Bell, 2015). The objective is governance for long-term civilisational survival. The Communist Party frames itself as the contemporary upholder of the “Mandate of Heaven,” responsible for collective welfare. Political legitimacy is derived from delivery of stability and prosperity.
The West’s System: The “Arena” State. Western liberal democracy, particularly in its U.S. form, is a contest of ideas, personalities, and interest groups. Legitimacy is derived from the procedural act of election. While capable of brilliance, this system incentivises short-term focus (electoral cycles), polarisation, and the influence of capital over long-term planning (Fukuyama, 2014). Expertise is often subordinated to popularity.
3. The Social Contract: Infrastructure & Security vs. Liberty & Opportunity
China’s Deliverables: Post-1978 reforms shifted focus to development, but within the framework of the party-state. The state prioritises and invests heavily in tangible foundations: universal literacy, poverty alleviation, high-speed rail networks, urban housing, and food security (World Bank, 2022). The social contract is explicit: public support in exchange for continuous improvement in material living standards and national prestige.
The West’s Deliverables: The Western social contract, historically, promised upward mobility and individual liberty protected by rights. However, the late-stage extractive economic model has led to the decline of public goods: crumbling infrastructure, unaffordable higher education, for-profit healthcare, and eroded social safety nets (Piketty, 2013). The contract feels broken, leading to societal discord.
4. Global Engagement: Symbiotic Mercantilism vs. Extractive Hegemony
China’s Method: Development as Diplomacy. China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is the archetype of its approach: offering infrastructure financing and construction to developing nations, facilitating trade integration on its terms. It is a form of state-led, long-term strategic mercantilism aimed at creating interdependent networks (Rolland, 2017). Its “soft power” is not primarily cultural, but commercial and infrastructural.
The West’s Method: The post-WWII U.S.-led order, while providing public goods, has been characterised by asymmetric extraction: structural adjustment programs, financial dominance, and military interventions to secure resources and political alignment (Harvey, 2003). It maintains a core-periphery relationship with much of the world.
Conclusion: The Durability of Patterns
The West’s mistake is viewing China through the simple dichotomy of “Communist vs. Democratic.” This ignores the 4,000-year-old continuum of the Chinese statecraft that values unity, hierarchical order, and scholarly bureaucracy. China is not “learning from Communism”; it is learning from the Tang Dynasty, the Song economic revolutions, and the catastrophic lessons of the 19th and 20th centuries.
China’s course is different because its definition of empire is different. It seeks a Sinic-centric world system of stable, trading partners, not necessarily ideological clones. Its focus is internal development and peripheral stability, not universal ideological conversion. Its potential weakness lies in demographic shifts and the challenge of innovation under political constraints. The West’s weakness is its accelerating internal decay and inability to reform its extractive, short-termist model.
Two imperial models are now in full view. One, the West, is a flickering, brilliant flame from Rome, burning its fuel recklessly. The other, China, is a slowly rekindled hearth fire, banked for the long night, its heat directed inward to warm its own house first. History is not ending; it is presenting its bill, and the civilisations that prepared their ledger will write the next chapter.
References…………………………..
When the USSR and China saved humanity: How they won the World Anti-Fascist War.
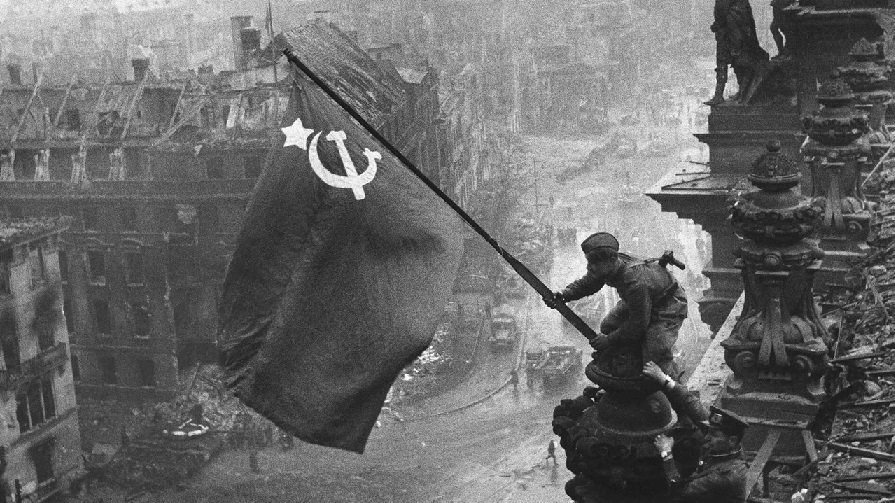

December 28, 2025 , By Ben Norton, https://geopoliticaleconomy.com/2025/12/26/ussr-china-world-anti-fascist-war/
It was the Soviet Union and China that defeated fascism in WWII. Their heroic contribution was later erased by the West. In the First Cold War, the US recruited former Nazis.
2025 marked the 80th anniversary of the defeat of fascism in World War Two. Unfortunately, the history of this extremely important conflict is not very well understood today.
It was not the United States and its Western allies that defeated fascism in WWII. That is a myth that is promoted by Hollywood movies.
In reality, it was the Soviet Union and China that defeated fascism in WWII. However, their heroic contribution was later erased by the West, when the US waged the First Cold War against the global socialist movement.
The vast majority of Nazi casualties, approximately 80%, were on the Eastern Front, in the Third Reich’s savage, scorched-earth battles against the Soviet Red Army.
