New Radiation Protection Standards in 2026?

Tony Webb – November 2025.
In May 2025 US President Donald Trump ordered the US Nuclear Regulatory
Commission (NRC) to review US radiation protection standards for workers and the public. The order claims that these and other NRC regulatory processes hinder development of US nuclear power generation and need to be revised – in line with another set of his ‘alternative facts’ that overturn almost all the established principles that provide the basis of national and international protection standards.
This latest diktat will result in a significant weakening of current protection at a time when we have mounting scientific evidence that the existing standards need to be significantly improved/tightened. Permissible radiation exposures to workers will likely increase five-fold. Exposures to the public could be 100 times greater than currently permitted. Changes in the USA will lead to pressure for similar changes to standards in other countries, including Australia. Whether we end up with better or worse protection will require a sustained awareness and advocacy campaign. This will need to involve exposed workers, trade unions, environment and public health
interests arguing: first that our government and radiation protection agencies should reject the US approach, and second that new and improved national standards in line with the latest evidence should be adopted.
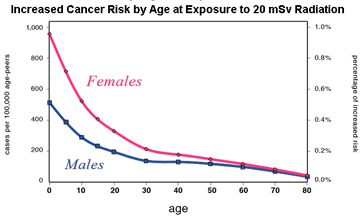
Health effects of radiation exposure
It has long been recognised that all radiation exposures present a risk to human health. Put simply there is no safe level of radiation – whether naturally occurring or artificially generated. Some we cannot avoid. Some like diagnostic medical x-rays we accept as having other countervailing benefits. High doses, like those received
by Japanese residents of Hiroshima and Nagasaki from nuclear bombs in 1945, or some of the first responders to the Ukrainian Chernobyl nuclear reactor meltdown in 1986, cause ‘radiation sickness’ where whole organs are damaged often with fatal
effects.
The results from high-dose exposures are what are known as ‘determinate’ effects.
Above a threshold dose these effects occur with severity determined by the dose. Radiation standards are set to keep exposures below the threshold, so these do not occur.
Lower doses cause a different kind of damage. Particularly concerning are increased rates of a wide range of cancers and genetic damage being passed on to future generations. These are referred to as ‘stochastic’ effects. The damage is not ‘determinate’ with a threshold below which they do not occur. Stochastic damage is a ‘hit and miss’ affair. You either get this type of health damage or you don’t. And if you do the scale of the damage isn’t related to the radiation dose you received.
The initial damage occurs at the cellular level where a radiation strike can have one of three outcomes. (i) It may simply pass through causing no damage. Alternatively, (ii) the radiation may kill the cell which isn’t a problem, unless too many cells are killed at once affecting functioning of whole organs. Our bodies are eliminating and replacing dead and dying cells all the time. Problems arise however when (iii) the cell is merely damaged and goes on to replicate in this damaged form.
Our bodies do have well developed repair mechanisms that often result in adequate repair of the damage. There is even some evidence suggesting that some such radiation damage and repair may assist the body’s capacity for repair in the future.
But where radiation leaves the damaged cell to survive and replicate uncontrollably in this damaged form the result is what we call a cancer – sometimes detectable only decades after the initial radiation damage. The process can be complicated further as growth of some cancers involves a two-stage process – initiation, where damage (from radiation or other environmental pollutants) leaves the cell susceptible,
followed by promotion (again from radiation or other sources) which drives the cell-cancer process forward.
Stochastic radiation damage is real. it doesn’t involve a threshold dose. Any exposure can be the one that causes the initial and/or subsequent damage leading to the health effects. We are in the world of ‘probability’ – far from certainty at the individual level but with fairly predictable outcomes at the population level which allow us to assess the risk (i.e., probability of an adverse outcome) individuals face from receiving small, sometimes repeated, doses of radiation.
Radiation protection principles.
In light of these established mechanisms for harm from radiation, standard setting bodies have long adopted three principles – that any exposure needs to be: (i) justified as necessary against some social benefits; (ii) kept as low as reasonably achievable (the ALARA principle); and (iii) kept below specified limits set in regulations.
The last of these has been the subject of much controversy over the years.
Standards have been set for workers’ occupational exposures and for public exposures. These, first, ensure exposures are below the threshold levels where deterministic effects might occur. Below these high levels, they have been set such that the risk of stochastic effects – particularly cancers and genetic damage are at levels deemed ‘acceptable’. There have been arguments over both what is ‘acceptable’ and how the probable level of risk from any given low dose is estimated.
Estimates of risk
A number of early studies of patients exposed as part of medical procedures indicated a problem with radiation exposure and some early estimates of the stochastic risk. Since then, the bulk of the data for the estimates of risk has come from studies of survivors of the Japanese nuclear bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945. These Life Span Studies (LSS) have consistently shown
increases in cancer rates among survivors higher than those in the non-exposed population. There are a number of problems with this data – not least that survivors were not wearing film badges when the bombs went off, so all doses have had to be estimated later. They were also the ‘hardy’ survivors of wide-ranging traumatic
events, perhaps less vulnerable to damage from radiation Most of these survivors received relatively high doses as a single exposure or within a relatively short time period. More accurate measures of small exposures repeated over longer time periods to a general population, might be expected to yield different results.
However, these were the best data to be had. The risks at lower doses are estimated using the assumption that, if there is no safe level of exposure, no threshold below which stochastic effects do not occur, we can estimate lower dose risks on a straight line from these higher LSS doses. This Linear No Threshold (LNT) assumption, though adopted by all stands setting bodies, has at times been contested. Some have suggested a sub-linear relationship with a threshold for any effects. Others have made the case for a super-linear or marginally higher effect at lower doses where these are spread over longer time periods or result from radiative material that gets inside the body.
For now all the significant agencies agree that radiation protection for workers and the public should be based on LNT and the three radiation protection principles: justification, ALARA, and Specific Exposure Limits. These agencies include: the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) the United Nations
Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) the US National Academy of Sciences Committee on the Biological Effects of Ionising Radiation (known as the BEIR Committee) and national agencies like the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA). The cancer risk from low
dose radiation is estimated to be in the range of 4-6% per Sievert (1000 mSv) of exposure. The risk of genetic damage (first two generations only) is estimated to be around 1.5% per Sievert.
These estimates have resulted in national protection bodies setting standards that limit annual exposures. For workers the annual limit is 20 mSv as a target – but with 50 mSv allowed in any year provided the average over five years does not exceed 20 mSv. The annual limit for public exposures is 1 mSv. All of these are for
exposures in addition to what might be received from natural background radiation or exposures due to medical procedures such as diagnostic x-rays and nuclear medicine.
Change is coming – one way or another.
It is these protection principles and the exposure standards for workers and the public that the Presidential directive to the US NRC seeks to overturn. It calls on the NRC to reconsider reliance on LNT (and ALARA) as the basis for standard setting at low doses, where there is a need to protect against probable stochastic effects and
directs that instead the NRC set standards based on deterministic effects.
This will likely result in a significant weakening of the current standards at a time when the evidence strongly suggests that they are in need of further tightening. The current standards have been in place since 1991. Revisions at that time were the result of a sustained campaign throughout the 1980s led by trade unions in the UK, Europe, USA and Canada for reduction of the then 50 mSv occupational and 5 mSv public limits -justified in large part by emerging evidence from the Japanese lifespan studies. As previously noted, estimates of risk from these was based on one-off
short-term exposure to relatively high doses (at and above 100 mSv). Since then, studies in Europe and North America of workers exposed over years of work in nuclear industries to doses below the current occupational limits, indicate the risks are around 2 to 3 times greater than those used for setting the current standards.
They also show a doubling of expected rates of cardio-vascular diseases: strokes, arthro-sclerosis, and heart damage. In addition, studies of populations living close to nuclear facilities in Europe and the USA show childhood cancer rates significantly higher than expected. This evidence is cause for concern, suggesting that the
current standards provide inadequate protection and need to be tightened.
A new campaign for improved protection?
Past experience suggests that persuading national and international bodies to improve radiation protection standards is far from easy but not impossible. In the short term, a campaign would be seeking clear and unequivocal statements from national protection agencies that reject the US president’s directive that the NRC abandon the fundamental principles which have formed the basis for regulating worker and public exposures. If implemented Trump’s proposals would likely result in occupational exposure limits five times higher than presently allowed, and public exposure limits could be 100 times greater.
The campaign should seek assurances that there will be no change to the established principles underpinning radiation protection: that there is no safe level of radiation, that all exposures should be kept as low as can be reasonably achievable; and that occupational and public limits need to be based on the best scientific evidence of risk to human populations.
Raising the concern about, and seeking rejection of, the likely US NRC changes will require building an informed coalition of trade union, environment and public health interests. Occupational and public radiation exposures are more widespread that commonly appreciated. Workers are routinely exposed in mining, industry and medicine as well as those associated with the nuclear power industry. The. campaign could involve local initiatives that focus concerns of workers in , and people living close to sites of: proposed nuclear power plants; existing uranium, mineral sands, and hard rock mines; proposed ‘rare earth’ mines; medical and other
radioactive waste storage sites; and other activities that routinely release radiative materials.
Opposing Trump’s latest proposals to weaken standards is fairly straightforward. If implemented by the NRC they would dismantle the whole edifice on which radiation protection has been built over the past 80 years – a framework that many concerned about radiation protection within the affected industries have invested time and energy to establish and maintain.
Pressing the claim for improvements is harder but not impossible given the evidence for greater harm that is emerging. The case can already be made for at least halving the permissible occupational and public exposure limits. If we are successful in pressing for improved protection standards, the nuclear industry is unlikely to thank President Trump for opening this can of worms with his NRC directive. Once opened it will be hard to close without increasing worker and public awareness of how any, and all radiation exposures increase health risks to workers the public and to future generations.
Tony Webb has worked as a researcher, consultant and advisor on radiation and health issues to politicians, trade unions, environment and public health groups in the UK, Europe, USA , Canada and Australasia since the late1970s. He can be contacted for information on how to assist the latest evolving international campaign via tonyrwebb@gmail.com.
No comments yet.
-
Archives
- March 2026 (139)
- February 2026 (268)
- January 2026 (308)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (376)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS




Leave a comment