The remnants of Chernobyl are still present in the Black Sea

Forty years have passed since Chernobyl, but Chernobyl-related radioactive contamination in the Black Sea has not ended. TENMAK’s research has revealed that the concentration of caesium-137 in the Black Sea is seven times higher than in the Mediterranean Sea.
BirGün Daily, Giriş: 07.11.2025 , https://www.birgun.net/haber/the-remnants-of-chernobyl-are-still-present-in-the-black-sea-667018
Nearly 40 years have passed since the Chernobyl disaster, considered one of the world’s three largest nuclear accidents, but the radioactive contamination caused by the accident continues to affect the Black Sea. At the IVth National Symposium on Monitoring and Assessment in the Seas, Dr Aysun Kılınçarslan, presenting on behalf of the Turkish Energy, Nuclear and Mining Research Institute (TENMAK), announced the results of monitoring studies on radioactive contamination in Turkey’s coastal waters and sediments.
Analyses conducted in coastal sediments between 2015 and 2023 detected high levels of caesium-137 and strontium-90. While an average of 21 becquerels of caesium-137 isotope per kilogram was observed in the Black Sea, this rate was recorded as only 3.2 becquerels in the Mediterranean Sea. Values that are relatively high in the Sea of Marmara decrease as one moves towards the Aegean and Mediterranean Seas. The highest value found in the analyses exceeds 82 becquerels. This figure is 10 times higher than the highest value observed in the Mediterranean Sea. When viewed on a regional basis, the highest caesium-137 value in sediments, 50 becquerels, was found in Hopa. Hopa is followed by Trabzon and Sinop.
HIGH FIGURES IN TRABZON AND HOPA
In measurements taken in coastal surface waters between 2014 and 2023, the caesium-137 concentration averaged 9 millibecquerels per litre in the Black Sea, while this figure dropped to 1.6 millibecquerels in the Mediterranean Sea. Rates in the Bosphorus, Marmara and Çanakkale ranged between 8.4 and 6.9 millibecquerels, while the amount of caesium-137 in the water decreased in the Aegean Sea, falling to 1.8 millibecquerels. The highest figures were found in Trabzon and Hopa, which have been affected by Chernobyl for years and where cancer rates have increased. Tekirdağ, Ordu, Karasu and İğneada stand out as other regions with high measurements. Although the study’s findings indicate that these levels do not pose a risk to human health or environmental pollution, the significant difference between the Black Sea and the Mediterranean clearly demonstrates the consequences of Chernobyl-related contamination.
CHERNOBYL FLOWS
Another noteworthy finding of the study was the detection of plutonium-239, which does not occur naturally and is produced by nuclear reactions, alongside caesium-137. While average values do not differ between seas, the locations most affected by this contamination include Erdek, the Bosphorus Strait, Hopa, and Sinop. Experts point out that the sources of contamination linked to these isotopes are nuclear power plant accidents, nuclear weapons tests, and operational nuclear reactors. Chernobyl is also cited as a source of contamination in the Black Sea. Radioactive pollution from the out-of-control melted reactor and the surrounding area reaches the Black Sea via groundwater and the Dnieper River.
MARINE ASSESSMENT IS NECESSARY
Prof. Dr. İnci Gökmen, who revealed high levels of radiation in tea after Chernobyl, points out that the radiation level detected at 21 becquerels per kilogram is quite high. Gökmen states that data collected from the seas and coasts also highlights the need to measure radiation levels in the soil, adding, “It is surprising to see plutonium in the seas, even at low levels. Strontium is not surprising. However, since strontium does not emit gamma radiation and must be measured by chemical separation, measurements were rarely taken despite the presence of strontium in the environment and food after Chernobyl. However, the strontium values immediately after the accident can be estimated from the current results. By looking at the caesium levels in coastal surface water in some areas, it would be good to calculate the doses that swimmers or those working at sea, such as fishermen, would receive. It would be appropriate to take measurements in fish, mussels and other seafood. Thirty-nine years have passed since Chernobyl. Caesium has only undergone one half-life. This means that radioactive elements will remain in the seas for a long time to come,” he said. WHAT IS CAESIUM (CS-137)?
The most common radioactive form of caesium is Cs-137. Caesium-137 is produced by nuclear reactions. External exposure to Cs-137 can cause burns, acute radiation sickness and even death. Exposure to large amounts of Cs-137 can result from the misuse of a powerful industrial Cs-137 source, a nuclear explosion, or a major nuclear accident. Under normal conditions, large amounts of Cs-137 are not found in the environment. Exposure to Cs-137 can increase the risk of cancer due to the presence of high-energy gamma radiation. Ingestion or inhalation of Cs-137 increases the risk of cancer by causing the radioactive material to spread to soft tissues, particularly muscle tissue. Vascular plants do not accumulate high levels of caesium through root uptake because caesium is strongly adsorbed to the soil. However, the accumulation of radioactive residues on flora with large surface areas, such as lichens or mosses, is significant. Animals that feed on these plants can consume large amounts of radiocaesium (and other radionuclides present in radioactive fallout). Human consumption of the meat of such animals leads to the uptake of these radionuclides into the body.
Note: This article is translated from the original article titled Çernobil’in izleri hâlâ Karadeniz’de, published in BirGün newspaper on November 7, 2025.
New Radiation Protection Standards in 2026?

Tony Webb – November 2025.
In May 2025 US President Donald Trump ordered the US Nuclear Regulatory
Commission (NRC) to review US radiation protection standards for workers and the public. The order claims that these and other NRC regulatory processes hinder development of US nuclear power generation and need to be revised – in line with another set of his ‘alternative facts’ that overturn almost all the established principles that provide the basis of national and international protection standards.
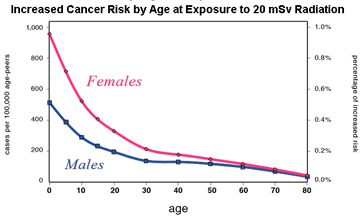
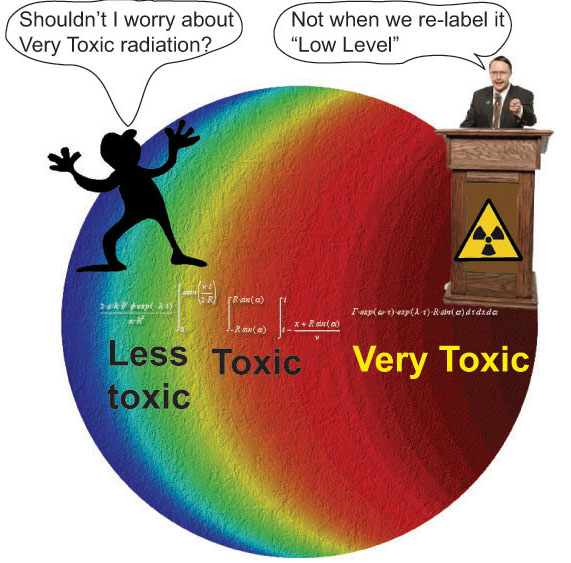
This latest diktat will result in a significant weakening of current protection at a time when we have mounting scientific evidence that the existing standards need to be significantly improved/tightened. Permissible radiation exposures to workers will likely increase five-fold. Exposures to the public could be 100 times greater than currently permitted. Changes in the USA will lead to pressure for similar changes to standards in other countries, including Australia. Whether we end up with better or worse protection will require a sustained awareness and advocacy campaign. This will need to involve exposed workers, trade unions, environment and public health
interests arguing: first that our government and radiation protection agencies should reject the US approach, and second that new and improved national standards in line with the latest evidence should be adopted.