More than 26 million Soviets died in the Nazi empire’s genocidal war. Compare that to the just over 400,000 US Americans who died, and the roughly 450,000 Brits who lost their lives.
This means that 62 Soviets were killed for every US American who died in WWII. Yet, tragically, their sacrifice has been forgotten in the West – or, better said, erased from public consciousness for political reasons.
The fact that the USSR defeated Nazi Germany was even admitted by the inveterate anti-communist Winston Churchill, an explicit racist, colonialist, and erstwhile admirer of Hitler who oversaw the British empire’s extreme crimes, including a famine in Bengal in 1943.
In a speech in August 1944, Churchill acknowledged:
“I have left the obvious, essential fact to this point, namely, that it is the Russian Armies who have done the main work in tearing the guts out of the German army. In the air and on the oceans we could maintain our place, but there was no force in the world which could have been called into being, except after several more years, that would have been able to maul and break the German army unless it had been subjected to the terrible slaughter and manhandling that has fallen to it through the strength of the Russian Soviet Armies”.
Then, in October 1944, Churchill said, “I have always believed and I still believe that it is the Red Army that has torn the guts out of the filthy Nazis”.
Read more: When the USSR and China saved humanity: How they won the World Anti-Fascist War.In fact, the USSR wanted to crush fascism even earlier by proposing a surprise attack on Nazi Germany in 1939, weeks before Hitler invaded Poland. Soviet military officers made an official request to British and French officials to form an alliance against Nazi Germany in August 1939, but London and Paris were not interested. The USSR had a million troops ready to fight, but the Western European powers were not prepared.
What the capitalist countries in Western Europe and North America had hoped for was that Nazi Germany would attack the Soviet Union, which they considered their main enemy. This is why the Western imperial powers had long appeased Hitler, signing shameful deals like the 1938 Munich Agreement, which allowed the Nazi empire to expand in Europe.
What the Western capitalist “liberal democracies” and the fascist regimes shared in common was mutual hatred of communism. The rich oligarchs who controlled Western governments feared that they would lose their privileges if workers in their countries were inspired by the Bolshevik Revolution.
In the 1930s, the US State Department spoke positively of fascism as an alternative to communism, and the US chargé d’affaires in Germany praised the supposedly “more moderate section of the [Nazi] party, headed by Hitler himself … which appeal[s] to all civilized and reasonable people”.
It must be emphasized that, when the Japanese empire officially allied with Nazi Germany in 1936, the name of the deal they signed was the Agreement Against the Communist International, or the Anti-Comintern Pact. Benito Mussolini’s fascist regime in Italy subsequently signed the agreement in 1937, and the fascist regimes in Spain, Hungary, and other European countries joined in the following years. It was extreme, violent anti-communism that united all of these fascist powers.
While there is widespread ignorance about the Soviet Union’s leading role in crushing Nazi Germany in WWII, the heroic contribution that the people of China made to the defeat of the Japanese empire is even less well known.
For Europe, WWII began in 1939, when Nazi Germany invaded Poland. For the people of China, the war started much earlier, in 1931, when the Japanese empire invaded the Manchuria region of northern China.
For 14 years, the people of China resisted Japan’s aggression, as the imperial regime sought to colonize more and more Chinese territory.
By the end of the war in 1945, roughly 20 million Chinese had lost their lives. This means that approximately 48 Chinese were killed for every US American who died in WWII.
In China, WWII is known as the Chinese People’s War of Resistance Against Japanese Aggression, and it was part of a larger conflict called the World Anti-Fascist War.
China held an important event on 3 September 2025 commemorating the 80th anniversary of the defeat of fascism. It featured key leaders of countries that are today, once again, fighting against imperialism and fascism, including China’s President Xi Jinping, Russia’s President Vladimir Putin, the DPRK’s leader Kim Jong-un, Iran’s President Masoud Pezeshkian, and officials from other countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, including Cuba’s President Miguel Díaz-Canel and Nicaragua’s representative Laureano Ortega Murillo.
The United States has long taken credit for the defeat of the fascist Japanese empire, but this erases the enormous, heroic, 14-year contribution made by the Chinese people.
Although it is true that the United States was briefly allied with the USSR and China during WWII, and it did provide significant military assistance through its 1941 Lend-Lease Act, Washington immediately terminated that partnership in 1945.
In fact, even before WWII officially ended, the United States had already started to recruit fascists to help them wage the First Cold War. US intelligence agencies saved many Nazi war criminals in the infamous Operation Paperclip. Instead of facing justice, these genocidaires assisted Washington in its subsequent attacks on the Soviet Union and its communist allies in Eastern Europe.
Later, the CIA and NATO created Operation Gladio, in which they used fascist war criminals as foot soldiers of their new global imperialist war on socialism. The former top Nazi military officer Adolf Heusinger was appointed the chair of NATO’s military committee, and the ex Nazi Hans Speidel became commander of NATO’s land forces in Central Europe.
The United States even rehabilitated Nazi war criminal Reinhard Gehlen, who had directed Hitler’s military intelligence on the Eastern Front in WWII, and who later led the CIA-backed Gehlen Organization to help Washington wage its cold war against communists.
The United States did not defeat fascism; it rehabilitated and absorbed fascism into the capitalist empire that Washington built after WWII, centered in Wall Street and based on the dollar.
The contemporary German government published the results of a study in 2016, called the Rosenberg project, which sifted through classified documents from 1950 to 1973. It found that, at the height of the Cold War, the government of capitalist West Germany, which was a member of NATO, was full of former Nazis.
In fact, 77% of senior officials in West Germany’s Justice Ministry had been Nazis. Ironically, there had been a lower percentage of Nazi Party members in the Justice Ministry in Berlin when the genocidal dictator Adolf Hitler himself was in charge of the Third Reich.
Similarly, in Japan after WWII, US occupation forces released Japanese war criminals from prison and used them to construct an imperial client regime. The CIA helped to create and fund the powerful Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), which has essentially governed Japan as a one-party state, with few exceptions, since 1955.
Notorious war criminal Nobusuke Kishi had overseen genocidal crimes against humanity against the Chinese people as an administrator of the Japanese empire’s puppet regime of Manchukuo, in Manchuria, during WWII. After the war ended, the United States strongly supported Kishi, who led the LDP, established the de facto one-party state, and became prime minister of the country.
Still today, the Kishi dynasty is one of the most powerful families in Japan. Kishi’s grandson Shinzo Abe also led the LDP and served as prime minister from 2012 and 2020, closely allying Japan with the United States, while antagonizing China and rewriting the history of WWII.
In short, after the Soviet Union and China led the fight to defeat fascism in WWII, the US empire recruited fascists to fight its global war against socialism.
Today, it is extremely important to learn these facts and correct the historical record, because 2025 is the 80th anniversary of the end of WWII, and it is clear that the proper lessons have not been learned in the West.
The planet is still plagued by extreme imperial violence, and closer than ever to another world war.
The United States and Israel have been carrying out a genocide against the Palestinian people in Gaza, committing atrocities that are reminiscent of the fascists’ crimes against humanity in WWII.
Fascism has its roots in European colonialism. The genocidal tactics that the European empires used in Asia, Africa, and Latin America were later used by the fascists inside Europe.
Nazi leader Adolf Hitler was inspired by the genocidal crimes that the German empire had committed in southern Africa, and also by the genocide that the US colonialists had carried out against indigenous peoples in North America. The Nazis were likewise influenced by the US government’s racist laws against Black Americans, in its apartheid system known as Jim Crow.
Given the close links between fascism and Western imperialism, it is not surprising to see that, today, the US regime has become increasingly fascist. Politicians in Washington scapegoat immigrants and foreigners for the many domestic problems in their country, including the significant growth in inequality, poverty, and homelessness. They have no solutions other than more violence, racism, and war.
The increasing political desperation and instability in Washington is combining in a toxic mixture with the greed of US corporations in the military-industrial complex, which profit from war, and are thus incentivized to push for more conflict, not for peace.
The United States, as the leader of NATO, has already been waging a proxy war against Russia in Ukrainian territory, using the people of Ukraine as cannon fodder in an imperial war, tragically destroying an entire generation of Ukrainians in a vain attempt to maintain US global hegemony.
The US empire has also used its Israeli attack dog to wage war on the people of Iran, in an attempt to overthrow the revolutionary government in Tehran and impose a puppet regime, like the former king, the shah, who was propped up by Washington.
The number one target of the US empire today, however, is the People’s Republic of China. US imperialists fear that China is the only country powerful enough to not only challenge but to defeat Washington’s global hegemony.
The US empire is waging a Second Cold War against China, and it has weaponized everything in this hybrid war, imposing sanctions and tariffs to wage economic war, using its control over the dollar system in a financial war, and exploiting the media to spread disinformation and fake news as part of an information war.
Part of the US empire’s strategy in this information war is to erase the Chinese people’s major contribution to the defeat of fascism and imperialism in WWII.
This is why it is so crucial to defend the facts, and to teach the true history of WWII to people today. If we don’t correct the historical record, the fascists and imperialists of the 21st century will weaponize ignorance in order to carry out the same crimes that their ideological brethren committed in the 20th century.
‘Pay price for wrongdoing’: China Sanctions 20 US defence firms after Trump approves Taiwan arms sale
China on December 27 announced sanctions on 20 U.S. defense companies and 10 senior executives, including Palmer Luckey of Anduril Industries, following the Trump administration’s approval of an $11.1 billion arms package for Taiwan.
by Aditi, December 27, 2025 , https://www.financialexpress.com/world-news/pay-price-for-wrongdoing-china-sanctions-20-us-defence-firms-after-trump-approves-taiwan-arms-sale/4089711/
China announced sanctions against 20 US defence companies and 10 top executives on Friday — the latest in a series of tit-for-tat measures. The announcement came soon after the Trump administration approved a major weapons sale to Taiwan. The sanctions list includes well-known companies like Northrop Grumman and Boeing’s defence unit in St. Louis, as well as Palmer Luckey, founder of Anduril Industries.
China said it will freeze the assets of these companies in the country, block them from doing business with Chinese organisations, and prevent the executives from entering mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macau, according to a report from the Wall Street Journal. Both Washington and Beijing have also announced export controls, investment restrictions, visa and travel bans and curtailed use of sensitive technology over the past year.
The Chinese Foreign Ministry said the US arms sale “interferes in China’s internal affairs and seriously undermines China’s sovereignty and territorial integrity.” The sanctions were announced on December 27, and according to a Global Times report, took immediate effect. Officials said the US decision went against the one-China principle and the three China-US Joint Communiques.
China sanctions US defence firms over Taiwan arms sale
Under the new measures, China has imposed sanctions on 20 US defence-related companies that it claims are involved in supplying weapons to Taiwan in recent years. The companies named include Northrop Grumman Systems Corporation, L3Harris Maritime Services, Boeing in St. Louis, Gibbs & Cox, Advanced Acoustic Concepts, VSE Corporation, Sierra Technical Services, Red Cat Holdings, Teal Drones, ReconCraft, High Point Aerotechnologies, Epirus, Dedrone Holdings, Area-I, Blue Force Technologies, Dive Technologies, Vantor, Intelligent Epitaxy Technology, Rhombus Power, and Lazarus Enterprises.
China announced that all movable and immovable assets of these companies located within the country will be frozen. Chinese individuals and organisations have also been barred from doing business or cooperating with these firms in any form.
Sanctions extended to senior executives
In addition to companies, China has also imposed restrictions on 10 senior executives in the defence sector. Among them is Palmer Luckey, founder of Anduril Industries, along with top executives from companies such as L3Harris and VSE Corporation, according to ANI. According to the Foreign Ministry, these executives will face restrictions on assets located in China and activities related to the country.
Taiwan is a ‘red line’, says China
A spokesperson for the Chinese Foreign Ministry said the Taiwan issue is at the very core of China’s national interests and is a red line in China-US relations. The spokesperson warned that anyone attempting to provoke China on the Taiwan question would face a firm response. In a statement, the ministry said, “Anyone who attempts to cross the line and make provocations on the Taiwan question will be met with China’s firm response. Any company or individual who engages in arms sales to Taiwan will pay the price for the wrongdoing. No country or force shall ever underestimate the resolve, will and ability of the Chinese government and people to safeguard national sovereignty and territorial integrity.”
China claims Taiwan as part of its territory — contending that the autonomously governed island must eventually be reunified with the mainland. The United States does not officially recognise Taiwan as a sovereign nation under the ‘One China’ policy, but maintains unofficial ties with the administration.
US arms supply to Taiwan
The reaction from China comes after the administration of US President Donald Trump approved a major arms package for Taiwan last week. According to the US State Department, the proposed sales are valued at more than USD 10 billion and include medium-range missiles, howitzers, and drones.
According to Focus Taiwan, the potential sale involves eight arms packages, including HIMARS rocket systems, anti-tank missiles, and drones, with a total estimated cost of USD 11.1 billion.
A Serious Proposal: Russia and China Call for Global Strategic Stability

By Alice Slater, World BEYOND War, October 8, 2025
It’s ironic that the arms control community is protesting the idea of resuming nuclear test detonations. The nuclear test detonations have never stopped.
Although Bill Clinton signed the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT) in 1996, he swiftly funded the “Stockpile Stewardship” program at the US nuclear weapons complex, allowing the Dr. Strangeloves in their labs to continue to perform laboratory tests as well as blowup plutonium with chemical explosives,1,000 feet below the desert floor at the Nevada Test Site on Western Shoshone holy land.
Since there was no chain reaction causing criticality, Clinton claimed these “sub-critical” tests were not nuclear tests and didn’t violate the new treaty. Of course, Russia and China swiftly followed the US lead; the Russians continued to test at Novaya Zemlya, and China at Lop Nor.
Indeed, it was the US’s refusal to promise that the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty would be truly “comprehensive” that caused India and Pakistan to test their nuclear arsenals after the US rejected their pleas to include prohibitions against “sub-critical” and laboratory tests in the CTBT. Although Clinton signed the CTBT, the US, unlike Russia and China, never ratified it. Sadly, Russia announced during the Ukraine war that it was leaving the CTBT.
People of goodwill who are alarmed at new reports of proliferating nuclear weapons and would like to put the nuclear genie back in the bottle, stop the endless wars and huge budgets for useless atomic weapons, would do well to take some advice from Russia and China. On May 8, they issued a “Joint Statement by the Russian Federation and the People’s Republic of China on Global Strategic Stability” in the context of the 80th anniversary of the end of World War II.
They note “the serious challenges facing the international community” and lay out several recommendations that would strengthen “global strategic security”, acknowledging that “the destinies of all countries are interrelated” and urging that states not “seek to ensure their own security at the expense and to the detriment of the security of other states.”
U.S. “Golden Dome”

They proceed to explain a whole series of provocative actions that threaten the peace, including states deploying nuclear weapons and missiles outside their territories. They are particularly critical of the US “Golden Dome” program, which is expected to create a new battleground in space. Reiterating their pleas over many years to keep space for peace, they state the following:
The two sides oppose the attempts of individual countries to use outer space for armed confrontation. They will counter security policies and activities aimed at achieving military superiority, as well as at officially defining and using outer space as a ” warfighting domain”. The two Sides confirm the need to start negotiations on a legally binding instrument based on the Russian-Chinese draft of the treaty on the Prevention of the Placement of Weapons in Outer Space and of the Threat or Use of Force Against Outer Space Objects as soon as possible, that would provide fundamental and reliable guarantees for preventing an arms race in outer space, weaponization of outer space and the threat or use of force against outer space objects or with their help. To safeguard world peace, ensure equal and indivisible security for all, and improve the predictability and sustainability of the exploration and peaceful use of outer space by all States, the two Sides agree to promote on a global scale the international initiative/political commitment not to be the first to deploy weapons in outer space.
The US and its allies, sheltering under the US nuclear umbrella, would do well to take Russia and China up on their offers for making a more peaceful world! With Mother Earth sending cascading warnings about the need for nations to cooperate, we can ill afford business as usual. Time to change course!
*Alice Slater serves on the Boards of World BEYOND War and the Global Network Against Weapons and Nuclear Power in Space. She is an NGO representative at the UN for the Nuclear Age Peace Foundation.
China’s New Underwater Drones Could Blindside the U.S. Navy

1945, By Reuben Johnson, 10 Dec 25
Key Points and Summary – China is quietly opening a new front in undersea warfare. Beijing’s latest AI-enabled underwater drones can execute zero-radius turns, recharge at submerged stations, datalink with each other, and reportedly operate below 90 decibels—making them extremely hard to detect.
-Designed to block shipping lanes, threaten warships, and autonomously target and attack, these systems fit neatly into China’s broader effort to keep U.S. and allied navies away from Taiwan.
China continues to make progress in drone technology—especially in aerial combat designs.
Their vehicles are similar to those being developed in the West, such as Collaborative Combat Aircraft or “loyal wingman” programs.
On Sept. 3, observers in Beijing were able to get a glance at one of China’s latest military innovations—a platform that could cause headaches for the U.S. and its allies.
The new design is for an unmanned underwater drone system controlled by what is described as advanced AI capabilities.
This new technology developed for the People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) could be a disruptive development and a ground-breaking capability in anti-submarine warfare.
The new underwater drones are purportedly capable of zero-radius turns and can operate in almost any maritime environment.
They are also promoted as being difficult to detect by modern sonar and other underwater sensor networks, since any noise they generate during operations is below 90 decibels.
According to a recent report by the South China Morning Post, the PLAN’s newest unmanned systems do not have to operate as solo platforms—they will datalink and coordinate with each other to carry out a host of different missions.
These would include blocking shipping lanes, threatening naval vessels at sea, and launching attacks on seaborne targets.
Detection Impossible
China’s new underwater drone systems are reportedly also capable of long-endurance missions, as they can recharge batteries at underwater stations.
Since they will operate in an almost self-aware mode using AI, they will be able to autonomously identify a target, develop a firing solution, and attack any platform they deem a threat.
The endurance capability, ability to operate without a datalink to an operator, and the extreme ranges at which they will be able to strike would all be new advancements in underwater unmanned vehicles.
However, the real worry for adversaries is these undersea drones’ unprecedented ability to evade detection.
As one recent article points out, “this could disrupt the current global maritime security governance.”….. https://www.19fortyfive.com/2025/12/chinas-new-underwater-drones-could-blindside-the-u-s-navy/
China releases arms control white paper in new era; ‘document injects positive energy, safeguards developing nations’ rights

Global Times By Liu Xuanzun and Guo Yuandan, : Nov 27, 2025
China’s State Council Information Office on Thursday released a white paper titled “China’s Arms Control, Disarmament, and Nonproliferation in the New Era.” An expert told the Global Times that at a time when the existing international arms control mechanisms are facing challenges, the white paper issued by China injects positive energy into the global arms control and nonproliferation process and fully safeguards the rights of developing countries.
Apart from the preface, conclusion, and annexes, the white paper has five sections: “Grim Realities: International Security and Arms Control,” “Position and Policies: China’s Arms Control in the New Era,” “Playing a Constructive Role in International Arms Control,” “Leading International Security Governance in Emerging Fields,” and “Strengthening International Cooperation on Nonproliferation and Peaceful Uses of Science and Technology.”
The white paper reiterated that China upholds a firm commitment to a policy of no-first-use of nuclear weapons and a nuclear strategy of self-defense. It said that China was compelled to make the strategic choice to develop nuclear weapons at a particular point in history to deal with nuclear threats and blackmail, break the existing nuclear monopoly, and prevent nuclear wars. China’s nuclear weapons are not intended to threaten other countries, but for defense and self-protection. China has never used nuclear weapons to threaten other countries nor deployed nuclear weapons outside its own territories, and has never provided a nuclear umbrella for other countries.
China releases arms control white paper in new era; ‘document injects positive energy, safeguards developing nations’ rights’
By
Liu Xuanzun and Guo YuandanPublished: Nov 27, 2025 10:25 PM
latest news
China’s State Council Information Office on Thursday released a white paper titled “China’s Arms Control, Disarmament, and Nonproliferation in the New Era.” An expert told the Global Times that at a time when the existing international arms control mechanisms are facing challenges, the white paper issued by China injects positive energy into the global arms control and nonproliferation process and fully safeguards the rights of developing countries.
Apart from the preface, conclusion, and annexes, the white paper has five sections: “Grim Realities: International Security and Arms Control,” “Position and Policies: China’s Arms Control in the New Era,” “Playing a Constructive Role in International Arms Control,” “Leading International Security Governance in Emerging Fields,” and “Strengthening International Cooperation on Nonproliferation and Peaceful Uses of Science and Technology.”
The white paper reiterated that China upholds a firm commitment to a policy of no-first-use of nuclear weapons and a nuclear strategy of self-defense. It said that China was compelled to make the strategic choice to develop nuclear weapons at a particular point in history to deal with nuclear threats and blackmail, break the existing nuclear monopoly, and prevent nuclear wars. China’s nuclear weapons are not intended to threaten other countries, but for defense and self-protection. China has never used nuclear weapons to threaten other countries nor deployed nuclear weapons outside its own territories, and has never provided a nuclear umbrella for other countries.
