Nuclear industry veterans warn some radioactive waste destined for Ontario disposal facility should not be accepted
Observer, Natasha Bulowski • Feb 16, 2024 •
Approval of a nuclear waste disposal site near the Ottawa River hinged on a promise that only low-level radioactive waste would be accepted. But former nuclear industry employees and experts warn some waste slated for disposal contains unacceptably high levels of long-lived radioactive material.
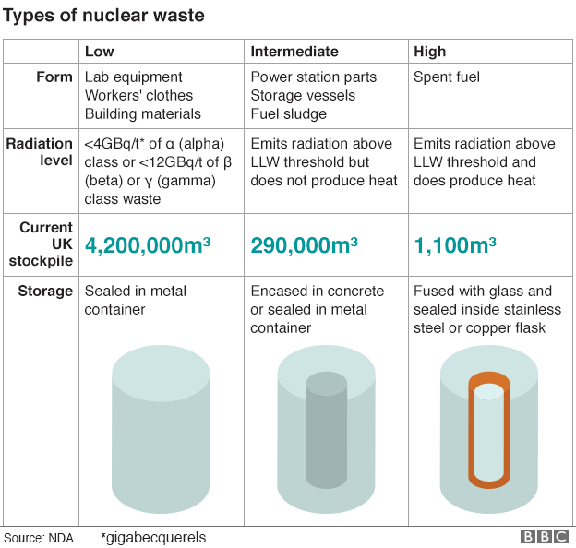
The “near-surface disposal facility” at Chalk River Laboratories (CRL) will store up to one million cubic metres of current and future low-level radioactive waste inside a shallow mound about one kilometre from the river, which provides drinking water to millions of people in the region. But former employees who spent decades working at the labs in waste management and analysis say previous waste-handling practices were inadequate, imprecise and not up to modern standards. Different levels of radioactive material were mixed together, making it unacceptable to bury in the mound.
“Anything pre-2000 is anybody’s guess what the hell they have on their hands,” said Gregory Csullog, a retired waste inventory specialist and former longtime employee of Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL), the Crown corporation that ran the federal government’s nuclear facilities before the Harper government privatized it in 2015.
Csullog described the waste during this earlier time as an unidentifiable “mishmash” of intermediate- and low-level radioactivity because there were inadequate systems to properly label, characterize, store and track what was produced at Chalk River or shipped there from other labs. “Literally, there were no rules,” said Csullog, who was hired in 1982 to develop waste identification and tracking systems.
International safety standards state low-level radioactive waste is suitable for disposal in various facilities, ranging from near the surface to 30 metres underground, depending primarily on how long it remains radioactive. High-level waste, like used fuel rods, must be buried hundreds to thousands of metres underground in stable rock formations and remain there, effectively forever. Intermediate-level waste is somewhere in the middle and should be buried tens to hundreds of metres underground, not in near-surface disposal facilities, according to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
Radioactive waste is recognized by many health authorities as cancer-causing and its longevity makes disposal a thorny issue. Even short-lived radioactive waste typically takes hundreds of years to decay to extremely low levels and some radioactive isotopes like tritium found in the waste — a byproduct of nuclear reactors — are especially hard to remove from water.
Canadian Nuclear Laboratories (CNL) originally wanted its near-surface disposal facility to take intermediate- and low-level waste when it first proposed the project in 2016. Backlash was swift and concerned groups, including Deep River town council and multiple experts, argued it would transgress international standards to put intermediate-level waste in that type of facility. In 2017, CNL changed its proposal and promised to only accept low-level waste. The announcement quelled the Deep River town council’s concern, but some citizen groups, scientists, former employees and many Algonquin Nations aren’t buying it.
CNL says its waste acceptance criteria will ensure all the waste will be low-level and comply with international and Canadian standards. Eighty seven per cent of the waste will be loose soil and debris from environmental remediation and decommissioned buildings. The other 13 per cent “will have sufficiently high radionuclide content to require use of packaging” in containers, drums or steel boxes in the disposal facility, according to CNL.
However, project opponents note that between 2016 and 2019, about 90 per cent of the intermediate-level waste inventory at federal sites was reclassified as low-level, according to data from AECL and a statement from CNL. The timing of the reclassification raised the alarm for critics, who took it to mean intermediate-level waste was inappropriately categorized as low-level so it could be stored in the Chalk River disposal facility. CNL said the 2016 estimate was based on overly “conservative assumptions” and the waste was reclassified after some legacy waste was retrieved, examined and found to be low-level.
The disposal facility will also accept waste generated over the next two decades and some shipments from hospitals and universities.
The history of Chalk River Laboratories
To fully understand the nuclear waste problem, you first have to know the history of Chalk River Lab’s operations and accidents,…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… more https://www.pembrokeobserver.com/news/local-news/nuclear-industry-veterans-warn-some-radioactive-waste-destined-for-ontario-disposal-facility-should-not-be-accepted Natasha Bulowski is a Local Journalism Initiative reporter working out of Canada’s National Observer. LJI is funded by the Government of Canada.
No comments yet.
-
Archives
- March 2026 (51)
- February 2026 (268)
- January 2026 (308)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (376)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS





Leave a comment