Health effects of radiation exposure
It has long been recognised that all radiation exposures present a risk to human health. Put simply there is no safe level of radiation – whether naturally occurring or artificially generated. Some we cannot avoid. Some like diagnostic medical x-rays we accept as having other countervailing benefits. High doses, like those received
by Japanese residents of Hiroshima and Nagasaki from nuclear bombs in 1945, or some of the first responders to the Ukrainian Chernobyl nuclear reactor meltdown in 1986, cause ‘radiation sickness’ where whole organs are damaged often with fatal
effects.
The results from high-dose exposures are what are known as ‘determinate’ effects.
Above a threshold dose these effects occur with severity determined by the dose. Radiation standards are set to keep exposures below the threshold, so these do not occur.
Lower doses cause a different kind of damage. Particularly concerning are increased rates of a wide range of cancers and genetic damage being passed on to future generations. These are referred to as ‘stochastic’ effects. The damage is not ‘determinate’ with a threshold below which they do not occur. Stochastic damage is a ‘hit and miss’ affair. You either get this type of health damage or you don’t. And if you do the scale of the damage isn’t related to the radiation dose you received.
The initial damage occurs at the cellular level where a radiation strike can have one of three outcomes. (i) It may simply pass through causing no damage. Alternatively, (ii) the radiation may kill the cell which isn’t a problem, unless too many cells are killed at once affecting functioning of whole organs. Our bodies are eliminating and replacing dead and dying cells all the time. Problems arise however when (iii) the cell is merely damaged and goes on to replicate in this damaged form.
Our bodies do have well developed repair mechanisms that often result in adequate repair of the damage. There is even some evidence suggesting that some such radiation damage and repair may assist the body’s capacity for repair in the future.
But where radiation leaves the damaged cell to survive and replicate uncontrollably in this damaged form the result is what we call a cancer – sometimes detectable only decades after the initial radiation damage. The process can be complicated further as growth of some cancers involves a two-stage process – initiation, where damage (from radiation or other environmental pollutants) leaves the cell susceptible,
followed by promotion (again from radiation or other sources) which drives the cell-cancer process forward.
Stochastic radiation damage is real. it doesn’t involve a threshold dose. Any exposure can be the one that causes the initial and/or subsequent damage leading to the health effects. We are in the world of ‘probability’ – far from certainty at the individual level but with fairly predictable outcomes at the population level which allow us to assess the risk (i.e., probability of an adverse outcome) individuals face from receiving small, sometimes repeated, doses of radiation.
Radiation protection principles.
In light of these established mechanisms for harm from radiation, standard setting bodies have long adopted three principles – that any exposure needs to be: (i) justified as necessary against some social benefits; (ii) kept as low as reasonably achievable (the ALARA principle); and (iii) kept below specified limits set in regulations.
The last of these has been the subject of much controversy over the years.
Standards have been set for workers’ occupational exposures and for public exposures. These, first, ensure exposures are below the threshold levels where deterministic effects might occur. Below these high levels, they have been set such that the risk of stochastic effects – particularly cancers and genetic damage are at levels deemed ‘acceptable’. There have been arguments over both what is ‘acceptable’ and how the probable level of risk from any given low dose is estimated.
Estimates of risk
A number of early studies of patients exposed as part of medical procedures indicated a problem with radiation exposure and some early estimates of the stochastic risk. Since then, the bulk of the data for the estimates of risk has come from studies of survivors of the Japanese nuclear bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945. These Life Span Studies (LSS) have consistently shown
increases in cancer rates among survivors higher than those in the non-exposed population. There are a number of problems with this data – not least that survivors were not wearing film badges when the bombs went off, so all doses have had to be estimated later. They were also the ‘hardy’ survivors of wide-ranging traumatic
events, perhaps less vulnerable to damage from radiation Most of these survivors received relatively high doses as a single exposure or within a relatively short time period. More accurate measures of small exposures repeated over longer time periods to a general population, might be expected to yield different results.
However, these were the best data to be had. The risks at lower doses are estimated using the assumption that, if there is no safe level of exposure, no threshold below which stochastic effects do not occur, we can estimate lower dose risks on a straight line from these higher LSS doses. This Linear No Threshold (LNT) assumption, though adopted by all stands setting bodies, has at times been contested. Some have suggested a sub-linear relationship with a threshold for any effects. Others have made the case for a super-linear or marginally higher effect at lower doses where these are spread over longer time periods or result from radiative material that gets inside the body.
For now all the significant agencies agree that radiation protection for workers and the public should be based on LNT and the three radiation protection principles: justification, ALARA, and Specific Exposure Limits. These agencies include: the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) the United Nations
Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) the US National Academy of Sciences Committee on the Biological Effects of Ionising Radiation (known as the BEIR Committee) and national agencies like the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA). The cancer risk from low
dose radiation is estimated to be in the range of 4-6% per Sievert (1000 mSv) of exposure. The risk of genetic damage (first two generations only) is estimated to be around 1.5% per Sievert.
These estimates have resulted in national protection bodies setting standards that limit annual exposures. For workers the annual limit is 20 mSv as a target – but with 50 mSv allowed in any year provided the average over five years does not exceed 20 mSv. The annual limit for public exposures is 1 mSv. All of these are for
exposures in addition to what might be received from natural background radiation or exposures due to medical procedures such as diagnostic x-rays and nuclear medicine.
Change is coming – one way or another.
It is these protection principles and the exposure standards for workers and the public that the Presidential directive to the US NRC seeks to overturn. It calls on the NRC to reconsider reliance on LNT (and ALARA) as the basis for standard setting at low doses, where there is a need to protect against probable stochastic effects and
directs that instead the NRC set standards based on deterministic effects.
This will likely result in a significant weakening of the current standards at a time when the evidence strongly suggests that they are in need of further tightening. The current standards have been in place since 1991. Revisions at that time were the result of a sustained campaign throughout the 1980s led by trade unions in the UK, Europe, USA and Canada for reduction of the then 50 mSv occupational and 5 mSv public limits -justified in large part by emerging evidence from the Japanese lifespan studies. As previously noted, estimates of risk from these was based on one-off
short-term exposure to relatively high doses (at and above 100 mSv). Since then, studies in Europe and North America of workers exposed over years of work in nuclear industries to doses below the current occupational limits, indicate the risks are around 2 to 3 times greater than those used for setting the current standards.
They also show a doubling of expected rates of cardio-vascular diseases: strokes, arthro-sclerosis, and heart damage. In addition, studies of populations living close to nuclear facilities in Europe and the USA show childhood cancer rates significantly higher than expected. This evidence is cause for concern, suggesting that the
current standards provide inadequate protection and need to be tightened.
A new campaign for improved protection?
Past experience suggests that persuading national and international bodies to improve radiation protection standards is far from easy but not impossible. In the short term, a campaign would be seeking clear and unequivocal statements from national protection agencies that reject the US president’s directive that the NRC abandon the fundamental principles which have formed the basis for regulating worker and public exposures. If implemented Trump’s proposals would likely result in occupational exposure limits five times higher than presently allowed, and public exposure limits could be 100 times greater.
The campaign should seek assurances that there will be no change to the established principles underpinning radiation protection: that there is no safe level of radiation, that all exposures should be kept as low as can be reasonably achievable; and that occupational and public limits need to be based on the best scientific evidence of risk to human populations.
Raising the concern about, and seeking rejection of, the likely US NRC changes will require building an informed coalition of trade union, environment and public health interests. Occupational and public radiation exposures are more widespread that commonly appreciated. Workers are routinely exposed in mining, industry and medicine as well as those associated with the nuclear power industry. The. campaign could involve local initiatives that focus concerns of workers in , and people living close to sites of: proposed nuclear power plants; existing uranium, mineral sands, and hard rock mines; proposed ‘rare earth’ mines; medical and other
radioactive waste storage sites; and other activities that routinely release radiative materials.