Whether confronted with nuclear threats or blackmail during the Cold War, or in a complex international security environment with growing strategic security threats at present, China has always committed to its policy of no-first-use of nuclear weapons, firmly upheld a nuclear strategy of self-defense, and promoted the modernization of its nuclear forces to safeguard China’s own strategic security and overall global strategic stability, according to the white paper………………………………………
…………….China previously issued white papers on arms control in 1995 and 2005. Pointing out new highlights in the new version, Guo told the Global Times that this white paper, for the first time, puts forward China’s vision for arms control – justice, cooperation, balance and effectiveness – emphasizing the balance of rights and obligations. It explicitly opposes abusing the concept of national security and export control measures, and exerting restrictions on developing countries’ rights to peaceful use of technology, Guo said.
Second, it is the first time to specifically address international security governance in emerging fields, detailing governance in the areas of outer space, cyberspace, and artificial intelligence, Guo said, noting that China advocates for strengthening the construction of a global governance system that takes into account the positions and interests of developing countries.
Third, the white paper summarizes China’s arms control policies and practices since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, highlighting many new practices and approaches. For example, in the field of nuclear arms control, in 2024, China submitted a working paper to the second session of the Preparatory Committee for the Eleventh Review Conference of the Parties to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT), calling on the five nuclear-weapon states to conclude a treaty on mutual no-first-use of nuclear weapons, and also maintaining that nuclear-weapon states should undertake not to use or threaten to use nuclear weapons against non-nuclear-weapon states, Guo said. ………………..
…………………..The white paper said that China upholds a firm commitment to a policy of no-first-use of nuclear weapons and a nuclear strategy of self-defense, stressing that China’s greatest contribution to international nuclear arms control lies in the fact that it has the most stable, consistent and predictable nuclear policy among all nuclear-weapon states. “China’s nuclear weapons policy has remained remarkably consistent since 1964, consistently keeping its nuclear capabilities at the minimum level required for national security,” the expert noted………………………………………
…………………… n the chapter “Playing a Constructive Role in International Arms Control,” the white paper urged Japan to thoroughly destroy the chemical weapons it abandoned in China. During World War II, in flagrant violation of international law, invading Japanese troops used chemical weapons on a large scale in China. A total of 1,791 instances of chemical weapon use have been documented with confirmed dates, locations, and casualty records. The resulting casualties exceeded 200,000. After its defeat, Japan abandoned a large quantity of chemical weapons in China to cover up its crimes. Since the end of World War II, these abandoned chemical weapons have resulted in more than 2,000 poisoning casualties, gravely endangered the lives and property of the Chinese people as well as the environment.
“The Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) clearly stipulates that a state party which has abandoned chemical weapons on the territory of another state party shall provide all necessary financial, technical, expert, facility as well as other resources for the purpose of destroying these weapons. After the CWC entered into force, the governments of China and Japan signed two memorandums, in 1999 and 2012, on destroying the chemical weapons abandoned by Japan, to advance the destruction process. However, due to insufficient attention and input from the Japanese side, the destruction plan has missed four deadlines. To date, the Japanese side has not yet provided comprehensive, detailed and accurate information on the whereabouts of its abandoned chemical weapons.
…………………………..Introducing the white paper, Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Guo Jiakun said at a regular press conference on Thursday that this year marks the 80th anniversary of the victory in the Chinese People’s War of Resistance against Japanese Aggression and the World Anti-Fascist War, as well as the 80th anniversary of the founding of the UN. ……………………………………………………………………… https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202511/1349241.shtml
China warns of severe consequences if Japan fails to retract its threats of military intervention over Taiwan
Japan, like most of the countries in the world, officially recognizes Taiwan as part of China. Both the countries signed an agreement in 1972 according to which Japan recognizes the one-China policy.
Though Japan recognizes the “one-China policy”, earlier this month its prime minister, Sanae Takaichi, threatened military intervention if China tried to unify Taiwan with the mainland.
November 20, 2025 by Abdul Rahman, https://peoplesdispatch.org/2025/11/20/china-warns-of-severe-consequences-if-japan-fails-to-retract-its-threats-of-military-intervention-over-taiwan/
China reiterated its demand that Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi retract her statement threatening military intervention in the event that China tries to forcefully integrate Taiwan into the mainland. It warned of strong counter measures otherwise.
The “Japanese prime minister’s erroneous remarks on Taiwan have fundamentally eroded the political foundation of China-Japan relations and triggered strong outrage and condemnation from the Chinese people,” said official spokesperson of the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Mao Ning, in response to a question on Wednesday, November 19.
“Retract the erroneous remarks, stop making provocations on issues concerning China, take practical steps to admit and correct the wrongdoing, and uphold the political foundation of China-Japan relations,” Mao reiterated.
Speaking in the country’s parliament, newly elected Takaichi had said on November 7 that her country may respond militarily to any “situation threatening Japan’s survival” including an attempt to force the unification of Taiwan with China.
She also added that if a US warship sent to break a possible blockade on Taiwan is attacked it would invite a similar Japanese military response.
Japan hosts the largest contingent of American forces anywhere outside the US territory.
Despite strong Chinese protests and a diplomatic spat last week, Takaichi is still refusing to retract her comments, claiming that they were “hypothetical” in nature. She also said she would not repeat them in future.
However, China has demanded a complete retraction, saying Takaichi’s statement violates the fundamental principle of China-Japan relations and amounts to interference in its domestic affairs, a red line.
Indications of Japanese militarism
Mao also objected to Takaichi’s invocation of phrases such as “survival threatening situation” and “collective self defense” in the case of Taiwan, saying that it is a pretext for “Japanese militarism to launch aggression” in the region.
Takaichi, of Japan’s Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), is widely seen as an ultra nationalist and a hawk who wants to reverse the demilitarization of Japan imposed post the Second World War.
After assuming power in October she pushed the country’s defense budget up and even talked about revisiting Japan’s long held no-nuclear policy and manufacture of heavy weapons.
Takaichi’s Taiwan statement is based on the country’s military strategy, which provoked widespread popular protests in the country when it was adopted in 2015.
Mao reminded that similar aggressions and excuses had been used by the Japanese to justify its occupation of Chinese territories in the last century and to bring the Second World War into the region.
“In 1931, Japan called its seizure of Manchuria as ‘survival-threatening’, and used that as a pretext to carry out the September 18th incident and invaded and occupied Northeast China,” Mao reminded.
“Japan later claimed that to defend ‘the greater East Asia co-prosperity sphere’ was an existential battle” for it and expanded its war of aggression to the entire Asian region, Mao pointed out, asking “whether to attack Pearl Harbor was also deemed as survival-threatening to Japan, which ignited the Pacific War.”
“As we mark the 80th anniversary of the victory of the Chinese People’s War of Resistance against Japanese Aggression and the World Anti-Fascist War the international community must guard against and firmly thwart any attempt of reviving militarism, jointly uphold the post-WWII international order and safeguard world peace,” she emphasized.
Chinese counter measures
Japan, like most of the countries in the world, officially recognizes Taiwan as part of China. Both the countries signed an agreement in 1972 according to which Japan recognizes the one-China policy.
On November 12, China had underlined that Taiwan is the core of its national interest and a red line which no external force should cross. It asked the Japanese to respect the agreement signed between the two countries, including adherence to the “one-China policy”.
Since Takaichi’s remarks, China has taken several counter measures, including issuing a travel advisory asking its citizens to avoid traveling to Japan and restricting the sale of Japan’s seafood products in the country, among others.
China and Japan had a mutual trade of around USD 300 billion in 2024. Chinese visitors to Japan bring substantial revenue to the Japanese economy, according to one estimate, around USD 14 billion dollars each year.
“If Japan refuses to retract them or even continue to pursue the wrong course, China will have to take strong and resolute countermeasures and all consequences arising therefrom will be borne by Japan,” Mao warned.
China to reimpose ban on Japanese seafood imports amid row over Taiwan, reports say
Japan Times, By Jesse Johnson, STAFF WRITER, Nov 19, 2025
China will reimpose a ban on imports of Japanese seafood products, media reports said Wednesday, as the diplomatic row over Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi’s recent comments on Taiwan escalated and officials girded for a prolonged dispute.
The ban would effectively be a return to one put in place in August 2023, following Japan’s release of treated wastewater from the Fukushima No. 1 nuclear power plant. Tokyo and Beijing reached an agreement in September last year to resume imports, with Japan confirming the first shipment of seafood to China less than two weeks ago.
NHK said China had explained that the ban was necessary in order to monitor the wastewater being released from the No. 1 plant, with the import halt lasting “for the foreseeable future.”…………………………………………… https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2025/11/19/japan/politics/japan-china-relations-marine-products/
Coalition of the unlikely: How Australia and China could save the planet.

Cooperation between Australia and China could send a useful message to the Trump regime and other countries around the world about both the possibility of developing alternatives to failing American leadership and the institutional order it did so much to create.
By Mark Beeson | 17 November 2025, https://independentaustralia.net/politics/politics-display/coalition-of-the-unlikely-how-australia-and-china-could-save-the-planet,20387
If we are to survive, unprecedented levels of cooperation are needed, no matter how unlikely. Mark Beeson writes.
GLOBAL GOVERNANCE is failing. Nothing highlights this reality more dramatically than our collective inability to address the degradation of the natural environment adequately. Addressing an unprecedented problem of this magnitude and complexity would be difficult at the best of times. Plainly, these are not the best of times.
Even if climate change could be dealt with in isolation, it would still present a formidable challenge. But when it is part of a polycrisis of intersecting issues with the capacity to reinforce other more immediate, politically sensitive economic, social and strategic problems, then the prospects for effective cooperative action become more remote.
Indeed, the polycrisis makes it increasingly difficult to know quite which of the many threats to international order and individual well-being we ought to focus on. The “we” in this case is usually taken to be the “international community”, which has always been difficult to define, generally more of an aspiration than a reality, frequently more noteworthy for its absence than its effectiveness.
Nation-states, by contrast, can still act, even if we don’t always like what they do. The quintessential case in point now, of course, is the administration of U.S. President Donald Trump. Because it is by any measure still the most powerful country in the world, what America does necessarily affects everyone. This is why its actions on climate change – withdrawing from the Paris Agreement, gutting the Environmental Protection Authority, encouraging fossil fuel companies – matter so much.
But nation-states can also be forces for good and not just for those people who live within the borders of countries in the affluent global North. On the contrary, states that oversee a reduction in CO2 emissions are not only helping themselves, but they are also helping their neighbours and setting a useful example of “good international citizenship”.
When global governance is failing and being actively undermined by the Trump regime, it is even more important that other countries try to fill the void, even if this means cooperating with the unlikeliest of partners. Australia and China really could offer a different approach to climate change mitigation while simultaneously defusing tensions in the Indo-Pacific and demonstrating that resistance to the Trump agenda really is possible.
Friends with benefits
In the long term, if there still is one, environmental breakdown remains the most unambiguous threat to our collective future, especially in Australia, the world’s driest continent. And yet Australia’s strategic and political elites remain consumed by the military threat China supposedly poses, rather than the immediate, life-threatening impact of simultaneous droughts, fires and floods.
One of the only positives of the climate crisis is that it presents a common threat that really ought to generate a common cause. Some countries are no doubt more responsible for the problem and more capable of responding effectively, so they really ought to overcome the logic of first-mover disadvantage. No doubt, some other country will take over Australian coal markets, but someone has to demonstrate that change is possible.
China is possibly at even greater risk from the impact of climate catastrophes because of water shortages and, paradoxically enough, rising sea levels that will eventually threaten massive urban centres like Guangzhou and Shanghai. While there is much to admire about the decrease in poverty in the People’s Republic, it has come at an appalling cost to the natural environment. China also has powerful reasons to change its ways.
Unfortunately, Chinese policymakers, like Australia’s and their counterparts everywhere else, are consumed with more traditional threats to national strategic and economic security. This may be understandable enough in a world turned upside down by an unpredictable administration bent on creating a new international order that puts America first and trashes the environment in the process.
But in the absence of accustomed forms of leadership from the U.S. and the international community, for that matter, states must look to do what they can where they can, even if this means thinking the unthinkable and working with notional foes. China and Australia really do have a common cause when it comes to the environment and they could and should act on it.
Yes, this does all sound a bit unlikely. But if we are to survive in anything like a civilised state, unprecedented levels of cooperation would seem to be an inescapable part of limiting the damage our current policies have inflicted on the environment. In this context, Australia and China really could lead the way by simply agreeing to implement coordinated domestic actions designed to set a good example and address a critical global problem.
Leading by example
As two of the biggest consumers and producers of coal, Australia and China could make an outsize contribution to a global problem that would almost certainly win near universal praise, not to say disbelief. In short, China could agree not to build any more coal-fired power stations and Australia could commit to not opening any more new mines and rapidly moving to close down existing ones.
This would be a challenge for both countries, no doubt, but if we are ever going to address the climate challenge seriously, this is the sort of action that will be needed. There are no easy or painless solutions. But voluntarily abandoning the use of one of the most polluting fossil fuels is a potentially feasible and effective gesture that would make a difference. After all, China is a world leader in the development and use of green energy already, so the transition would be difficult but doable.
Australia has a shameful record of exporting carbon emissions and could live without the coal industry, which produces most of them, altogether. Coal extraction doesn’t employ many people and Australia is a rich enough country to compensate those affected by the loss of what are awful jobs in a dirty industry. If Australia can find $368 billion for submarines that will likely never arrive, to counter an entirely notional threat from China, it ought to be able to find a couple of billion to deal with a real one.
No doubt there would be significant pushback from coal industry lobbyists and politicians who think their future depends on being “realistic”, even if it means wrecking the planet. And yet it is possible, even likely, that such actions on the part of Australia and China would be very well received by regional neighbours, who would directly benefit from their actions and who might also be encouraged to consider meaningful cooperative actions themselves.
Given the failure of regional organisations like ASEAN to tackle these issues, normative pressure could be useful.
China might even get a significant boost to its soft power and regional reputation. President Xi Jinping frequently talks about the need to develop an “ecological civilisation”. Moving away from coal and collaborating with an unlikely partner for the collective good would be an opportunity to demonstrate China’s commitment to this idea, and to offer some badly needed environmental leadership.
If that’s not an example of what Xi calls win-win diplomacy, it’s hard to know what is.
A sustainable world order?
In the absence of what U.S. Senator Bernie Sanders calls a “revolution” in American foreign policy, multilateralism may well be in terminal decline. Indeed, it is an open question whether interstate cooperation will survive another four years of Trumpism, especially when the United Nations faces a funding crisis and politics in the European Union is moving in a similarly populist and authoritarian direction.
Cooperation between Australia and China could send a useful message to the Trump regime and other countries around the world about both the possibility of developing alternatives to failing American leadership and the institutional order it did so much to create. American hegemony was frequently self-serving, violent and seemingly indifferent to its impact on the global South, but we may miss it when it’s gone.
If multilateralism is likely to be less effective for the foreseeable future, perhaps minilateralism or even bilateralism can provide an alternative pathway to cooperation. Narrowly conceived notional strategic threats could be usefully “decoupled” from the economic and environmental varieties. In such circumstances, geography may be a better guide to prospective partners than sacrosanct notions about supposed friends and enemies.
Someone somewhere has to show leadership on climate change and restore hope that at least one problem, arguably the biggest one we collectively face, is being taken seriously. There really isn’t any choice other than to contemplate unprecedented actions for an unprecedented problem. Australia and China may not save the world, but they could make things a bit less awful and inject some much-needed creativity and hope into international politics.
Mark Beeson is an adjunct professor at the University of Technology Sydney and Griffith University. He was previously Professor of International Politics at the University of Western Australia.
-
Archives
- March 2026 (99)
- February 2026 (268)
- January 2026 (308)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (376)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS




