Can reactor fuel debris be safely removed from Fukushima Daiichi?
Can reactor fuel debris be safely removed from Fukushima Daiichi?, Science Daily, :January 25, 2022Source:University of Helsinki
Summary:Decommissioning and clean-up are ongoing at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP); however, many difficult problems remain unaddressed. Chief amongst these problems is the retrieval and management of fuel debris.
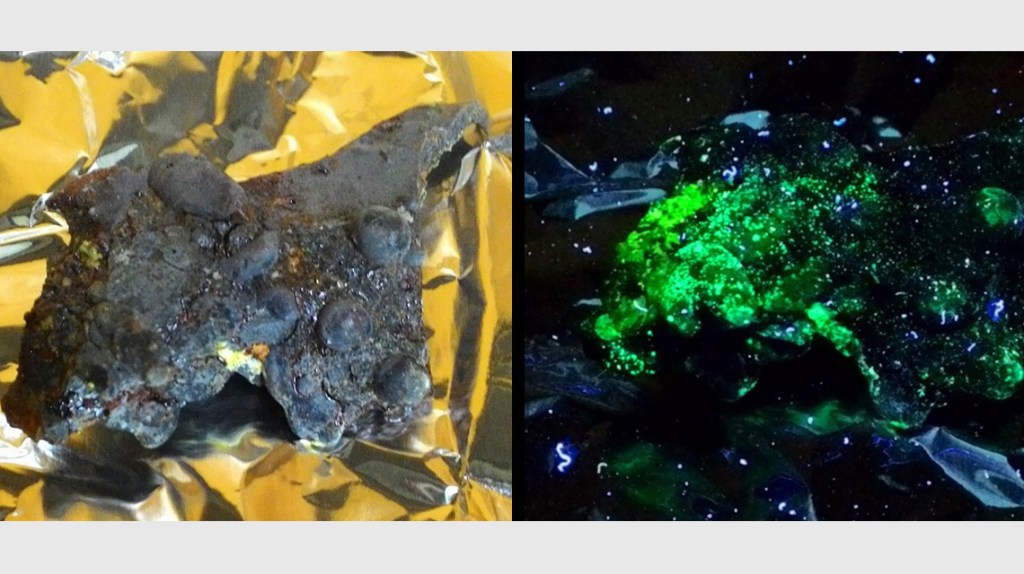
Decommissioning and clean-up are ongoing at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP); however, many difficult problems remain unaddressed. Chief amongst these problems is the retrieval and management of fuel debris. Fuel debris is the name given to the solidified mixture of melted nuclear fuel and other materials that now lie at the base of each of the damaged reactors (reactor Units 1 — 3). This material is highly radioactive and it has potential to generate enough neutrons to trigger successive nuclear fission reactions (uranium-235 breaks into two elements after capturing neutrons, emitting enormous amounts of energy, radiation, and more neutrons). Successive fission reactions would present a serious safety and material management risk.
One of the materials in nuclear reactors that can lower the number of neutrons interacting with uranium-235 is boron carbide (B4C). This was used as the control rod material in the FDNPP reactors, and it may now remain within the fuel debris. If so, it may limit fission events within the fuel debris.
Can the fuel debris be safely removed?
On March 11th 2011, the control rods were inserted into the FDNPP reactors to stop the fission reactions immediately after the earthquake, but the later tsunami destroyed the reactor cooling systems. Fuel temperatures soon became high enough (>2000 °C) to cause reactor meltdowns. Currently, the fuel debris material from each reactor is cooled and stable; however, careful assessment of these materials, including not only their inventories of radioactive elements but as well their boron content, a neutron absorber, is needed to ascertain if successive fission reactions and associated neutron flux could occur in the fuel debris during its removal. Many important questions remain: was boron from the control rods lost at high temperature during the meltdown? If so, does enough boron remain in the fuel debris to limit successive fission reactions within this material? These questions must be answered to support safe decommissioning.
Study shows direct evidence of volatilization of control rods during the accident.
Despite the importance of this topic, the state and stability of the FDNPP control rod material has remained unknown until now. However, work just published in the Journal of Hazardous Materials now provides vital evidence that indicates that most of the control rod boron remains in at least two of the damaged FDNPP reactors (Units 2 and/or 3).
The study was an international effort involving scientists from Japan, Finland, France, and the USA………………….. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/01/220125093041.htm
No comments yet.
-
Archives
- February 2026 (141)
- January 2026 (308)
- December 2025 (358)
- November 2025 (359)
- October 2025 (376)
- September 2025 (258)
- August 2025 (319)
- July 2025 (230)
- June 2025 (348)
- May 2025 (261)
- April 2025 (305)
- March 2025 (319)
-
Categories
- 1
- 1 NUCLEAR ISSUES
- business and costs
- climate change
- culture and arts
- ENERGY
- environment
- health
- history
- indigenous issues
- Legal
- marketing of nuclear
- media
- opposition to nuclear
- PERSONAL STORIES
- politics
- politics international
- Religion and ethics
- safety
- secrets,lies and civil liberties
- spinbuster
- technology
- Uranium
- wastes
- weapons and war
- Women
- 2 WORLD
- ACTION
- AFRICA
- Atrocities
- AUSTRALIA
- Christina's notes
- Christina's themes
- culture and arts
- Events
- Fuk 2022
- Fuk 2023
- Fukushima 2017
- Fukushima 2018
- fukushima 2019
- Fukushima 2020
- Fukushima 2021
- general
- global warming
- Humour (God we need it)
- Nuclear
- RARE EARTHS
- Reference
- resources – print
- Resources -audiovicual
- Weekly Newsletter
- World
- World Nuclear
- YouTube
-
RSS
Entries RSS
Comments RSS

Leave a comment