Opposing Trump’s latest proposals to weaken standards is fairly straightforward. If implemented by the NRC they would dismantle the whole edifice on which radiation protection has been built over the past 80 years – a framework that many concerned about radiation protection within the affected industries have invested time and energy to establish and maintain.
Pressing the claim for improvements is harder but not impossible given the evidence for greater harm that is emerging. The case can already be made for at least halving the permissible occupational and public exposure limits. If we are successful in pressing for improved protection standards, the nuclear industry is unlikely to thank President Trump for opening this can of worms with his NRC directive. Once opened it will be hard to close without increasing worker and public awareness of how any, and all radiation exposures increase health risks to workers the public and to future generations.
Tony Webb has worked as a researcher, consultant and advisor on radiation and health issues to politicians, trade unions, environment and public health groups in the UK, Europe, USA , Canada and Australasia since the late1970s. He can be contacted for information on how to assist the latest evolving international campaign via tonyrwebb@gmail.com.
Three workers at nuclear fuel reprocessing plant possibly exposed to internal radiation
AOMORI – https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2025/10/29/japan/society/nuclear-plant-internal-exposure/
Three workers may have suffered internal radiation exposure while working in a spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in Rokkasho, Aomori Prefecture, Japan Nuclear Fuel has said.
The men in their 20s to 40s are employees of a partner company sent to work in a controlled area of the plant, according to an announcement by Japan Nuclear Fuel on Monday.
Radiation was detected inside the nasal cavity of one of the three, who is in his 40s, prompting the company to check whether all three had been internally exposed.
None of them has reported any change in their health condition so far, Japan Nuclear Fuel said.
According to the company, the three were working to replace filters that remove radioactive materials from gas emitted from a tank, in a building used for denitration of uranium-plutonium mixed solution, when radiation levels rose at around 11:10 a.m. Friday.
After they left the area, as instructed, contamination was found on the outer surface of the filters of their protective masks.
When contamination is detected, workers are typically instructed to cover air intake filters with tape to prevent further contamination and replace the filter while holding their breath.
However, two of the three breathed without filters for up to three minutes, according to Japan Nuclear Fuel. It is not clear when that occurred.
The company is still investigating why the two men breathed without filters. It is also analyzing urine and stool samples from the three workers to determine whether internal radiation exposure occurred, and investigating the cause of the increase in radiation levels.
Dounreay waste particle ‘most radioactive’ find for three years

Steven McKenzie, Highlands and Islands reporter and Rachel Grant, BBC Scotland. 23 Oct 25
A fragment of waste found near the decommissioned experimental nuclear power facility in Dounreay in April was the most radioactive to be detected in the past three years, the Highland site’s operator has said.
The fragment, categorised as “significant”, was discovered during monitoring work around the nuclear power plant near Thurso. It is the latest in a long line of particle discoveries in the area.
Dounreay was built in the 1950s as the UK’s centre of fast reactor research, but during the 1960s and 1970s sand-sized particles of irradiated nuclear fuel got into the drainage system.
Work to clear the pollution began in the 1980s, after particles were found washed up on the nearby foreshore.
The facility closed in 1994. The multi-billion pound decommissioning process involves hundreds of workers and is expected to last into the 2070s.
The full decontamination of the site is expected to take more than 300 years.
A Dounreay spokesperson said: “Particles are a legacy of industrial practices dating back to the early 1960s and our commitment today to environmental protection includes their monitoring and removal from the marine environment and transparent reporting of our activities.”
A group of independent experts, who advise the Scottish Environment Protection Agency (Sepa) and Dounreay, classify particles by the radioactivity of their caesium-137 content.
The categories are minor, relevant and significant.
Significant means a reading greater than one million becquerels of CS-137.
A becquerel is the standard unit of radioactivity.
The particle was found on the western part of Dounreay’s foreshore on 7 April. Eight other finds reported since then have been categorised as “minor” or “relevant”.
A significant-category particle was last discovered in March 2022.
Thousands of particles of different categories have been removed from beaches, foreshore and seabed at Dounreay.
The site’s operator said monitoring on the site on the north Caithness coast continued to be done on a fortnightly basis.
On occasions it said the scheduled work could be interrupted by bad weather or the presence of protected species of ground-nesting birds……………………………………………………..
What risk is there to the public?
According to official reports, risk to people on local beaches is very low.
Guidance issued by the UK government’s Nuclear Restoration Services says the most at-risk area is not accessible to the public.
The particles found along the coast vary in size and radioactivity with smaller and less active particles generally found on beaches used by the public.
Larger particles have only been found only on the foreshore at Dounreay, which is not used by the public.
The particles found on beaches are believed to come from the disintegration of larger fragments in the seabed near Dounreay. The area is continuously monitored for traces of radioactive materials.
Harvesting of seafood is prohibited within a 2km (1.2 mile) radius of a point near Dounreay. This is where the largest and most hazardous fragments have been detected.
Dounreay’s radioactive history
- 1954 – A remote site on the north coast of Scotland is chosen as the site of a new type of nuclear reactor. Modern homes were built in Caithness to attract workers to the sparsely populated area.
- 1957 – A chain reaction which provided sustained and controlled nuclear energy is achieved for the first time.
- 1959 – A new disposal site for radioactive waste called the Shaft opens. It drops 65.4m (214.5ft) below ground.
- 1962 – The fast reactor inside the dome is the first in the world to provide electricity to a national grid.
- 1977 – The original “golf ball” reactor is shut down and waste disposal in the Shaft ends after an explosion.
- 1994 – Dounreay nuclear power generating facility closes.
- 1998 – Decommissioning programme is announced.
- 2008 – Operation to scour the seabed for hazardous material begins and the Shaft shaft is encircled in a boot-shaped ring of grout to prevent contamination.
- 2020 – Clean-up begins of the highly contaminated Shaft – a three decades-long project.
- 2333 – Decontamination expected to be complete, making the 148-acre site available for other uses. https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cz91nx0lv59o
Generational RADIATION IMPACT Project

Uncovering Radiation’s Hidden Dangers
Protecting Women and Future Generations
Our Mission
The Generational Radiation Impact Project (GRIP) leads a global effort to bring gender-specific insights into radiation safety. Women are twice as likely to develop radiation-related cancer, yet this crucial fact is missing from most regulations. We aim to change that by conducting groundbreaking research, educating the public, and advocating for policy change. We envision a future where everyone has access to information about radiation risks, especially women and children, who are disproportionately affected. Learn more about how radiation affects women.
Why This Matters Now
Every day, millions of women and children are exposed to radiation through medical treatments, environmental pollution, and consumer goods. Yet, safety standards are based on outdated models that overlook biological differences between men and women. This leaves women—especially those of reproductive age—at greater risk for radiation-induced cancers. We are working to change this. With your support, we will continue our research to inform better policies and protect future generations.
…………………… Generational Radiation Impact Project works at the intersection of public health, medicine, and public policy. We are an educational and funding group that brings together top thinkers to understand the role biological sex plays in harm from radiation.
While this public health threat impacts us all, the risk is dramatically greater for girls and women. For every two men who develop cancer through exposure to ionizing radiation, three women will get the disease. Now we must learn why. https://www.radiationproject.org/
Major radiation warning as Israel says it’s ‘on verge of destroying 10 nuclear sites’

International Atomic Energy Agency director Rafael Mariano Grossi said protective measures need to be put in place due to the risk of radiation at the Natanz nuclear facility.
Chiara Fiorillo News Reporter, 17 Jun 2025, https://www.mirror.co.uk/news/world-news/major-radiation-warning-israel-says-35407962
A major radiation warning has been issued after Israel’s Defence Minister said his country is “on the verge” of destroying “more than 10 nuclear targets” in Iran. Israel Katz said the Israeli Air Force will strike “very significant targets, strategic targets, targets of the regime and infrastructure” in Tehran today. One of the targets include the underground Fordow facility which Katz said is “an issue that will certainly be addressed.”
The Natanz nuclear facility has already been hit by Israeli strikes and after the latest warning from Israel, the head of the UN nuclear watchdog agency, Rafael Mariano Grossi, warned of the widespread risks posed by attacks on such facilities. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) said there is a risk of of both radiological and chemical contamination within Iran’s main nuclear enrichment facility.
“Based on continued analysis of high resolution satellite imagery collected after Friday’s attacks, the IAEA has identified additional elements that indicate direct impacts on the underground enrichment halls at Natanz,” the agency said on X. “No change to report at Esfahan and Fordow,” the IAEA added.
The radiation poses significant danger if uranium is inhaled or ingested. Appropriate protective measures are needed to manage the risk, including using respiratory protection devices while inside the facilities. Mr Grossi said currently, radiation levels outside complex are normal.
Located 220km (135 miles) southeast of Tehran, the Natanz facility was protected by anti-aircraft batteries, fencing and Iran’s paramilitary Revolutionary Guard. The underground part of the facility is buried to protect it from airstrikes and contains the bulk of the enrichment facilities at Natanz, with 10,000 centrifuges that enrich uranium up to 5 per cent, experts assess.
The IAEA had earlier reported that Israeli strikes had destroyed an above-ground enrichment hall at Natanz and knocked out electrical equipment that powered the facility. However, most of Iran’s enrichment takes place underground.
Although Israel has struck Natanz repeatedly and claims to have inflicted significant damage on its underground facilities, Tuesday’s IAEA statement marked the first time the agency has acknowledged impacts there.
Iran has not discussed the damage done in depth at Natanz as the country is reeling from the ongoing Israeli strikes that are dismantling its air defence and killing its top military commanders.
The facility is located 220km southeast of Tehran(Image: Satellite image ©2021 Maxar Tech)
Israel says its sweeping assault on Iran’s top military leaders, nuclear scientists, uranium enrichment sites and ballistic missile program is necessary to prevent its adversary from getting any closer to building an atomic weapon.
The strikes have killed at least 224 people in Iran. Iran has retaliated by launching more than 370 missiles and hundreds of drones at Israel. So far, 24 people have been killed in Israel.
The Israeli military said a new barrage of missiles was launched on Tuesday. Iran maintains its nuclear program is peaceful, and the United States and others have assessed Tehran has not had an organized effort to pursue a nuclear weapon since 2003.
But the head of the IAEA has repeatedly warned that the country has enough enriched uranium to make several nuclear bombs should it choose to do so.
Radioactive Mussels May Pose Threat to Food Chain in Pennsylvania

By Tom Howarth, Science Reporter (Nature) Jan 07, 2025, https://www.newsweek.com/radioactive-mussels-food-chain-bioaccumulation-pennsylvania-2011149?fbclid=IwY2xjawJG4pxleHRuA2FlbQIxMQABHXBgrVgNhUUy1s_U9SLYXUIeD-gugNuUk75xBSTL9AG1vQ6REzIVWJiVGw_aem_0EvCj7mKrreGjCLuSViY1Q
Radioactive contamination in freshwater mussels is potentially affecting the food chain in Pennsylvania, including iconic animals such as bald eagles and possibly even humans.
A study published last year by scientists from Penn State University found elevated levels of radium in mussels downstream from a waste treatment facility in Franklin, Pennsylvania. Now, experts are raising the alarm over the secondary impacts on the ecosystem.
While the facility no longer discharges oil and gas wastewater into the Allegheny River, its legacy of pollution persists, with radioactive material bioaccumulating in the ecosystem.
Why This Matters
The findings highlighted that radioactive materials could be climbing the food chain, affecting not just aquatic life but also land animals, birds and people. Bald eagles, a species reintroduced to Pennsylvania in 1983, are among those at risk. Their diet includes muskrats, a primary predator of freshwater mussels, which are now confirmed to carry radium.
Although freshwater mussels are not consumed by humans, other species higher in the food chain may serve as a bridge for contaminants to eventually affect people. Local fishing activity in the Allegheny River also raises questions about indirect exposure to radioactive material.
Exposure to high levels of radium can result in adverse health conditions like anemia, cataracts, fractured teeth, cancer (especially bone cancer) and death, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says.
What To Know
Freshwater mussels act as ecological barometers because of their fixed locations and long life spans.
In this study, researchers found that mussels downstream of the waste treatment facility had absorbed radioactive particles into their soft tissue and hard shells. Mussels closest to the discharge site perished from salinity, while those farther away adapted but at a cost—they absorbed contaminants instead.
The study also compared the mussels’ radioactivity to Brazil nuts, which naturally absorb radiation from the soil. While a typical 28-gram serving of Brazil nuts contains 0.47 to 0.80 microsieverts, the maximum radioactivity found in a single mussel was 63.42 μSv.
While the International Atomic Energy Agency recommends an annual exposure limit of 1,000 μSv—far exceeding the amount found in even the most radioactive mussel—the findings are concerning because of the potential for radiation to accumulate within food chains over time.
What People Are Saying
Evan Clark, the waterkeeper at Three Rivers Waterkeeper, told Newsweek: “One concern that I immediately thought of after reading [the study] was bioaccumulation. Mussels live pretty close to the bottom of the food chain, eating a lot of algae and bacteria—they are unselective filter feeders.
“Muskrats are one of the larger consumers of freshwater mussels, eating hundreds and hundreds in a lifetime. Those muskrats are going to be eaten by bald eagles, and those bald eagles are only recently making a strong comeback into western Pennsylvania.”
Katharina Pankratz, a co-author of the study, said in a statement: “Depending on the contaminant and its chemistry, if it is small enough to pass through the gills of the mussel, it has the potential to accumulate in their tissue or precipitate within the hard-shell structure. This information may help shape future regulations for wastewater disposal to surface water, especially in regions where mussels are harvested for food.”
Nathaniel Warner, the study’s corresponding author, said in the statement: “Mussels that were closest to the water discharges died off. Further downstream, the mussels found a way to tolerate the salinity and radioactive materials and instead absorbed them into their shells and tissues.”
What Happens Next
The study’s findings could inform future policies on wastewater management, its authors said. While the waste treatment facility in Franklin is no longer discharging waste into the waterways, its impacts still linger and could do so for some time.
Key questions, such as how much radioactive material is accumulating up the food chain, remain.
40% of workers cite radiation concerns at Fukushima plant

By KEITARO FUKUCHI/ Asahi Shimbun, Staff Writer, February 2, 2025
Forty percent of the workforce at the crippled Fukushima No. 1 nuclear plant worry about radiation issues on the job, a nearly three-fold spike over the previous year, a survey found.
More than half of those respondents cited fears of their body coming into contact with a radioactive substance.
Tokyo Electric Power Co., the plant operator that conducted the annual survey, said recent incidents at the plant probably contributed to the heightened concerns.
For example, two workers were hospitalized in October 2023 after they were accidentally splashed with waste liquid containing highly radioactive substances while cleaning piping in a contaminated water treatment facility.
The survey was carried out between September and October to improve the working environment. TEPCO distributed a questionnaire to all workers at the plant and received responses from 5,498 individuals, or 94.5 percent……………………….
Asked to choose specific issues they were concerned about, 52.2 percent, the largest percentage, picked “physical contamination,” up about seven points from 2023.
In another incident, about 1.5 tons of contaminated water flowed out of a water purification facility at the plant through an air exhaust opening in February 2024…… more https://www.asahi.com/ajw/articles/15609878
How Fukushima’s radioactive fallout in Tokyo was concealed from the public
Because of the controversy surrounding Satoshi’s paper and the lack of research on the health impacts of these particles, it remains unclear to what extent Tokyo residents have been exposed to dangerous radiation levels as a result of the Fukushima accident.
Because CsMPs are so small, typically two microns or less in diameter, if humans breathe them, they could potentially reach the bottom of the lung, and be lodged into sacs known as alveoli, where the lung generally cannot expel them.
By unit of mass, CsMPs are much more radioactive than even spent reactor fuel
Japanese radiochemist Satoshi Utsunomiya found that air samples from March 15, 2011, in Tokyo contained a very high concentration of insoluble cesium microparticles. He immediately realized the implications of the findings for public safety, but his study was kept from publication for years.
Bulletin, By François Diaz-Maurin, January 13, 2025 [excellent illustrations]
On March 14 and 15, 2011—three days after the Great East Japan Earthquake and its resulting tsunami hit the Fukushima nuclear power plant—explosions at two of the plant’s reactor buildings released a huge amount of invisible radioactivity. These radioactive plumes were blown away by the wind, descending over the surrounding area and into the ocean. Eventually, the radiation emitted from the Fukushima plants spread over the entire Northern Hemisphere. It also spread to Japan’s capital, Tokyo.
Following the explosions, Japanese researchers rushed to collect and study radioactive materials from the soil and the air to find out what had happened inside the reactors, believed now to have melted down because their cooling systems failed. On March 13, the Tokyo Metropolitan Industrial Technology Research Institute, the agency responsible for measuring the air quality of particulate matter in the Tokyo area, started to collect air samples more frequently. This effort was part of the Tokyo metropolitan government’s emergency monitoring program for environmental radiation, which aimed to detect gamma-emitting nuclides in airborne dust. The filters revealed that at around 10 a.m. on March 15, 2011, a large plume of radioactivity reached Tokyo, some 240 kilometers (149 miles) south of Fukushima. All samples taken on March 14 and March 15 showed spikes in radioactivity.
The institute’s researchers published their first results in the journal of the Japan Radioisotope Association in June 2011 (Nagakawa et al. 2011); they estimated the total exposure dose to humans from radioactive substances, including iodine 131 and cesium 137 found in airborne dust, foodstuffs, and drinking water from the Setagaya ward in the old Tokyo City. Extrapolating from their measurements from March 13 to May 31, they calculated the corresponding annual cumulative dose of radiation in that part of Tokyo as being 425.1 microsieverts, which is less than half the annual dose limit to the public recommended by the International Commission on Radiological Protection. In a second conference publication in English (Nagakawa et al. 2012), the researchers extended their monitoring period to October and estimated that the total annual effective dose due to inhalation for adults in the Tokyo metropolitan area from the Fukushima radioactive plumes was far lower, at 25 microsieverts.
But two years after the accident, Japanese scientists discovered a new type of highly radioactive microparticle in the exclusion zone around the Fukushima plant. The microparticles, which had been ejected from the Fukushima reactors, contained extremely high concentrations of cesium 137—a radioactive element that can cause burns, acute radiation sickness, and even death. Satoshi Utsunomiya, an environmental radiochemist from Kyushu University in southwestern Japan, soon found that these particles were also present in air filter samples collected in Tokyo in the aftermath of the Fukushima accident.
The controversy surrounding his attempts to publish his findings nearly cost him his career and prevented his results from being widely known by the Japanese public ahead of the 2020 Summer Olympics in Tokyo.[1] Scientists still don’t know if these highly radioactive microparticles present significant danger to people, and Satoshi is one of the very few scientists who is focused on trying to find out. “We have the measurements now that tell that the particles did pass over population centers and were being deposited in places,” Gareth Law, a radiochemist from the University of Helsinki, told me. “We should answer the question.”
The discovery
In May 2012, Toshihiko Ohnuki, an accomplished environmental radiochemist then at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), visited Yoshiyasu Nagakawa at the Tokyo Metropolitan Industrial Technology Research Institute, also known as TIRI. Nagakawa was the first author of two TIRI studies on radiation exposure in Tokyo, and Ohnuki asked Nagakawa if he could obtain some air samples for further analysis. Ohnuki had already studied how radioactive cesium fallout from Fukushima reacted with components of contaminated soil. Now, he wanted to do the same with the airborne dust samples from Tokyo.
Nagakawa gave Ohnuki five small filters that had been collected from the Setagaya ward in old Tokyo City at different times on March 15, 2011—the day the radioactive plume reached Tokyo. Ohnuki received the samples without restriction on their use, and no written agreement was made.[2]
Back in his laboratory at JAEA, Ohnuki performed autoradiography of the five samples, revealing many radioactive spots on all of them. The bulk radioactivity on each sample was measured to be between 300 counts per minute for the filter that covered the midnight to 7 a.m. period and 10,500 counts per minute between 10 a.m. and 11 a.m. on March 15.[3] The radiation rate was so high that Ohnuki had to cut some of the filters into small pieces, less than one square centimeter, to keep from saturating the scanning electron microscope. Ohnuki stored the unexamined filters for future analysis.
Months later, in August 2013, four researchers from the Meteorological Research Institute in Japan reported for the first time about a new type of spherical radioactive cesium-bearing particle that had been ejected in the early days of the Fukushima accident (Adachi et al. 2013). The researchers had collected air samples on quartz fiber filters at their institute in Tsukuba, located 170 kilometers southwest of the Fukushima plant. Their findings, published in Scientific Reports, were about to revolutionize the way environmental radiochemists understood the radioactive fallout from Fukushima.
Back in the lab, the researchers placed the filters on an imaging plate and inserted them into a portable radiography scanner. The images revealed many black dots, which indicated the presence of radioactive materials on the filters, with a maximum radioactivity level measured on the sample at 9:10 a.m. on March 15, 2011, four days after the Fukushima accident began. The researchers placed this sample under a scanning electron microscope and then into an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer to directly observe the shape and composition of the radioactive materials on the filters. What they saw stunned them………………………………………………………………
Shocking results
The newly discovered entities were initially called spherical cesium-bearing particles, but Satoshi and his co-workers coined the term cesium-rich microparticles, or CsMPs, in 2017, which is now what researchers call them generally (Furuki et al. 2017). CsMPs had not been noted in earlier major reactor accidents.
Scientists knew the microparticles came from the Fukushima reactors because their isotopic ratio between cesium 134 and cesium 137 matched the average ratio for the three damaged reactors calculated by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory.[5] Because these particles emanated from the Fukushima reactors, Satoshi and the other scientists studying them thought that they may contain evidence about reactions that occurred during the accident. But the environmental radiochemist’s curiosity was also triggered by the unique features of these microparticles: Their size is very small, typically two to three microns, even smaller than one micron in some cases.[6] And the cesium concentration in each of the particles is very high relative to their size.
After Satoshi obtained four small pieces of the Tokyo air filters, he designed what he calls “a very simple procedure” to find out whether the filters contained cesium-rich microparticles. In April 2015, he took autoradiograph images of the four pieces, confirming what Ohnuki had already seen with a digital microscope at JAEA. Then Satoshi moved to characterize the structural and chemical properties of the particles using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Although the procedure’s design was simple, executing these steps would prove to be extremely difficult.
In July 2015, as Satoshi was busy working on the Tokyo air filters in his lab at Kyushu University, Ohnuki received a note from Nagakawa, the TIRI researcher who had provided the samples, asking him to return them so they could be reanalyzed. In his e-mail, Nagakawa did not specify the motive for his request, which appeared innocuous: “Please return at least some of the materials we gave you for reanalysis … if the location is unknown, it can’t be helped.”
Ohnuki immediately sent Nagakawa two filters from March 15, including the filter from 10 a.m. to 11 a.m. that had the highest level of radioactivity and contained the largest number of radioactive spots. Ohnuki added that he had discarded the other three filters after he analyzed them in 2013.
Nagakawa also asked Ohnuki whether he was planning to publish papers based on the samples. Ohnuki explained that he stopped analyzing them after his inconclusive attempts in 2013, but did not mention he had given Satoshi part of the filters for study.[9]
Satoshi was now ready to publish his results in a scientific journal. These were important findings that the scientific community needed to know. But Satoshi also understood that they could create a public relations crisis in Japan because his findings contradicted previous statements that played down the implications for public health of Fukushima fallout in Tokyo.
The Goldschmidt Conference—the foremost such international meeting on geochemistry—that year was held in the Japanese city of Yokohama. Satoshi was invited to give a plenary talk and present his research on environmental contamination from the Fukushima disaster (Utsunomiya 2016). During the talk, he presented his new findings on the Tokyo air filters. His talk received a lot of attention and was even reported by several Japanese and international newspapers. After his presentation, the scientific chair of the conference, Hisayoshi Yurimoto, said: “Very interesting results. And also very shocking results.”[1
In April and June 2016, Satoshi conducted dissolution experiments and quickly confirmed that the CsMPs were insoluble in water. The experiments also showed that most of the cesium activity on these filters came from CsMPs. In fact, up to 90 percent of the cesium radioactivity came from these microparticles, not from soluble forms of cesium—meaning that most of the cesium radioactivity detected during the March 15 plume in Tokyo was from CsMPs.
Between 2016 and 2019, a Kafkaesque sequence of events circled about Ohnuki, the former JAEA researcher who gave Satoshi the Tokyo air filter samples, and Satoshi. During that sequence of events, Satoshi’s research paper was accepted for publication by a prestigious scientific journal after peer review—but the journal delayed publication of the paper for years, eventually deciding not to publish it based on mysterious accusations of misconduct that, it turned out, were unwarranted. As a result, Satoshi’s findings were not made widely known, saving the Japanese authorities a possible public relations crisis as the summer Olympics in Tokyo neared. Because of the controversy surrounding Satoshi’s paper and the lack of research on the health impacts of these particles, it remains unclear to what extent Tokyo residents have been exposed to dangerous radiation levels as a result of the Fukushima accident.
I worked to reconstruct the sequence of events related to Satoshi’s research paper to find out whether the controversy over its publication was the result of some unethical practice on his part; competition between research laboratories; or attempted suppression of scientific results. The account that follows is based on the review of dozens of e-mails, letters, reports, and transcripts of phone conversations the Bulletin has obtained, as well as on multiple interviews with people directly involved in the events.
In August 2016, the leader of Nagakawa’s research group at TIRI, Noboru Sakurai, sent an e-mail to Ohnuki urging him to return filter samples he had earlier obtained from TIRI to the Tokyo Institute of Technology, where Ohnuki was now employed. Ohnuki responded that the filters had already been sent, but Sakurai maintained they had not received them. Ohnuki had asked a staff member of the research group he used to work in at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency to send the samples he had left there, but the samples were not sent. Because the samples were studied in a controlled area, theymay have been disposed of together with other Fukushima-related samples that had been stored at JAEA.
In October, as Ohnuki dealt with insistent requests that he return the filter samples, Satoshi submitted two research manuscripts to the journal Scientific Reports, one on the first successful isotopic analysis of individual cesium-rich microparticles based on soil samples collected from the exclusion zone at Fukushima, and one on the first characterization of the CsMPs from the Tokyo air filter samples that he had presented during his talk in Yokohama. Both articles were accepted in early January 2017 after peer review.[11]
The Tokyo paper, titled “Caesium fallout in Tokyo on 15th March, 2011 is dominated by highly radioactive, caesium-rich microparticles,” was co-authored by three graduate students from Satoshi’s lab—Jumpei Imoto, Genki Furuki, and Asumi Ochiai, who conducted the experiments—and three Japanese collaborators: Shinya Yamasaki from the University of Tsukuba who contributed to the measurement of samples; Kenji Nanba of Fukushima University, who contributed to the collection of samples; and Toshihiko Ohnuki, who had obtained the samples. The paper included two international collaborators who were world experts in the study of radioactive materials, Bernd Grambow of the French National Center for Scientific Research at the University of Nantes in France and Rodney C. Ewing of Stanford University, who contributed to the research ideas and participated in the analysis of the data. Satoshi was the lead author of the study.
……………………………………………..On the day of the visit, Moriguchi sent an e-mail to Ohnuki, pressing him to inform TIRI about the planned publication. “This type of information makes government agencies very sensitive,” Moriguchi wrote. “If the results obtained from these valuable sample collections conducted at a research institute under the administration were to incur the displeasure of government agencies and it becomes difficult to obtain cooperation from research institutions, we are concerned that this could hinder future research using these types of samples.”
…………………………………………………..Almost immediately, Sakurai moved to block the publication, according to e-mails obtained by the Bulletin.
………………………………………………………………………………………In July 2017, TIRI increased the pressure by sending a formal complaint to the Tokyo Institute of Technology, where Ohnuki was now employed. In a letter that the researchers were not able to see until a year after it was sent, TIRI accused Ohnuki of “suspected acts violating internal regulations, researcher’s ethics and code of conduct” in providing Satoshi with samples from TIRI without the institute’s consent.
As the issue became more political and involved more institutions, Satoshi continued his research on CsMPs and presented two other papers about Fukushima at the next Goldschmidt Conference in Paris in August 2017. Later that month, under pressure from the Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Industrial Technology, the Tokyo Institute of Technology opened a formal investigation of Ohnuki on suspicion of improper research activities with Satoshi. “It was like a court,” Satoshi said of being called before the compliance committee. Except that, unlike in a trial, he did not know the exact terms of what they were accused of. “The team at TIRI didn’t even allow Kyushu University to show me this letter,” Satoshi said. “So at that point, I didn’t understand what the problem was.”
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. Cleared but still harassed
During the investigation, Satoshi almost gave up on publishing the paper based on examination of the filters in Tokyo. He told the committee members that he would probably withdraw the paper, then “in press,” from Scientific Reports. Both the committee members and TIRI were pleased. “But then I talked to Rod [Ewing], and we did something clever,” Satoshi explained. They would not withdraw the paper; instead, they would keep it “in press” until the investigation was over.
…………………………………………………………………………….Tokyo Tech initiated a pressure campaign against Ohnuki and Satoshi to get the samples back…………………………………..
Satoshi did not want to give the samples away. “These are the only evidence to prove our article,” he said.
………………………………………………………“I sent all the samples to Stanford,” Satoshi said. Satoshi sent the air filter samples through regular postal services “in a UPS package.”[15] On September 13, Kyushu University’s executive vice president, Koji Inoue, called Satoshi to his office and yelled at him, urging him to give back the samples. Satoshi told Inoue that it was too late; he had already sent the samples to Stanford “for further investigation.”
Now the samples were secured, but Satoshi still needed his paper to be published.
……………………………………………………………………….. Thompson’s article in Scientific American was published on March 11, 2019, mentioning the fact that the paper had been rejected (Thompson 2019).
In June 2019, Satoshi and his co-authors posted their paper on arXiv (Utsunomiya et al. 2019), thereby making the findings public—two-and-a-half years after its acceptance by Scientific Reports. Ohnuki’s name does not appear in the list of co-authors on the arXiv paper, and Satoshi did not acknowledge TIRI for providing the samples.
……………………………………………………………………………………. After the paper was made public, the researchers received some attention, but not the visibility commensurate with the implications that the study had for public health in Japan.[16] The three institutions—TIRI, Tokyo Tech, and Kyushu University—were all “very happy,” Satoshi said. “People may think that we lost, but for me, we actually protected science.“
New risks
In the early days after the Fukushima accident, radiochemists thought that the situation was very different from Chernobyl. The three reactor-core damage events at Fukushima were considered to be of low energy, meaning that no actual explosion of the reactors had occurred, as was the case for Chernobyl. This led radiochemists to assume that radioactive particles probably had not come out of the reactors or, at least, not in large volume. A lot of the early post-accident research, therefore, focused on the traditional environmental radiochemist approach of collecting soils and sediments, doing bulk analysis, and learning from that.
It was only after scientists discovered the existence of cesium-rich microparticles that researchers, including Satoshi, realized that particles had actually been ejected from the reactors.
…………………………………………………………………………Because they were unknown until recently, CsMPs pose new risks that are still underappreciated by the research community and public authorities.
Once formed, radioactive cesium 137 has a half-life of about 30 years, after which half of the nuclides will have decayed into stable barium 137, whereas the other half will remain radioactive. CsMPs tend to accumulate, forming hotspots that contain many of the particles.[17] Hotspots of the microparticles have been found inside and outside abandoned buildings in the Fukushima exclusion zone and in other places (Fueda et al. 2023; Ikenoue et al. 2021; Utsunomiya 2024a). “They’re actually there in great numbers in many places, and then that’s when the health questions start to come in,” Law said. Despite their great numbers and potential risks, hotspots of CsMPs have not been systematically mapped around Fukushima. “When we visited the exclusion zone, we could still see some hot spot occurrences on the roadside without any protection,” Satoshi said. “We shouldn’t be able to access freely that kind of hot spots.”
Because CsMPs are so small, typically two microns or less in diameter, if humans breathe them, they could potentially reach the bottom of the lung, and be lodged into sacs known as alveoli, where the lung generally cannot expel them.[18] Scientists don’t know what would happen then. For instance, a typical immune system response would consist of some kind of clearance mechanism that seeks out foreign bodies and tries to either envelop or dissolve them. But it is still unknown how exactly CsMPs would dissolve in lung fluids.
Most knowledge about breathing and radioactive particulates is based on the assumption that particles dissolve, and researchers have calculated the rates for their dissolution in the human body. But because CsMPs don’t dissolve easily, once inhaled, they will likely stay longer in the human body. Researchers believe that, because CsMPs are so slow to dissolve, they may stay much longer—certainly for several months, maybe longer—in the body, compared to hours or days for suspended cesium.[19]
By unit of mass, CsMPs are much more radioactive than even spent reactor fuel. Some researchers from the Japan Atomic Energy Agency have shown that cultured cells exposed to the radiation from suspended CsMPs display a stronger local impact compared to what is known from previous radiological simulation studies using soluble radionuclides (Matsuya et al. 2022). Scientists are only now seeing some emerging evidence that the point-source nature of the radioactivity from CsMPs could lead to damage to cell systems. This is qualitatively different from the conventional estimate of internal radiation dose at the organ level based on uniform exposure to soluble cesium.
Despite the new risks that CsMPs might pose, the study of their impacts has received little interest.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………….Satoshi continues to study CsMPs actively and regularly presents his results to the Goldschmidt Conference and publishes his results in scientific journals. He and his collaborators work relentlessly to understand better the fate of CsMPs in the environment and their impacts on human health. In 2024, Satoshi received the Geochemical Society’s Clair C. Patterson Award in recognition of his innovative contributions to the understanding of CsMPs.[21]……………… more https://thebulletin.org/premium/2025-01/how-fukushimas-radioactive-fallout-in-tokyo-was-concealed-from-the-public/?utm_source=SocialShare&utm_medium=Facebook&utm_campaign=Facebook&utm_term&fbclid=IwY2xjawHyUndleHRuA2FlbQIxMQABHb1H3gK2UVzfBC5I7-s75EVtx4t5Q9uUi2MspvTqpluEOqbarYJJnhIwUA_aem_ok6x3HQOxccGg2I-7KnZjA
Independent testing of radiation levels in air- Woolsey Fire and Santa Susana Field Lab Site.

 WOOLSEY FIRE: ARE YOU BREATHING TOXIC AND RADIOACTIVE AIR? http://lancasterweeklyreview.com/woolsey-fire-radiation-toxic-testing by fdr | Nov 14, 2018 Preliminary Independent Radiation Test Results from US Nuclear Corporation from The Woolsey Fire and Santa Susana Field Lab Site
WOOLSEY FIRE: ARE YOU BREATHING TOXIC AND RADIOACTIVE AIR? http://lancasterweeklyreview.com/woolsey-fire-radiation-toxic-testing by fdr | Nov 14, 2018 Preliminary Independent Radiation Test Results from US Nuclear Corporation from The Woolsey Fire and Santa Susana Field Lab Site
After various complaints and talking with numerous concerned parents The Lancaster Weekly Review has ordered a commission in a preliminary study in order to finally answer some of the community’s concerns regarding potential toxic materials released from the Woolsey Fire as well as radiation from the Santa Susana Field Laboratory. The Field Lab was the site of a nuclear meltdown in 1959 with many locals and doctors condemning subpar cleanup efforts that point to high cancer rates which are 60% higher for those people living within a 2 mile radius of the SSFL. A lingering effect of the various toxins within the Field Labs vicinity.
It appears that the recent Woolsey Fire which has devastated swathes of Ventura and northwestern Los Angeles Counties, originated at the Santa Susa Field Lab and Testing Site with varied reports to the damage to the facility as well as the contamination area of the nuclear meltdown. The Southern California Edison Chatsworth Substation which is on the SSFL site shut down 2 minutes prior to start of the Woolsey Fire.
An independent study of air testing was conducted by US Nuclear Corporation of Canoga Park on Tuesday, November 13, five days after the Woolsey fire began. The owner, Mr. Bob Goldstein, was more than happy to help with the study and dispatched David Alban and Detwan Robinson to the Santa Susana Field Laboratory on Tuesday, November 13th at 3PM. They took two types of measurements for radiation with the US Nuclear Fast-Cam Air Monitor and another with a filter air tape. Twenty minute samples were taken at high flow rate of 40cfm at the Lab Entrance, which is up wind from the Lab. Another 20 minute sample was taken on the down wind side, which is North of the Lab. Given the proximity of the company’s headquarters to the Woolsey Fire US Nuclear Corporation’s team also took indoor samples at their office in Canoga Park.
It appears that many of the preliminary tests are picking up increased levels of Radon. Mr. Goldstein of US Nuclear Corporation commented, “Ordinary background radiation from minerals in the soil (and also from the solar wind and from cosmic rays) gives a dose rate of 0.015mR/hr (milliRem per hour) in the San Fernando Valley. But at the Santa Susana Field Laboratory background levels were found to be elevated to 0.040mR/hr. which is 0.025mR/hr higher than expected.”
Mr. Goldstein also stated, “The radioactivity collected on the filters decayed down to undetectable levels within 3 hours, leading us to conclude that this radioactive material is from Radon gas which decays after a short half life.” Overall, the tests that were conducted found that the area’s Radon levels are about 3 times higher than the surrounding San Fernando Valley.
Additional independent testing of other contaminants and toxins will take place in the coming days and will be published as soon as testing has taken place.
Protect your girls: We show that biological sex IS a factor in radiation outcomes, WIDELY

Mary Olson, GENDER AND RADIATION IMPACT PROJECT, 1 Jan 25
NEWS: We show in a new paper that the finding that girls and women suffer greater harm from radiation exposure compared to boys and men (who are also harmed) can be seen WIDELY in recent radiation research literature.
Dr Amanda Nichols, University of California at Santa Barbara, lead author, joins Mary Olson, founder of Gender and Radiation Impact Project in the new paper, entitled “Gender and Ionizing Radiation: Towards a New Research Agenda Addressing Disproportionate Harm.”
The paper is available to view or download at no charge, from the publisher: United Nations Institute for Disarmament Research .
The news here is the simple difference between standing on a relatively slender branch, and standing on a robust limb—apply this image to research and it is the difference between evidence found in a limited case, versus the same evidence being FOUND widely—beyond what could have been limited application.
In terms of radiation—a finding was made that radiation harms girls and women more than boys and men in one set of data as early as 2006. That data was in the National Academy of Science (NAS) watershed report called the Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation VII (BEIR VII).
Now, thanks to the invitation by the UN Institute for Disarmament Research (UNIDIR), I and my co-author Dr Amanda Nichols have sampled the research literature since 2006 (post-BEIR VII) and find that in studies that report data on males and females separately (now common) the sex-based difference can be seen, and in all cases where it is seen, females are harmed more than males. ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. more https://www.genderandradiation.org/blog/2024/12/31/protect-your-girls-we-show-that-biological-sex-is-a-factor-in-radiation-outcome-widely
Improved way to gauge radiation doses developed for Fukushima
Asahi Shimbun, By KEITARO FUKUCHI/ Staff Writer, December 31, 2024
[Ed. they studied only 30 people]
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency said it has developed a more accurate method to estimate radiation exposure doses among people who spend time around the stricken Fukushima No. 1 nuclear plant.
The JAEA has adapted the method, based on daily life patterns, into program format and is offering it for free on a municipal government website and elsewhere.
When the central government designated evacuation zones following the 2011 triple meltdown at the plant operated by Tokyo Electric Power Co., it estimated radiation doses among residents using a simple evaluation method that assumed they spent eight hours outdoors and 16 hours indoors a day.
That method allowed for quick estimation, but it tended to overestimate the doses.
Other existing evaluation methods also have shortcomings, including a failure to reflect the actual environment.
The JAEA began developing the new method in 2017.
JAEA researchers drew on data compiled by the Nuclear Regulation Authority to calculate average air dose rates for 100-meter-by-100-meter areas.
They also took into account where and for how long the residents and workers frequented near the plant, and how they moved between different locations, such as on foot or by car, the officials said.
They asked around 30 people working in former and current evacuation zones to carry personal dosimeters and then compared the measurements and estimates for their exposure doses in 106 patterns……………………………………………………………….. https://www.asahi.com/ajw/articles/15553626?fbclid=IwY2xjawHh0Y9leHRuA2FlbQIxMQABHRIRfUukVbNPX60rGOQi_qUp5oMiYFThXBvPZN4h0XJiPQ_xn8trGYEIkA_aem_GwPtrY24MPxB4L0v2u8SuA
High tide for Holtec

The study — Model-Based Study of Near-Surface Transport in and around Cape Cod Bay, Its Seasonal Variability, and Response to Wind — found that contrary to Holtec’s claims, the wastewater would not immediately disperse into the ocean, but would linger potentially for months, and wash up on the shores of area communities.
by beyondnuclearinternational, Linda Pentz Gunter
Tritium dumped into Cape Cod Bay will wash back onto community shores, says a new report
Holtec, the company that has purchased a number of permanently closed nuclear reactors in order to decommission them, has encountered yet another obstacle to its “dilution is the solution to pollution” plans.
One of the reactor sites Holtec has taken over is Pilgrim in Plymouth, Massachusetts, on the Cape Cod Bay, which closed permanently in 2019. Holtec’s not-so-little problem there is what do with what started out as at least 1.1 million gallons of radioactively contaminated wastewater stored at the site.
The company first suggested it would simply release the wastewater into Cape Cod Bay, assuring residents and the immediately alarmed fishing community not to worry because (a) the wastewater isn’t dangerous anyway (b) everyone does this all the time at reactor sites and no one has gotten sick so far and (c) it would quickly disperse into the wider ocean. Holtec chose this disposal method for one reason alone: it is the cheapest.
The proposal was vigorously fought by citizens, the state, and powerful Massachusetts Democrat, Senator Ed Markey. The state of Massachusetts effectively banned the discharge option, a decision Holtec is contesting.
That Final Determination to Deny Application to Modify a Massachusetts Permit to Discharge Pollutants to Surface Waters was issued by the Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection Division of Watershed Management on July 18, 2024. A month later, Holtec launched its appeal to reverse the decision, something that could take months or longer to find its way to court.
In the meantime, help has come from a new quarter in the form of an in-depth study by the prestigious Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, also, as it happens, based on the Massachusetts shoreline, near Falmouth.
The study — Model-Based Study of Near-Surface Transport in and around Cape Cod Bay, Its Seasonal Variability, and Response to Wind — found that contrary to Holtec’s claims, the wastewater would not immediately disperse into the ocean, but would linger potentially for months, and wash up on the shores of area communities.
“We found virtually no out-of-the-Bay transport in winter and fall and slightly larger, but still low, probability of some of the plume exiting the Bay in spring and summer,” said Woods Hole study leader and physical oceanographer, Irina Rypina.
The radioactively contaminated wastewater stored at Pilgrim is contaminated with what Holtec and the Massachusetts Department of Public Health have described as “four gamma emitters —Manganese-54, Cobalt-60, Zinc-65 and Cesium-137 along with Tritium, a beta radiation emitter”.
While the Woods Hole Study did not look at the health outcomes of releasing the radioactive water into Cape Cod Bay — only at the plume pathway — there are plenty of data that demonstrate the harmful effects of these radioisotopes on human health, especially women and children…………………………………………………….. https://beyondnuclearinternational.org/2024/12/29/high-tide-for-holtec/
Did Israel explode a small nuclear bomb in Syria? Spike in radiation report says…

Story by support@india.com (India.com News Desk), 25 Dec 24, https://www.msn.com/en-in/news/world/did-israel-explode-a-small-nuclear-bomb-in-syria-spike-in-radiation-report-says/ar-AA1wqXyT
In a step that has shocked the whole world, the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) carried out an airstrike on the weapons depot in Tartus, Syria on 16 December 2024. Through the massive strike, Israel reportedly destroyed the Scud missile facility. However, reports are speculating that the damage caused by the strike was much more and a small nuclear weapon might have been used. Here are the details you need to note about the Israeli strike on Syria.
As a result of the attack, an earthquake of magnitude 3 also occurred along with the massive explosion. The earthquake was so huge that it was felt up to Iznik in Turkey, 820 km away. Moreover, Russian media organization Sputnik had then said that Israel had targeted it with a new missile from a warship. However, some reports also claim that the B61 nuclear bomb developed by America was used here.
Reports have also added that the European Union’s Radioactive Environmental Monitoring surprisingly found that the amount of radiation increased in Turkey and Cyprus 20 hours after the intense blast, pointing towards a small nuclear attack.
Israeli army in the Golan Heights after UN extends peacekeeping mission between Syria, Israel
Israeli forces continued to operate along the Syria-Israel ceasefire line in the Golan Heights on Sunday (December 22) after the United Nations Security Council on Friday (December 20) extended a long-running peacekeeping mission between the two countries.
The UN mission was extended for six months and the security council expressed concern that military activities in the area could escalate tensions.
Ouster of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad
Since a lightning rebel offensive ousted Syrian President Bashar al-Assad earlier this month, Israeli troops have moved into the demilitarized zone – created after the 1973 Arab-Israeli war – that is patrolled by the UN Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF).
Israeli officials have described the move as a limited and temporary measure to ensure the security of Israel’s borders but have given no indication of when the troops might be withdrawn. Armed forces from Israel and Syria are not allowed in the demilitarized zone – a 400-square-km (155-square-mile) “Area of Separation” – under the ceasefire arrangement.
(With inputs from agencies)
-
Archives
- February 2026 (161)
- January 2026 (308)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (376)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
- March 2025 (319)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS
